Embedded Systems Engineers specialize in designing and developing hardware-software integration for devices with dedicated functions, emphasizing real-time processing and low-level programming. IoT Engineers focus on connecting these embedded devices to networks, enabling data exchange, cloud integration, and remote management through protocols and cybersecurity measures. Both roles require knowledge of embedded systems, but IoT Engineers prioritize connectivity and data analytics to create smart, interconnected solutions.
Table of Comparison
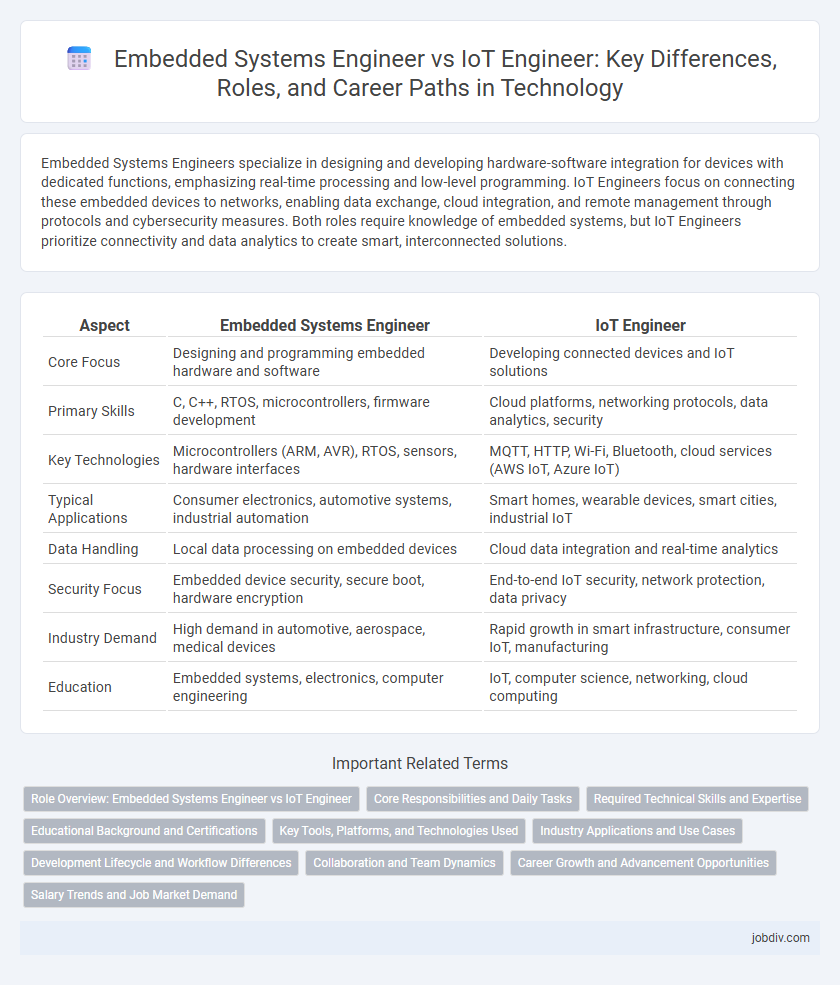
| Aspect | Embedded Systems Engineer | IoT Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Core Focus | Designing and programming embedded hardware and software | Developing connected devices and IoT solutions |
| Primary Skills | C, C++, RTOS, microcontrollers, firmware development | Cloud platforms, networking protocols, data analytics, security |
| Key Technologies | Microcontrollers (ARM, AVR), RTOS, sensors, hardware interfaces | MQTT, HTTP, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cloud services (AWS IoT, Azure IoT) |
| Typical Applications | Consumer electronics, automotive systems, industrial automation | Smart homes, wearable devices, smart cities, industrial IoT |
| Data Handling | Local data processing on embedded devices | Cloud data integration and real-time analytics |
| Security Focus | Embedded device security, secure boot, hardware encryption | End-to-end IoT security, network protection, data privacy |
| Industry Demand | High demand in automotive, aerospace, medical devices | Rapid growth in smart infrastructure, consumer IoT, manufacturing |
| Education | Embedded systems, electronics, computer engineering | IoT, computer science, networking, cloud computing |
Role Overview: Embedded Systems Engineer vs IoT Engineer
An Embedded Systems Engineer focuses on designing, developing, and maintaining hardware-centric software for microcontrollers and real-time operating systems, ensuring efficient performance of embedded devices. An IoT Engineer specializes in integrating devices into networks, managing data communication protocols, and enabling cloud connectivity for smart applications and remote monitoring. Both roles require expertise in hardware-software interfacing, but IoT Engineers emphasize network security, data analytics, and scalability across interconnected devices.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Embedded Systems Engineers specialize in designing, developing, and testing hardware and firmware for devices with real-time constraints, focusing on microcontrollers and low-level programming. IoT Engineers concentrate on integrating connected devices into networks, managing data communication protocols, cloud services, and security for scalable IoT architectures. Both roles require expertise in sensor integration and embedded software development, but IoT Engineers emphasize connectivity and data analytics to enable smart ecosystems.
