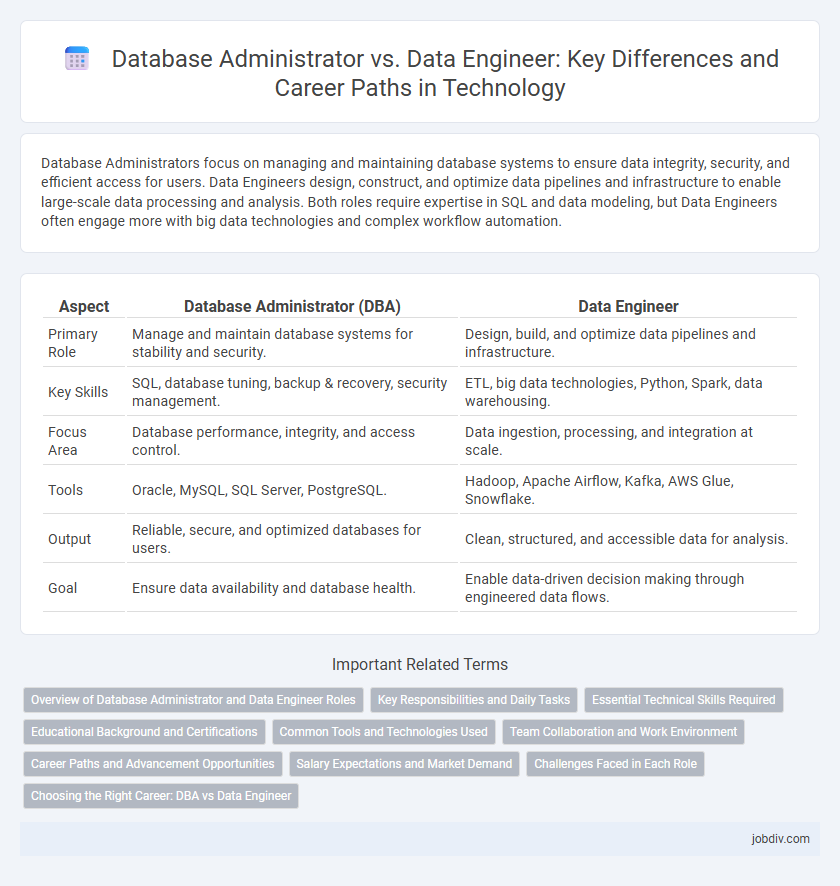
Database Administrators focus on managing and maintaining database systems to ensure data integrity, security, and efficient access for users. Data Engineers design, construct, and optimize data pipelines and infrastructure to enable large-scale data processing and analysis. Both roles require expertise in SQL and data modeling, but Data Engineers often engage more with big data technologies and complex workflow automation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Database Administrator (DBA) | Data Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage and maintain database systems for stability and security. | Design, build, and optimize data pipelines and infrastructure. |
| Key Skills | SQL, database tuning, backup & recovery, security management. | ETL, big data technologies, Python, Spark, data warehousing. |
| Focus Area | Database performance, integrity, and access control. | Data ingestion, processing, and integration at scale. |
| Tools | Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL. | Hadoop, Apache Airflow, Kafka, AWS Glue, Snowflake. |
| Output | Reliable, secure, and optimized databases for users. | Clean, structured, and accessible data for analysis. |
| Goal | Ensure data availability and database health. | Enable data-driven decision making through engineered data flows. |
Overview of Database Administrator and Data Engineer Roles
Database Administrators (DBAs) focus on the installation, configuration, maintenance, and security of database systems to ensure data integrity and availability. Data Engineers design, build, and manage data pipelines, enabling the seamless flow and transformation of large-scale data for analytics and machine learning applications. Both roles require strong expertise in database technologies, but DBAs emphasize operational stability while Data Engineers prioritize scalable data architecture.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Database Administrators specialize in managing and maintaining database systems, ensuring data integrity, security, and optimal performance through tasks like backup, recovery, and access control. Data Engineers design, build, and optimize data pipelines and architectures, enabling efficient data collection, transformation, and storage for analytics and machine learning applications. While DBAs focus on operational database management, Data Engineers emphasize large-scale data processing and integration across diverse systems.
