A Waste Auditor evaluates an organization's waste streams through data collection and analysis to identify inefficiencies and compliance issues, providing detailed reports on waste generation and disposal practices. A Waste Consultant offers strategic advice and develops tailored waste management plans aimed at reducing environmental impact, improving sustainability, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Both roles are essential for effective waste reduction but differ in scope, with auditors focusing on assessment and consultants on long-term solutions.
Table of Comparison
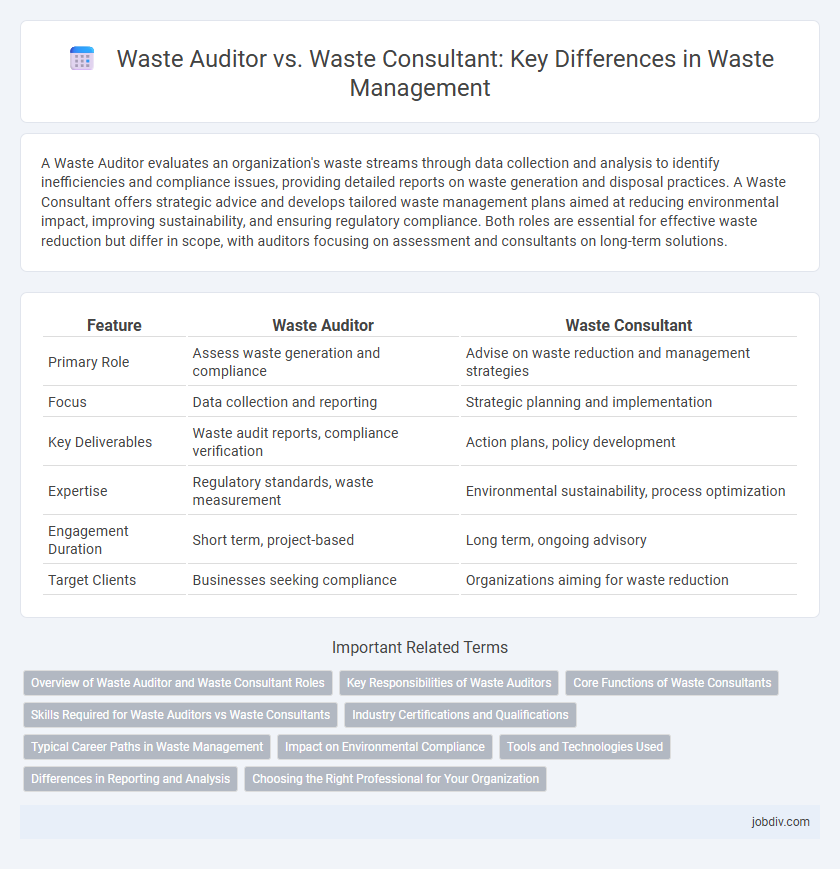
| Feature | Waste Auditor | Waste Consultant |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Assess waste generation and compliance | Advise on waste reduction and management strategies |
| Focus | Data collection and reporting | Strategic planning and implementation |
| Key Deliverables | Waste audit reports, compliance verification | Action plans, policy development |
| Expertise | Regulatory standards, waste measurement | Environmental sustainability, process optimization |
| Engagement Duration | Short term, project-based | Long term, ongoing advisory |
| Target Clients | Businesses seeking compliance | Organizations aiming for waste reduction |
Overview of Waste Auditor and Waste Consultant Roles
Waste auditors systematically evaluate waste streams to identify inefficiencies and opportunities for reduction, ensuring regulatory compliance and cost savings. Waste consultants provide strategic guidance and customized waste management solutions, focusing on sustainability goals and long-term environmental impact. Both roles contribute to optimizing waste processes but differ in approach--auditors concentrate on data analysis and reporting, while consultants emphasize advisory and implementation strategies.
