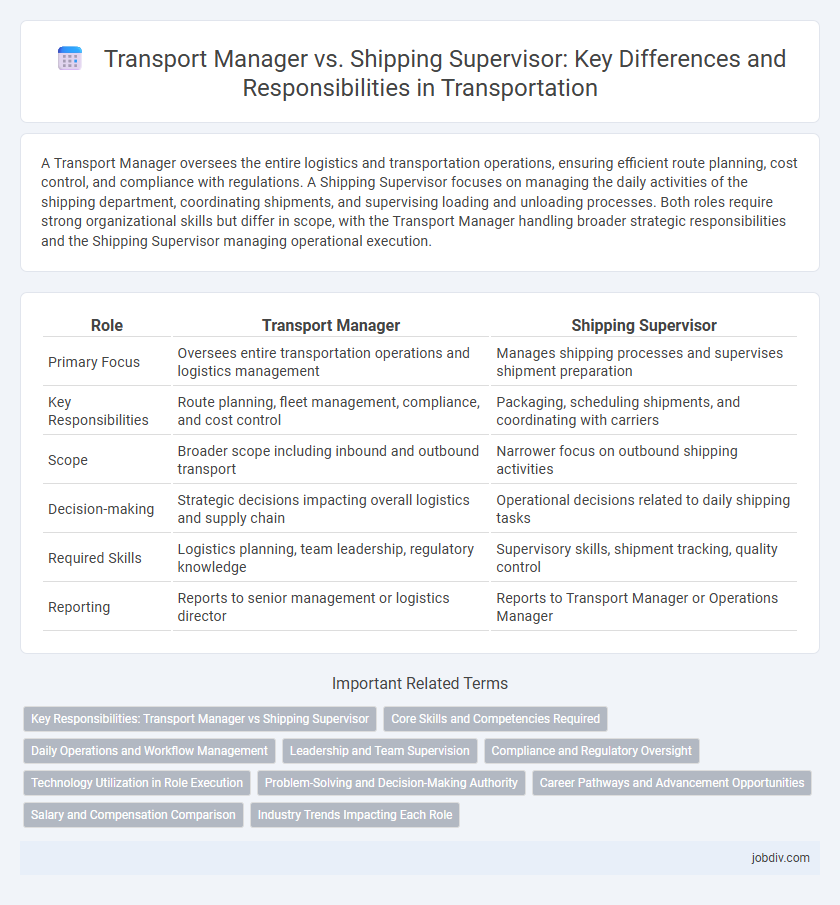
A Transport Manager oversees the entire logistics and transportation operations, ensuring efficient route planning, cost control, and compliance with regulations. A Shipping Supervisor focuses on managing the daily activities of the shipping department, coordinating shipments, and supervising loading and unloading processes. Both roles require strong organizational skills but differ in scope, with the Transport Manager handling broader strategic responsibilities and the Shipping Supervisor managing operational execution.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Transport Manager | Shipping Supervisor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Oversees entire transportation operations and logistics management | Manages shipping processes and supervises shipment preparation |
| Key Responsibilities | Route planning, fleet management, compliance, and cost control | Packaging, scheduling shipments, and coordinating with carriers |
| Scope | Broader scope including inbound and outbound transport | Narrower focus on outbound shipping activities |
| Decision-making | Strategic decisions impacting overall logistics and supply chain | Operational decisions related to daily shipping tasks |
| Required Skills | Logistics planning, team leadership, regulatory knowledge | Supervisory skills, shipment tracking, quality control |
| Reporting | Reports to senior management or logistics director | Reports to Transport Manager or Operations Manager |
Key Responsibilities: Transport Manager vs Shipping Supervisor
Transport Managers oversee the planning, coordination, and optimization of transportation operations to ensure efficient delivery schedules and regulatory compliance. Shipping Supervisors manage the day-to-day shipping activities, including cargo handling, packaging inspection, and coordination with carriers to facilitate timely dispatch. Both roles require strong organizational skills, but Transport Managers focus on strategic logistics and compliance, while Shipping Supervisors emphasize operational execution and workforce supervision.
