UI designers focus on crafting visually appealing and intuitive interfaces, ensuring every element enhances user interaction and aesthetic appeal. UX designers concentrate on the overall user journey, conducting research and usability testing to create seamless, efficient experiences that meet user needs. Both roles collaborate closely, blending functionality with design to deliver products that are both usable and engaging.
Table of Comparison
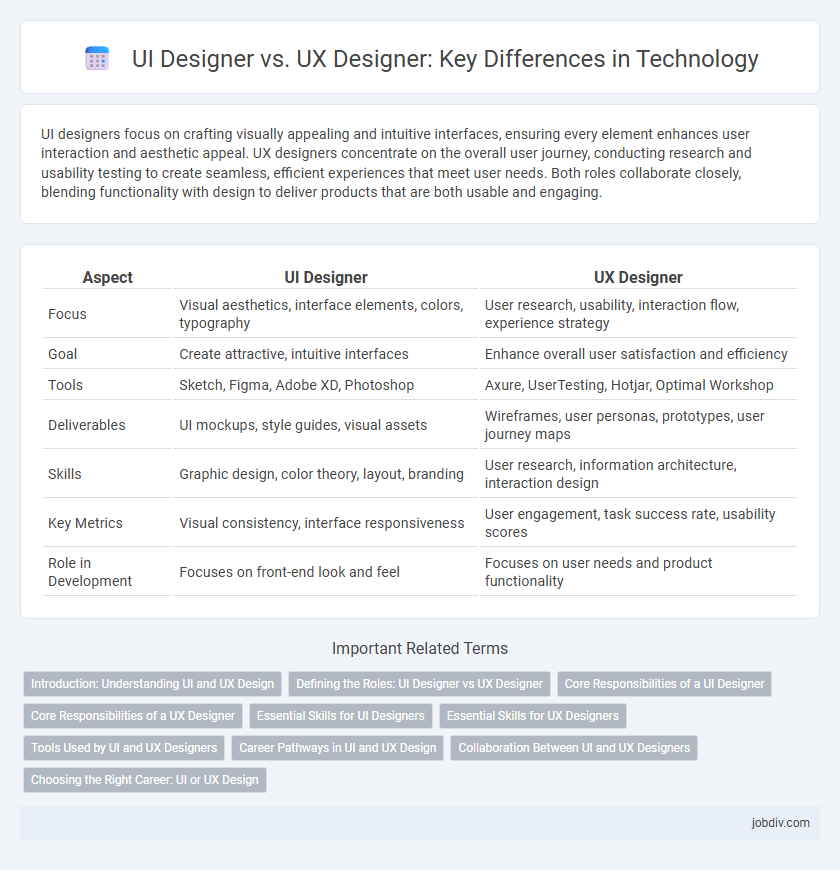
| Aspect | UI Designer | UX Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Visual aesthetics, interface elements, colors, typography | User research, usability, interaction flow, experience strategy |
| Goal | Create attractive, intuitive interfaces | Enhance overall user satisfaction and efficiency |
| Tools | Sketch, Figma, Adobe XD, Photoshop | Axure, UserTesting, Hotjar, Optimal Workshop |
| Deliverables | UI mockups, style guides, visual assets | Wireframes, user personas, prototypes, user journey maps |
| Skills | Graphic design, color theory, layout, branding | User research, information architecture, interaction design |
| Key Metrics | Visual consistency, interface responsiveness | User engagement, task success rate, usability scores |
| Role in Development | Focuses on front-end look and feel | Focuses on user needs and product functionality |
Introduction: Understanding UI and UX Design
UI designers prioritize the visual aspects of digital products, crafting interfaces that are aesthetically appealing and easy to navigate. UX designers focus on the overall user journey, ensuring functionality, usability, and satisfaction throughout the interaction with the product. Together, UI and UX design create seamless digital experiences by combining appearance with user-centric functionality.
Defining the Roles: UI Designer vs UX Designer
UI designers concentrate on crafting visually compelling interfaces with attention to typography, color schemes, and layout to enhance user interaction and aesthetic appeal. UX designers focus on optimizing the overall user experience by conducting research, creating user personas, and designing seamless user flows that improve usability and accessibility. The distinction lies in UI being concerned with the product's look and feel, while UX centers around the functionality and user satisfaction across the entire interaction.
Core Responsibilities of a UI Designer
UI Designers primarily focus on the visual elements of a digital product, including layout, color schemes, typography, and interactive components to enhance aesthetic appeal and usability. They create detailed design systems, wireframes, and prototypes to ensure consistency across interfaces and devices. Collaboration with UX Designers and developers ensures that the visual design aligns with user experience goals and technical feasibility.
Core Responsibilities of a UX Designer
A UX Designer focuses on optimizing user satisfaction by enhancing the usability, accessibility, and interaction experience of a product. They conduct user research, develop personas, create wireframes and prototypes, and perform usability testing to ensure the product meets user needs effectively. Their core responsibilities include analyzing user behavior, defining user flows, and collaborating with developers to implement intuitive design solutions.
Essential Skills for UI Designers
UI designers must excel in visual design principles, including typography, color theory, and layout composition, to create aesthetically pleasing interfaces. Proficiency in design tools such as Sketch, Figma, and Adobe XD is essential for crafting interactive prototypes and high-fidelity mockups. Strong knowledge of user interface guidelines and responsiveness across multiple devices ensures seamless user experiences tailored to different platforms.
Essential Skills for UX Designers
UX Designers excel in user research, wireframing, and usability testing to create intuitive digital experiences. Proficiency in tools such as Sketch, Figma, and Adobe XD enhances their ability to design user flows and interactive prototypes. Strong analytical skills, empathy, and understanding of human-computer interaction principles are crucial for optimizing usability and accessibility in product design.
Tools Used by UI and UX Designers
UI Designers primarily utilize tools like Adobe XD, Sketch, and Figma to create visually appealing interfaces and interactive prototypes. UX Designers often rely on software such as Axure RP, Optimal Workshop, and UserTesting to conduct usability research, wireframing, and user journey mapping. Both roles increasingly incorporate collaboration platforms like InVision and Miro to streamline feedback and iteration processes.
Career Pathways in UI and UX Design
UI Designers typically specialize in visual design, creating aesthetically appealing interfaces with a strong focus on typography, color theory, and layout to enhance user interaction. UX Designers concentrate on user research, information architecture, and usability testing to optimize the overall user experience and ensure functionality meets user needs. Career pathways in UI design often lead to roles such as Visual Designer or Interaction Designer, while UX design careers progress toward positions like UX Researcher, Product Designer, or UX Strategist.
Collaboration Between UI and UX Designers
UI designers and UX designers collaborate closely to create cohesive, user-friendly digital products by blending visual aesthetics with functional usability. UX designers conduct user research and define interaction flows, while UI designers translate these insights into visually engaging interfaces that enhance user experience. Effective collaboration involves continuous communication, iterative feedback, and alignment on design goals to ensure a seamless and intuitive user journey.
Choosing the Right Career: UI or UX Design
Choosing between UI and UX design requires understanding their core focuses: UI design centers on crafting visually appealing and interactive interfaces, while UX design emphasizes enhancing overall user satisfaction through research and usability testing. Professionals should consider their strengths in creativity and aesthetics for UI roles or analytical skills and user empathy for UX positions. Career growth in both fields is strong, with UI designers often specializing in visual communication and UX designers excelling in user journey optimization.
UI Designer vs UX Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com