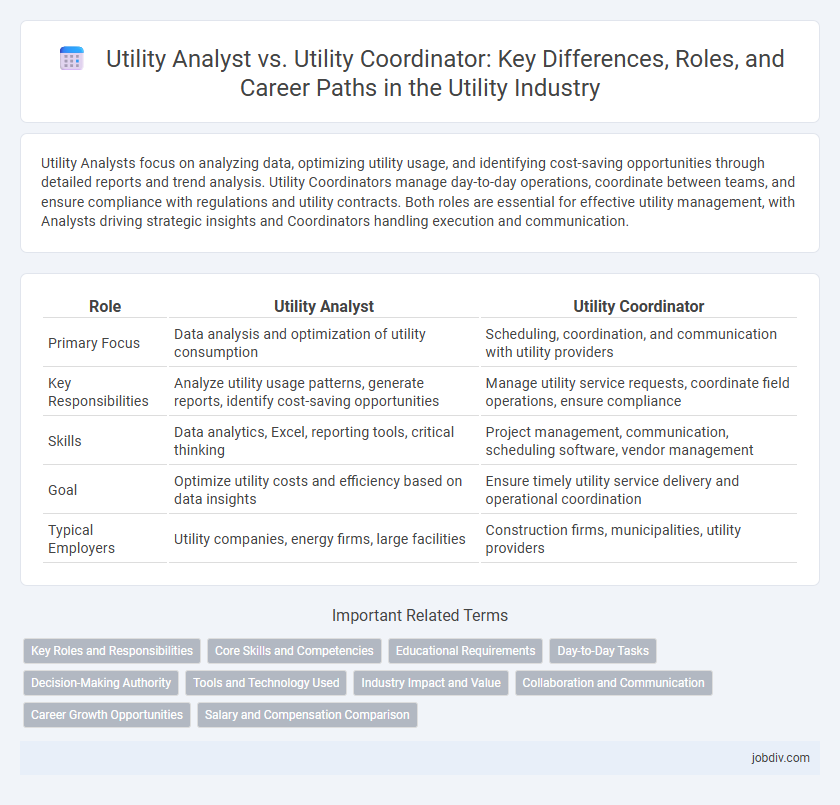
Utility Analysts focus on analyzing data, optimizing utility usage, and identifying cost-saving opportunities through detailed reports and trend analysis. Utility Coordinators manage day-to-day operations, coordinate between teams, and ensure compliance with regulations and utility contracts. Both roles are essential for effective utility management, with Analysts driving strategic insights and Coordinators handling execution and communication.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Utility Analyst | Utility Coordinator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Data analysis and optimization of utility consumption | Scheduling, coordination, and communication with utility providers |
| Key Responsibilities | Analyze utility usage patterns, generate reports, identify cost-saving opportunities | Manage utility service requests, coordinate field operations, ensure compliance |
| Skills | Data analytics, Excel, reporting tools, critical thinking | Project management, communication, scheduling software, vendor management |
| Goal | Optimize utility costs and efficiency based on data insights | Ensure timely utility service delivery and operational coordination |
| Typical Employers | Utility companies, energy firms, large facilities | Construction firms, municipalities, utility providers |
Key Roles and Responsibilities
A Utility Analyst primarily focuses on analyzing utility data to identify cost-saving opportunities, monitoring utility consumption patterns, and preparing detailed reports for budget forecasting. In contrast, a Utility Coordinator manages daily utility operations, coordinates maintenance schedules, liaises with vendors and service providers, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards. Both roles require strong attention to detail, but the Analyst emphasizes data-driven decision making, while the Coordinator prioritizes operational efficiency and communication.
Core Skills and Competencies
Utility Analysts excel in data analysis, financial modeling, and regulatory compliance, enabling strategic decision-making and utility rate forecasting. Utility Coordinators specialize in project management, stakeholder communication, and scheduling, ensuring efficient utility operations and timely service delivery. Both roles require strong problem-solving abilities and knowledge of utility regulations but differ in focus between analytical assessment and operational coordination.
Educational Requirements
A Utility Analyst typically requires a bachelor's degree in fields such as finance, economics, or engineering, emphasizing analytical and data management skills. A Utility Coordinator often holds a degree in business administration or project management, focusing on organizational and communication abilities for managing utility operations. Both roles benefit from industry-specific certifications and relevant experience but differ primarily in the scope of educational focus related to analysis versus coordination.
Day-to-Day Tasks
Utility Analysts primarily focus on data analysis, monitoring utility consumption, identifying cost-saving opportunities, and generating detailed reports to inform decision-making. Utility Coordinators manage daily operations, coordinating maintenance schedules, overseeing vendor communications, and ensuring regulatory compliance within utility services. Both roles require collaboration with internal teams but differ in task execution, with Analysts concentrating on data-driven insights and Coordinators handling operational logistics.
Decision-Making Authority
A Utility Analyst primarily provides data-driven insights and detailed reports to support decision-making processes within utility companies, focusing on analyzing consumption patterns, costs, and efficiency metrics. In contrast, a Utility Coordinator holds stronger decision-making authority, managing operational activities, implementing strategies, and coordinating between departments to ensure utility services run smoothly. The Utility Coordinator typically has the power to approve budgets, allocate resources, and directly influence policy execution, whereas the Utility Analyst's role centers on advising and recommending based on data analysis.
Tools and Technology Used
Utility Analysts primarily utilize data analytics software, geographic information systems (GIS), and advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) tools to monitor and optimize utility performance. Utility Coordinators rely heavily on work order management systems, asset management software, and communication platforms to coordinate maintenance activities and field operations efficiently. Both roles leverage specialized utility management software, but the Analyst emphasizes data-driven insights while the Coordinator focuses on operational workflow tools.
Industry Impact and Value
Utility Analysts drive industry impact by analyzing consumption patterns and optimizing resource allocation, leading to significant cost savings and enhanced operational efficiency. Utility Coordinators ensure seamless utility management by scheduling maintenance and liaising between vendors and stakeholders, directly influencing service reliability and regulatory compliance. Both roles deliver critical value by improving utility performance and supporting sustainable energy practices.
Collaboration and Communication
Utility Analysts focus on data analysis and reporting to provide insights that support strategic decisions, requiring clear communication of complex findings to stakeholders. Utility Coordinators manage workflow and facilitate collaboration among field teams, suppliers, and clients to ensure timely project completion and operational efficiency. Effective collaboration between Analysts and Coordinators enhances utility management by aligning data-driven insights with practical execution on the ground.
Career Growth Opportunities
Utility Analysts typically focus on data analysis to optimize resource management and cost efficiency, providing a strong foundation for advancing into strategic planning or management roles. Utility Coordinators manage operational workflows and interdepartmental communications, gaining hands-on experience that can lead to supervisory positions in utility operations or project management. Career growth for Utility Analysts leans toward data-driven leadership roles, whereas Utility Coordinators often progress into roles emphasizing operational management and team coordination.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
A Utility Analyst typically earns a median salary ranging from $60,000 to $80,000 annually, reflecting their focus on data analysis and efficiency optimization within utility companies. In contrast, a Utility Coordinator's salary generally falls between $50,000 and $70,000, emphasizing operational management and coordination responsibilities. Compensation packages for Utility Analysts often include performance bonuses and data-driven project incentives, whereas Utility Coordinators may receive benefits tied to team management and compliance oversight.
Utility Analyst vs Utility Coordinator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com