Core Skills and Competencies Required
Transport Managers require expertise in logistics planning, fleet management, regulatory compliance, and strategic decision-making to optimize transportation operations. Shipping Supervisors focus on coordinating shipping schedules, managing warehouse staff, ensuring accurate documentation, and maintaining shipment quality and efficiency. Both roles demand strong leadership, communication skills, and a thorough understanding of supply chain processes, but Transport Managers emphasize broader operational oversight while Shipping Supervisors concentrate on day-to-day shipping activities.
Daily Operations and Workflow Management
A Transport Manager oversees the entire transportation network, optimizing routing, fleet utilization, and compliance with safety regulations to ensure efficient daily operations. Shipping Supervisors focus on coordinating loading, documentation, and shipment scheduling, managing warehouse staff and quality control to maintain smooth workflow execution. Both roles require strong communication and problem-solving skills but differ in scope, with Transport Managers handling strategic planning and Shipping Supervisors managing tactical execution.
Leadership and Team Supervision
Transport Managers oversee overall logistics operations, ensuring efficient coordination and strategic planning across multiple teams to optimize transportation workflows. Shipping Supervisors focus on direct team supervision, managing day-to-day shipping tasks, workforce scheduling, and quality control to guarantee timely dispatch and delivery. Both roles demand strong leadership skills, but Transport Managers emphasize broad operational leadership while Shipping Supervisors concentrate on tactical team management.
Compliance and Regulatory Oversight
Transport Managers ensure strict adherence to transportation laws, safety regulations, and company policies, managing compliance audits and maintaining necessary certifications. Shipping Supervisors focus on enforcing regulatory requirements related to cargo handling, documentation accuracy, and hazardous material protocols within shipping operations. Both roles collaborate to uphold industry standards, minimize legal risks, and guarantee regulatory compliance throughout the supply chain.
Technology Utilization in Role Execution
Transport Managers leverage advanced logistics software and GPS tracking systems to optimize route planning and fleet management, ensuring efficient delivery schedules. Shipping Supervisors utilize warehouse management systems and barcode scanning technology to streamline inventory control and expedite loading processes. Both roles increasingly adopt real-time data analytics and IoT devices to enhance operational visibility and decision-making accuracy in transportation workflows.
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making Authority
Transport Managers hold broader decision-making authority, overseeing entire logistics operations and solving complex issues like route optimization and regulatory compliance. Shipping Supervisors focus on day-to-day problem-solving related to shipment accuracy, staff coordination, and immediate operational challenges. The Transport Manager's strategic role drives long-term efficiency, while the Shipping Supervisor ensures smooth execution of daily shipping tasks.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Transport Managers typically oversee entire logistics operations, coordinating fleets, managing budgets, and ensuring regulatory compliance, which positions them for senior roles such as Logistics Director or Operations Manager. Shipping Supervisors concentrate on daily shipping activities, supervising staff, and ensuring accurate order fulfillment, with career advancement often leading to Transport Manager or Logistics Coordinator roles. Both pathways demand strong organizational skills but differ in scope, with Transport Managers gaining broader strategic experience suited for executive leadership.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Transport Managers typically earn a higher salary than Shipping Supervisors, with average annual earnings ranging from $60,000 to $90,000, compared to $45,000 to $65,000 for Shipping Supervisors. Compensation for Transport Managers often includes performance bonuses and profit-sharing options, reflecting their broader responsibility over logistics operations. Shipping Supervisors usually receive standard hourly wages with potential overtime pay, making their total compensation more dependent on hours worked than performance incentives.
Industry Trends Impacting Each Role
Evolving automation and digitalization significantly reshape the Transport Manager role by emphasizing strategic oversight, data analytics, and regulatory compliance to optimize fleet efficiency. Shipping Supervisors face increased pressure from real-time tracking technologies and sustainability mandates, driving enhanced operational coordination and environmental impact reduction. Both roles must adapt to industry trends like electrification, last-mile delivery innovations, and supply chain resilience to maintain competitive advantage.
Transport Manager vs Shipping Supervisor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com