Quality Assurance Engineers concentrate on the overall software quality by designing comprehensive testing strategies, performing manual tests, and ensuring compliance with industry standards. Test Automation Engineers specialize in developing and maintaining automated test scripts to increase testing efficiency and accuracy, often using tools like Selenium or Jenkins. Both roles are essential for delivering reliable, high-quality software, but Quality Assurance Engineers have a broader scope while Test Automation Engineers focus on technical automation expertise.
Table of Comparison
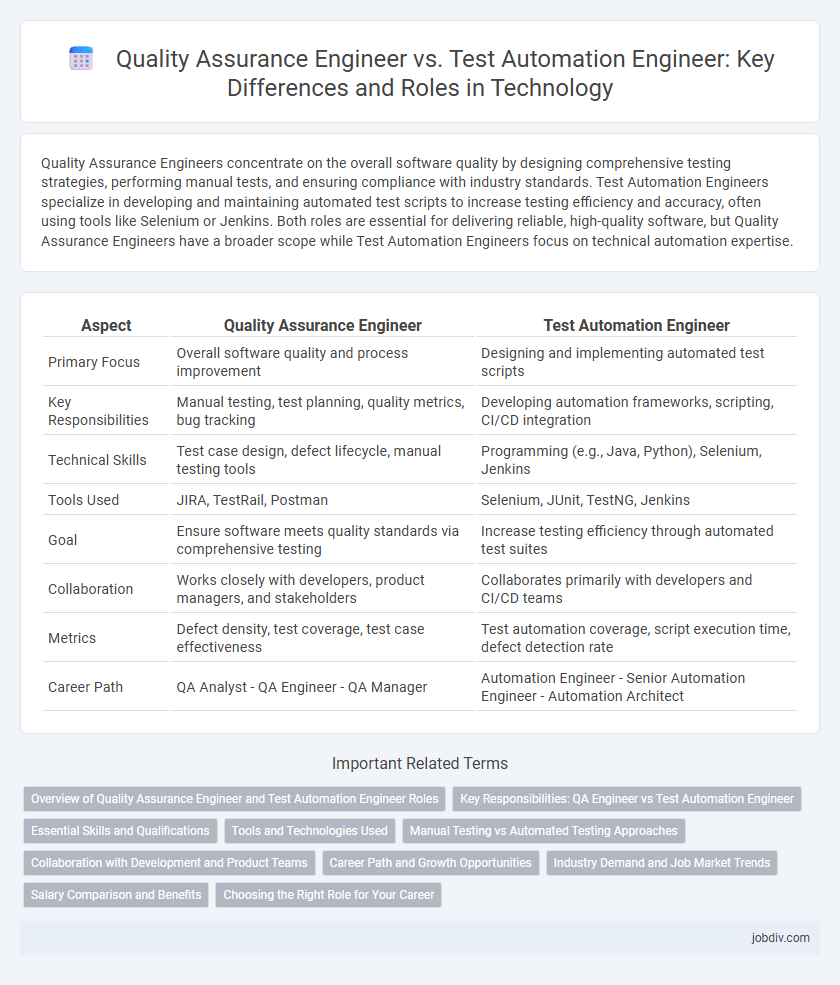
| Aspect | Quality Assurance Engineer | Test Automation Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Overall software quality and process improvement | Designing and implementing automated test scripts |
| Key Responsibilities | Manual testing, test planning, quality metrics, bug tracking | Developing automation frameworks, scripting, CI/CD integration |
| Technical Skills | Test case design, defect lifecycle, manual testing tools | Programming (e.g., Java, Python), Selenium, Jenkins |
| Tools Used | JIRA, TestRail, Postman | Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, Jenkins |
| Goal | Ensure software meets quality standards via comprehensive testing | Increase testing efficiency through automated test suites |
| Collaboration | Works closely with developers, product managers, and stakeholders | Collaborates primarily with developers and CI/CD teams |
| Metrics | Defect density, test coverage, test case effectiveness | Test automation coverage, script execution time, defect detection rate |
| Career Path | QA Analyst - QA Engineer - QA Manager | Automation Engineer - Senior Automation Engineer - Automation Architect |
Overview of Quality Assurance Engineer and Test Automation Engineer Roles
Quality Assurance Engineers focus on ensuring software meets quality standards through manual testing, process improvement, and defect tracking, emphasizing overall product reliability and user experience. Test Automation Engineers specialize in designing, developing, and maintaining automated test scripts using tools like Selenium or Appium to increase testing efficiency and coverage. Both roles collaborate to deliver robust software but differ in approach, with QA Engineers prioritizing manual assessments and Test Automation Engineers driving automation frameworks.
