IT support encompasses a broad range of services including network management, system administration, and cybersecurity, ensuring overall technology infrastructure stability. Desktop support specifically addresses end-user issues such as software installation, hardware troubleshooting, and peripheral device setup. Both roles are crucial for maintaining seamless technology operations but differ in scope and technical responsibilities.
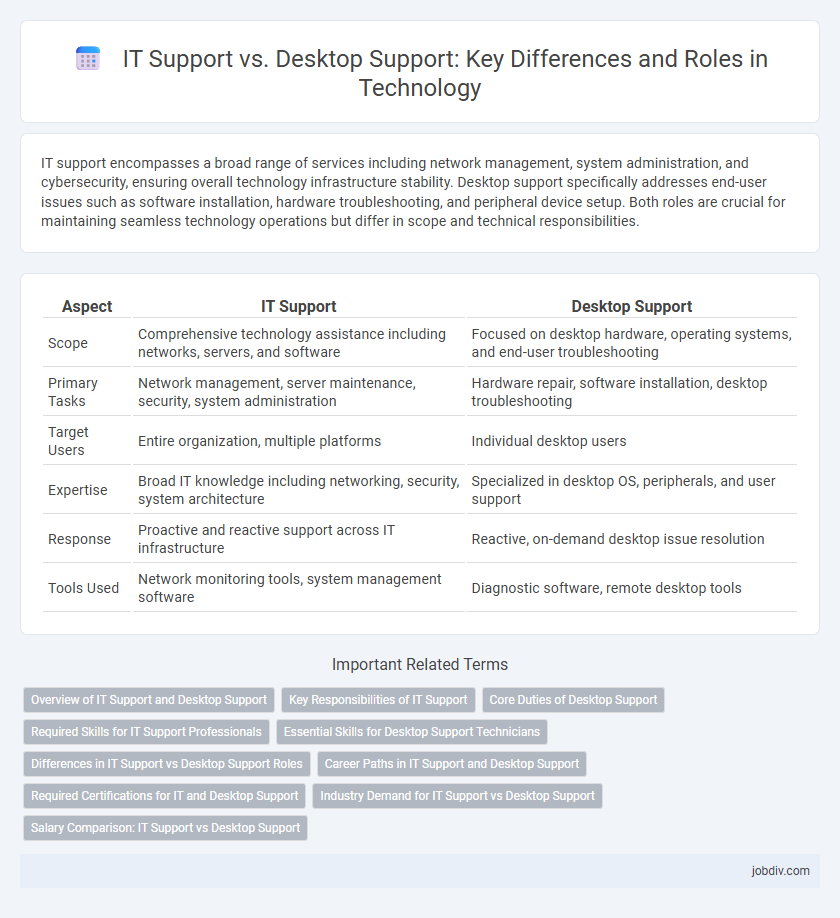
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | IT Support | Desktop Support |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Comprehensive technology assistance including networks, servers, and software | Focused on desktop hardware, operating systems, and end-user troubleshooting |
| Primary Tasks | Network management, server maintenance, security, system administration | Hardware repair, software installation, desktop troubleshooting |
| Target Users | Entire organization, multiple platforms | Individual desktop users |
| Expertise | Broad IT knowledge including networking, security, system architecture | Specialized in desktop OS, peripherals, and user support |
| Response | Proactive and reactive support across IT infrastructure | Reactive, on-demand desktop issue resolution |
| Tools Used | Network monitoring tools, system management software | Diagnostic software, remote desktop tools |
Overview of IT Support and Desktop Support
IT Support encompasses a broad range of services including network administration, server management, and cybersecurity, ensuring overall system functionality and security. Desktop Support focuses specifically on troubleshooting and maintaining end-user devices such as laptops, desktops, and peripherals to optimize user productivity. Both functions are critical for organizational IT infrastructure but serve distinct roles to address different technical needs.
