Data Engineers build and maintain the infrastructure and architecture for data generation, ensuring data is clean, reliable, and accessible. Data Analysts interpret and analyze this data to extract actionable insights and support business decision-making. While Data Engineers focus on data pipeline and storage solutions, Data Analysts concentrate on data visualization and reporting techniques.
Table of Comparison
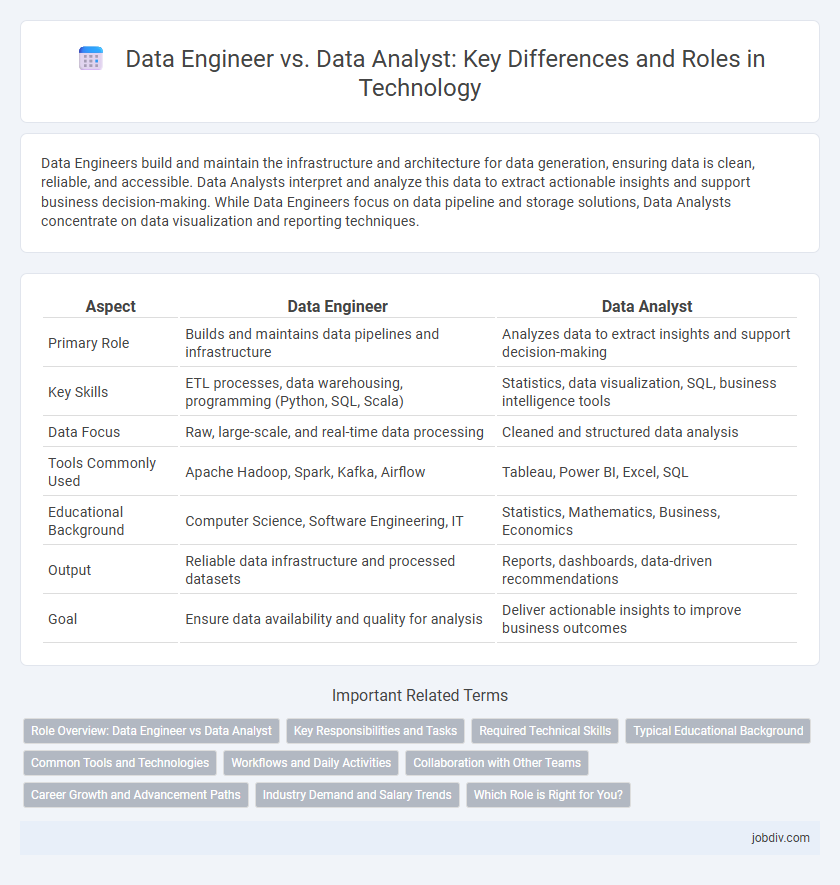
| Aspect | Data Engineer | Data Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Builds and maintains data pipelines and infrastructure | Analyzes data to extract insights and support decision-making |
| Key Skills | ETL processes, data warehousing, programming (Python, SQL, Scala) | Statistics, data visualization, SQL, business intelligence tools |
| Data Focus | Raw, large-scale, and real-time data processing | Cleaned and structured data analysis |
| Tools Commonly Used | Apache Hadoop, Spark, Kafka, Airflow | Tableau, Power BI, Excel, SQL |
| Educational Background | Computer Science, Software Engineering, IT | Statistics, Mathematics, Business, Economics |
| Output | Reliable data infrastructure and processed datasets | Reports, dashboards, data-driven recommendations |
| Goal | Ensure data availability and quality for analysis | Deliver actionable insights to improve business outcomes |
Role Overview: Data Engineer vs Data Analyst
Data Engineers design, build, and maintain scalable data pipelines and infrastructure to facilitate data storage, processing, and accessibility across platforms. Data Analysts interpret complex datasets by using statistical tools and data visualization techniques to generate actionable business insights. While Data Engineers focus on data architecture and workflow optimization, Data Analysts concentrate on data interpretation and reporting to support decision-making processes.