Required Technical Skills and Expertise
Embedded Systems Engineers require expertise in microcontroller programming, real-time operating systems (RTOS), hardware-software integration, and low-level programming languages such as C and Assembly. IoT Engineers emphasize proficiency in network protocols (MQTT, CoAP), cloud platforms (AWS IoT, Azure IoT), data security, and sensor integration, along with skills in higher-level programming languages like Python and JavaScript. Both roles demand strong problem-solving abilities and knowledge of system architecture, but IoT Engineers prioritize connectivity and data analytics, whereas Embedded Systems Engineers focus on embedded hardware efficiency and firmware development.
Educational Background and Certifications
Embedded Systems Engineers typically hold degrees in electrical engineering, computer engineering, or computer science, with strong foundations in hardware design, real-time operating systems, and microcontrollers. IoT Engineers often pursue education in software engineering, networks, or information technology, emphasizing cloud computing, cybersecurity, and wireless communication protocols. Certifications like Certified Embedded Systems Engineer (CESE) and Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) IoT validate expertise and enhance career prospects in their respective fields.
Key Tools, Platforms, and Technologies Used
Embedded Systems Engineers primarily use tools like Keil, IAR Embedded Workbench, and hardware debugging platforms such as JTAG and SWD to develop firmware for microcontrollers, focusing on real-time operating systems (RTOS) like FreeRTOS and platforms including ARM Cortex-M and AVR architectures. IoT Engineers leverage cloud platforms such as AWS IoT, Azure IoT Hub, and Google Cloud IoT, alongside protocols like MQTT and CoAP, and use edge computing devices like Raspberry Pi and ESP32 to integrate sensors, connectivity, and data analytics effectively. Both roles require proficiency in programming languages such as C/C++ for embedded firmware and Python or JavaScript for IoT application development and data processing.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Embedded Systems Engineers design and develop specialized hardware and software tailored for real-time control in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, ensuring seamless integration of microcontrollers and sensors for optimized performance. IoT Engineers focus on creating interconnected solutions across smart cities, agriculture, and healthcare by integrating IoT devices, cloud platforms, and data analytics to enable remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced decision-making. Both roles drive digital transformation but differ in scope: Embedded Systems Engineers optimize standalone devices, while IoT Engineers build comprehensive ecosystems connecting multiple devices and systems.
Development Lifecycle and Workflow Differences
Embedded Systems Engineers primarily focus on designing, developing, and testing software tightly integrated with hardware components, emphasizing real-time constraints and hardware-software co-design throughout the development lifecycle. IoT Engineers manage end-to-end solutions that involve sensor integration, cloud connectivity, data analytics, and device security, requiring a broader workflow that includes network protocols, cloud services, and scalable deployment. Development cycles for Embedded Systems often prioritize firmware optimization and low-level programming, whereas IoT workflows integrate cross-domain skills including embedded development, network communication, and cloud infrastructure management.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
Embedded Systems Engineers and IoT Engineers collaborate closely to develop integrated solutions that combine hardware and network connectivity. Their teamwork hinges on synchronizing firmware development with cloud-based analytics, optimizing performance across devices and platforms. Effective communication and interdisciplinary knowledge sharing enhance project success and innovation in smart technology ecosystems.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Embedded Systems Engineers benefit from strong demand in industries like automotive, aerospace, and industrial automation, with career paths leading to senior hardware design roles and systems architecture. IoT Engineers experience rapid growth due to expanding smart device integration, unlocking opportunities in cloud computing, cybersecurity, and data analytics, often advancing into IoT solution architect or product management positions. Both roles offer significant career advancement potential, but IoT Engineers typically encounter faster diversification and innovation-driven progression.
Salary Trends and Job Market Demand
Embedded Systems Engineers command competitive salaries, often ranging from $75,000 to $120,000 annually, driven by demand in automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics sectors. IoT Engineers typically see higher earning potential, with average salaries between $85,000 and $130,000, fueled by rapid growth in smart devices, industrial IoT, and connected infrastructure markets. Job market demand for IoT Engineers is accelerating faster due to expanding adoption of IoT technologies, while Embedded Systems Engineers maintain steady opportunities linked to legacy systems and real-time computing applications.
Embedded Systems Engineer vs IoT Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com