Key Responsibilities of Waste Auditors
Waste auditors specialize in assessing waste streams to identify inefficiencies and opportunities for reduction, conducting comprehensive waste audits to quantify types and volumes of waste generated by organizations. They analyze data to develop actionable recommendations for waste diversion, recycling improvements, and cost savings, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Waste auditors also prepare detailed reports that guide companies in implementing sustainable waste management practices and tracking progress over time.
Core Functions of Waste Consultants
Waste consultants specialize in assessing waste management systems, developing strategies for waste reduction, and ensuring regulatory compliance. They analyze waste streams, recommend sustainable practices, and support businesses in achieving environmental goals. Unlike waste auditors who focus primarily on evaluating current waste outputs, waste consultants provide comprehensive solutions for waste minimization and resource optimization.
Skills Required for Waste Auditors vs Waste Consultants
Waste Auditors require strong analytical skills, proficiency in data collection, and expertise in regulatory compliance to accurately assess waste management practices and identify inefficiencies. Waste Consultants need advanced knowledge in environmental policies, strategic planning, and client communication to develop tailored waste reduction solutions and sustainable management strategies. Both roles demand a solid understanding of waste types, recycling processes, and sustainability principles to optimize waste handling and minimize environmental impact.
Industry Certifications and Qualifications
Waste auditors typically hold certifications such as Certified Environmental Auditor (CEA) or Certified Waste Auditor (CWA), emphasizing expertise in data collection, waste stream analysis, and regulatory compliance. Waste consultants often possess broader qualifications like LEED Accredited Professional (LEED AP) or Certified Hazardous Materials Manager (CHMM), reflecting a strategic role in designing waste reduction programs and sustainability initiatives. Industry certifications for both roles ensure proficiency in environmental standards, risk management, and cost-saving waste solutions.
Typical Career Paths in Waste Management
Waste auditors typically begin their careers with backgrounds in environmental science or engineering, focusing on data collection and analysis related to waste generation and disposal. Waste consultants often advance from auditing roles to provide strategic advice on waste reduction, regulatory compliance, and sustainable practices for businesses and municipalities. Career progression in waste management frequently involves specialization in areas such as hazardous waste, recycling programs, or corporate sustainability initiatives.
Impact on Environmental Compliance
Waste auditors assess facility waste streams and identify areas of non-compliance with environmental regulations through detailed waste characterization and data analysis. Waste consultants develop and implement strategies that ensure adherence to environmental laws, improve waste management practices, and minimize potential regulatory penalties. Their combined efforts enhance a company's environmental compliance by reducing waste-related risks and promoting sustainable operations.
Tools and Technologies Used
Waste auditors rely heavily on measurement instruments such as scales, volume meters, and waste tracking software to quantify and analyze waste generation accurately. Waste consultants leverage advanced data analytics platforms, lifecycle assessment tools, and environmental management systems to develop strategic waste reduction plans tailored to organizational goals. Both roles increasingly utilize IoT sensors and real-time monitoring technologies to optimize waste management processes and improve sustainability outcomes.
Differences in Reporting and Analysis
Waste auditors provide detailed quantitative reports focused on waste composition and volume, utilizing precise data collection methods such as waste characterization studies. Waste consultants analyze these audit reports to develop strategic recommendations aimed at waste minimization, regulatory compliance, and cost reduction. The auditor's output is highly data-centric with an emphasis on accuracy and measurement, whereas the consultant's reporting incorporates broader contextual analysis and actionable insights for sustainable waste management.
Choosing the Right Professional for Your Organization
Selecting the right expert for managing organizational waste hinges on understanding key roles: a Waste Auditor systematically assesses waste streams to identify reduction opportunities, while a Waste Consultant provides strategic guidance on waste management policies and compliance. Waste Auditors deliver data-driven insights through site inspections and waste characterization, enabling targeted improvements in recycling and disposal practices. Waste Consultants leverage industry expertise to develop long-term sustainability plans, regulatory adherence strategies, and employee training programs, making the choice dependent on whether immediate operational analysis or comprehensive waste strategy is the priority.
Waste Auditor vs Waste Consultant Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com