Essential Technical Skills Required
Database Administrators (DBAs) require expertise in SQL, database management systems like Oracle, MySQL, and performance tuning to ensure data integrity and availability. Data Engineers must master programming languages such as Python or Scala, big data technologies like Hadoop and Spark, and data pipeline orchestration tools including Apache Airflow. Both roles demand strong knowledge of ETL processes, data modeling, and cloud platforms like AWS or Azure for efficient data architecture management.
Educational Background and Certifications
Database Administrators typically hold degrees in computer science, information technology, or related fields, emphasizing database management and SQL proficiency, while Data Engineers often possess degrees in software engineering, computer science, or data science, focusing more on programming, big data technologies, and system architecture. Certifications for Database Administrators include Oracle Certified Professional (OCP), Microsoft Certified: Azure Database Administrator Associate, and IBM Certified Database Administrator. Data Engineers frequently pursue certifications such as Google Cloud Professional Data Engineer, AWS Certified Data Analytics - Specialty, and Databricks Certified Data Engineer to validate expertise in cloud platforms and ETL processes.
Common Tools and Technologies Used
Database Administrators (DBAs) commonly use SQL Server, Oracle Database, and MySQL for managing and optimizing relational databases, along with tools like Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and Oracle Enterprise Manager for administration. Data Engineers frequently work with Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, and Amazon Redshift to build and maintain large-scale data pipelines and storage solutions, leveraging tools such as Apache Airflow for workflow orchestration and Kafka for real-time data streaming. Both roles intersect in the use of SQL, cloud platforms like AWS and Azure, and containerization technologies such as Docker to ensure scalable and efficient data management.
Team Collaboration and Work Environment
Database Administrators (DBAs) and Data Engineers collaborate closely to ensure seamless data management, with DBAs focusing on maintaining database integrity and performance while Data Engineers design and optimize data pipelines. Effective teamwork relies on clear communication and shared tools such as SQL, ETL platforms, and cloud-based data warehouses like AWS Redshift or Google BigQuery. The work environment fosters cross-functional collaboration between IT operations, analytics, and development teams to enhance data accessibility and system reliability.
Career Paths and Advancement Opportunities
Database Administrators (DBAs) focus on managing database performance, security, and backup, offering career growth through specialization in database platforms and certification in cloud database services. Data Engineers design, build, and optimize data pipelines and architectures, with advancement opportunities in big data technologies, machine learning integration, and leadership roles in data strategy. Both careers demand strong SQL skills, but Data Engineers typically expand into programming languages like Python and Scala, opening pathways to more diverse data roles.
Salary Expectations and Market Demand
Database Administrators typically earn an average salary ranging from $75,000 to $110,000 annually, while Data Engineers command higher salaries, often between $95,000 and $140,000 due to their specialized skills in building data pipelines and managing big data infrastructure. Market demand shows a growing preference for Data Engineers as businesses increasingly adopt cloud platforms and require scalable data solutions, driving higher compensation and more job openings in this field. Companies prioritize Data Engineer roles to optimize data flow and support advanced analytics, whereas Database Administrators remain essential for managing and securing structured databases.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Database Administrators (DBAs) face challenges such as ensuring data integrity, managing database performance, and maintaining security against unauthorized access. Data Engineers encounter obstacles related to building scalable data pipelines, integrating diverse data sources, and optimizing data workflows for analytics and machine learning. Both roles demand proficiency in database management systems, but DBAs focus more on system stability while Data Engineers emphasize data architecture and transformation.
Choosing the Right Career: DBA vs Data Engineer
Choosing between a Database Administrator (DBA) and a Data Engineer depends on your passion for database management versus data pipeline development. DBAs specialize in database optimization, security, and maintenance, ensuring data integrity and availability, while Data Engineers focus on designing and building scalable data architectures and ETL processes for analytics. Consider your interest in managing structured data environments versus creating complex data workflows to determine the ideal career path.
Database Administrator vs Data Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com