Key Responsibilities of IT Support
IT Support primarily focuses on diagnosing and resolving hardware, software, and network issues, ensuring seamless business operations through effective troubleshooting and maintenance. Key responsibilities include managing user accounts, deploying software updates, and providing technical assistance to end-users across multiple devices and platforms. IT Support professionals also handle system backups, cybersecurity measures, and collaborate with other IT teams to optimize overall infrastructure performance.
Core Duties of Desktop Support
Desktop Support primarily focuses on resolving hardware and software issues related to end-user computers, including installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of desktops, laptops, and peripherals. Core duties involve diagnosing operating system errors, managing software updates, and ensuring system security for user workstations. Unlike broader IT Support, Desktop Support specialists work directly with individual users to provide immediate technical assistance and improve daily computing productivity.
Required Skills for IT Support Professionals
IT support professionals must possess a diverse skill set that includes network troubleshooting, hardware and software diagnostics, and strong customer service abilities. Proficiency in operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux, alongside knowledge of security protocols and remote support tools, is essential for effective IT support. Familiarity with scripting languages and IT service management (ITSM) platforms enhances problem-solving efficiency and streamlines incident resolution.
Essential Skills for Desktop Support Technicians
Desktop support technicians must possess strong hardware troubleshooting skills, including diagnosing and repairing desktops, laptops, and peripheral devices to ensure seamless user experiences. Proficiency in operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux is essential for efficient software installation, configuration, and update management. Effective communication skills are critical for interpreting user issues accurately and providing clear technical guidance, facilitating faster problem resolution in IT environments.
Differences in IT Support vs Desktop Support Roles
IT Support primarily focuses on managing and resolving network issues, server maintenance, and overall IT infrastructure, while Desktop Support concentrates on troubleshooting hardware and software problems on individual user devices. IT Support roles often require knowledge of networking protocols, system administration, and cybersecurity, whereas Desktop Support technicians specialize in operating systems, peripheral device configuration, and direct user assistance. The scope of IT Support is broader and more strategic, encompassing enterprise-level technology management, compared to the more tactical, user-focused responsibilities of Desktop Support.
Career Paths in IT Support and Desktop Support
IT Support careers often encompass a broader range of responsibilities, including network troubleshooting, system administration, and software support, providing pathways to roles like Systems Administrator or IT Manager. Desktop Support specialists focus specifically on end-user hardware and software issues, making it an ideal entry point toward becoming a Help Desk Technician or Desktop Support Engineer. Both career paths offer foundational skills that can lead to advanced certifications such as CompTIA A+, Microsoft Certified: Modern Desktop Administrator, or Cisco CCNA, enhancing professional growth in the technology sector.
Required Certifications for IT and Desktop Support
IT Support professionals typically require certifications such as CompTIA A+, Network+, and Microsoft Certified: Azure Fundamentals, which validate a broad understanding of hardware, networking, and cloud technologies. Desktop Support specialists often benefit from certifications like CompTIA A+ and Microsoft Certified: Modern Desktop Administrator Associate, emphasizing expertise in desktop operating systems, troubleshooting, and end-user software. Both roles prioritize certifications that demonstrate technical proficiency and the ability to resolve hardware and software issues efficiently.
Industry Demand for IT Support vs Desktop Support
Industry demand for IT Support surpasses Desktop Support due to the increasing complexity of enterprise networks, cloud services, and cybersecurity needs. IT Support professionals are sought after for their ability to manage broader infrastructure, including servers, databases, and remote systems, whereas Desktop Support primarily handles hardware and software issues on individual workstations. The ongoing digital transformation drives higher demand for IT Support roles, reflecting a shift toward comprehensive technology management across industries.
Salary Comparison: IT Support vs Desktop Support
IT Support professionals typically earn a higher average salary compared to Desktop Support technicians due to their broader range of responsibilities and expertise in managing complex IT infrastructure. According to industry salary reports, IT Support roles command an average annual salary of $55,000 to $75,000, while Desktop Support salaries generally range from $40,000 to $60,000. Factors such as certifications, experience, and geographic location significantly influence salary variations within both IT and Desktop Support positions.
IT Support vs Desktop Support Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com