Key Responsibilities and Tasks
Data Engineers design, build, and maintain scalable data pipelines and architectures, ensuring the efficient collection, storage, and processing of large datasets using tools like Apache Spark and ETL frameworks. Data Analysts interpret and analyze processed data to generate actionable insights, employing statistical methods and visualization software such as Tableau or Power BI to support business decision-making. While Data Engineers focus on data infrastructure and integration, Data Analysts specialize in data querying, reporting, and communicating trends.
Required Technical Skills
Data Engineers require expertise in programming languages such as Python, Java, and Scala, alongside proficiency in SQL, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, and big data technologies like Hadoop, Spark, and Kafka. Data Analysts focus on statistical tools, data visualization platforms such as Tableau or Power BI, and advanced SQL skills to extract and interpret datasets efficiently. Both roles demand a solid understanding of database management, but Data Engineers prioritize building and maintaining data pipelines, while Data Analysts emphasize data interpretation and reporting.
Typical Educational Background
Data engineers typically hold degrees in computer science, software engineering, or information technology, emphasizing programming, databases, and systems architecture. Data analysts often have backgrounds in statistics, mathematics, or economics, focusing on data interpretation, visualization, and business intelligence. Both roles benefit from proficiency in SQL and data management but diverge in technical depth and analytical skills required.
Common Tools and Technologies
Data Engineers primarily use technologies such as Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, and SQL for building data pipelines and managing large-scale data storage systems like AWS S3 and Google BigQuery. In contrast, Data Analysts rely heavily on tools like Microsoft Excel, Tableau, and Power BI for data visualization and reporting, alongside SQL for querying databases. Both roles frequently utilize Python and R for data manipulation and analysis, but Data Engineers focus on data architecture while Data Analysts concentrate on interpreting data insights.
Workflows and Daily Activities
Data Engineers design, build, and maintain data pipelines, ensuring data is accessible, reliable, and optimized for large-scale processing using tools like Apache Spark and Hadoop. Their daily activities involve coding ETL workflows, managing databases, and monitoring data infrastructure for performance and scalability. Data Analysts focus on interpreting data through statistical analysis and visualization tools like SQL, Tableau, and Excel to generate actionable business insights and support decision-making processes.
Collaboration with Other Teams
Data Engineers design and maintain the infrastructure that enables seamless data flow, facilitating efficient data access for Data Analysts. Data Analysts interpret and analyze this data to generate actionable insights, relying on the robust pipelines created by Data Engineers. Effective collaboration between these roles ensures accurate data integration, optimized workflows, and data-driven decision-making across business units.
Career Growth and Advancement Paths
Data Engineers specialize in building and maintaining data pipelines, leveraging skills in ETL, big data frameworks like Apache Spark, and cloud platforms such as AWS or Azure, which positions them for advancement into roles like Data Architect or Machine Learning Engineer. Data Analysts focus on interpreting data using tools like SQL, Tableau, and Python to generate actionable insights, creating opportunities to progress into Business Intelligence Analyst or Analytics Manager positions. Career growth for Data Engineers typically emphasizes technical depth and system architecture, while Data Analysts advance through enhanced data interpretation, strategic decision-making roles, and domain expertise.
Industry Demand and Salary Trends
Data Engineers command higher average salaries, often ranging from $95,000 to $135,000 annually, reflecting their critical role in building and maintaining complex data architectures. Industry demand for Data Engineers is surging, especially in tech-driven sectors requiring scalable data pipelines and advanced analytics infrastructure. Data Analysts, with salaries typically between $60,000 and $85,000, remain essential for interpreting data insights, but the growing emphasis on big data solutions and cloud platforms drives stronger recruitment efforts and salary growth for Data Engineers.
Which Role is Right for You?
Data Engineers build and maintain the infrastructure for data generation, ensuring data pipelines are efficient, scalable, and reliable, making this role ideal for those skilled in programming, databases, and system architecture. Data Analysts focus on interpreting complex datasets to extract actionable business insights, leveraging statistical tools and data visualization techniques, suited for individuals strong in analytical thinking and communication. Choosing between these roles depends on your preference for developing data systems versus analyzing data to inform decision-making.
Data Engineer vs Data Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com