Key Responsibilities: QA Engineer vs Test Automation Engineer
Quality Assurance Engineers focus on defining quality standards, performing manual and exploratory testing, and overseeing the entire software development lifecycle to ensure product reliability and functionality. Test Automation Engineers design, develop, and maintain automated test scripts using tools like Selenium, JUnit, or Cypress to accelerate regression testing and increase test coverage. Both roles collaborate to ensure software quality, with QA Engineers emphasizing process and strategy, while Test Automation Engineers prioritize automation frameworks and execution efficiency.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
Quality Assurance Engineers require strong analytical skills, expertise in manual testing, and a deep understanding of software development life cycles to ensure comprehensive product quality. Test Automation Engineers must possess proficiency in scripting languages such as Python or Java, experience with automation frameworks like Selenium or Cypress, and the ability to design, develop, and maintain automated test scripts. Both roles demand knowledge of defect tracking tools, continuous integration systems, and effective communication skills for collaboration within Agile teams.
Tools and Technologies Used
Quality Assurance Engineers commonly utilize manual testing tools such as JIRA, TestRail, and Postman for bug tracking, test case management, and API testing, emphasizing comprehensive test coverage and defect identification. Test Automation Engineers focus on scripting and running automated tests using frameworks and languages like Selenium WebDriver, Appium, TestNG, and programming languages such as Java, Python, or C#, enabling continuous integration and faster regression testing. Both roles leverage CI/CD tools like Jenkins and version control systems like Git to enhance collaboration and deployment efficiency in software development lifecycles.
Manual Testing vs Automated Testing Approaches
Quality Assurance Engineers specialize in manual testing, meticulously verifying software functionality, usability, and user experience to identify defects that automated tests might overlook. Test Automation Engineers develop and maintain automated testing frameworks using tools like Selenium or Appium, enabling rapid, repeatable, and scalable test execution across multiple environments. While manual testing excels in exploratory and ad-hoc scenarios, automated testing ensures consistent regression coverage and accelerates the release cycle in agile development processes.
Collaboration with Development and Product Teams
Quality Assurance Engineers collaborate closely with development teams to identify defects early and ensure product functionality meets requirements through manual and exploratory testing. Test Automation Engineers work alongside both development and product teams to design and implement automated testing frameworks that increase efficiency and ensure continuous integration and delivery. Effective collaboration between these roles enhances software quality, accelerates release cycles, and aligns testing efforts with product goals.
Career Path and Growth Opportunities
Quality Assurance Engineers typically advance by deepening expertise in manual testing methodologies and transitioning into leadership roles such as QA Manager or Test Lead, emphasizing comprehensive test planning and process improvement. Test Automation Engineers experience rapid career growth through skills in scripting, automation frameworks, and continuous integration, often moving into DevOps or Software Development Engineer in Test (SDET) positions. Both career paths offer strong opportunities in technology companies, but automation skills generally command higher demand and salary growth due to industry trends toward efficient, scalable testing solutions.
Industry Demand and Job Market Trends
Quality Assurance Engineers remain essential for overseeing comprehensive testing processes and ensuring software meets functional and user requirements, maintaining high standards across diverse industries. Test Automation Engineers are increasingly in demand due to growing emphasis on accelerating development cycles and implementing continuous integration and delivery pipelines with automated testing frameworks. Current job market trends reveal stronger growth rates and higher salary prospects for Test Automation Engineers, driven by the adoption of AI-driven testing tools and cloud-based testing platforms.
Salary Comparison and Benefits
Quality Assurance Engineers typically earn a salary range between $70,000 and $100,000 annually, while Test Automation Engineers often command higher pay, ranging from $85,000 to $120,000, reflecting their specialized skills in scripting and automation tools. Benefits for Test Automation Engineers frequently include access to advanced training in AI-driven testing frameworks and greater opportunities for remote work, whereas Quality Assurance Engineers benefit from broader roles in manual testing, leading to diverse team collaboration experience. Both roles offer healthcare, retirement plans, and performance bonuses, but the automation focus tends to yield faster career growth and higher salary increments.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Career
Quality Assurance Engineers ensure software reliability through manual testing, process improvement, and defect tracking, emphasizing overall product quality. Test Automation Engineers specialize in developing and maintaining automated test scripts to increase testing efficiency and coverage. Choosing between these roles depends on whether you prefer hands-on quality processes and collaboration or a focus on coding skills and automation frameworks.
Quality Assurance Engineer vs Test Automation Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com