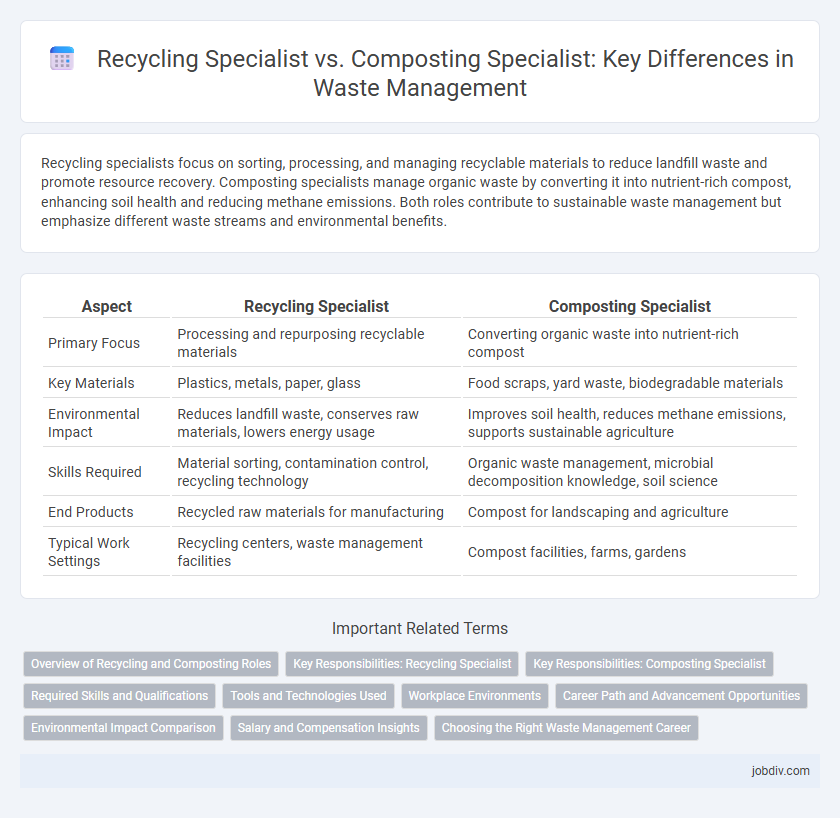
Recycling specialists focus on sorting, processing, and managing recyclable materials to reduce landfill waste and promote resource recovery. Composting specialists manage organic waste by converting it into nutrient-rich compost, enhancing soil health and reducing methane emissions. Both roles contribute to sustainable waste management but emphasize different waste streams and environmental benefits.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Recycling Specialist | Composting Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Processing and repurposing recyclable materials | Converting organic waste into nutrient-rich compost |
| Key Materials | Plastics, metals, paper, glass | Food scraps, yard waste, biodegradable materials |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste, conserves raw materials, lowers energy usage | Improves soil health, reduces methane emissions, supports sustainable agriculture |
| Skills Required | Material sorting, contamination control, recycling technology | Organic waste management, microbial decomposition knowledge, soil science |
| End Products | Recycled raw materials for manufacturing | Compost for landscaping and agriculture |
| Typical Work Settings | Recycling centers, waste management facilities | Compost facilities, farms, gardens |
Overview of Recycling and Composting Roles
Recycling specialists manage the collection, sorting, and processing of recyclable materials like paper, plastics, and metals to reduce landfill waste and promote resource recovery. Composting specialists focus on converting organic waste, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, into nutrient-rich compost through biological decomposition processes. Both roles aim to minimize environmental impact but target different waste streams and require specialized knowledge in material handling and treatment methods.
Key Responsibilities: Recycling Specialist
Recycling Specialists manage the sorting, processing, and distribution of recyclable materials to maximize waste diversion and environmental sustainability. They analyze waste streams, develop recycling programs, and ensure compliance with local regulations to enhance material recovery rates. Their expertise includes coordinating with municipalities and businesses to implement efficient recycling systems and reduce landfill reliance.
Key Responsibilities: Composting Specialist
Composting specialists manage organic waste decomposition by overseeing the aerobic breakdown of food scraps, yard waste, and biodegradable materials into nutrient-rich compost. They design and implement composting programs, monitor temperature and moisture levels, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations to optimize microbial activity and reduce landfill contributions. Their expertise supports sustainable waste diversion and soil health improvement through efficient organic waste transformation.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Recycling specialists require expertise in waste sorting, material recovery technologies, and knowledge of environmental regulations to optimize recycling processes and reduce landfill use. Composting specialists need skills in organic waste management, microbial biology, and soil science to facilitate effective decomposition and nutrient cycling for sustainable agriculture. Both roles demand strong analytical abilities, attention to detail, and proficiency in data collection for compliance reporting and process improvement.
Tools and Technologies Used
Recycling specialists utilize advanced sorting technologies like optical sorters, magnetic separators, and automated conveyor systems to efficiently separate plastics, metals, and paper for processing. Composting specialists rely on tools such as aeration equipment, temperature monitoring devices, and moisture sensors to manage organic waste decomposition and optimize microbial activity. Both professionals employ software for tracking waste streams and improving process efficiencies, tailored to their specific recycling or composting methodologies.
Workplace Environments
Recycling Specialists typically work in urban or industrial settings such as recycling centers, waste management facilities, or municipal operations, where they handle sorting, processing, and managing recyclable materials like plastics, metals, and paper. Composting Specialists are often found in agricultural sites, environmental organizations, or commercial composting facilities focused on organic waste decomposition and soil enrichment. Both roles require knowledge of waste segregation, but workplace environments differ in focus; recycling emphasizes material recovery, while composting prioritizes biodegradation and nutrient cycling.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Recycling specialists focus on managing and improving processes to sort, process, and repurpose recyclable materials, often advancing to managerial roles in waste management facilities or sustainability consulting. Composting specialists concentrate on organic waste decomposition, progressing to positions such as environmental coordinators or experts in soil health and sustainable agriculture. Both career paths offer growth through certifications, project leadership, and roles that influence corporate or municipal waste reduction strategies.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycling specialists enhance environmental sustainability by diverting materials such as plastics, metals, and paper from landfills, reducing resource extraction and energy consumption. Composting specialists focus on organic waste, transforming food scraps and yard trimmings into nutrient-rich soil amendments that improve soil health and sequester carbon. The combined efforts of both specialties significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions, with composting reducing methane from organic decay and recycling minimizing pollution from raw material processing.
Salary and Compensation Insights
Recycling specialists typically earn an average salary ranging from $45,000 to $65,000 annually, reflecting their technical expertise in waste sorting and material recovery processes. Composting specialists often receive compensation within the $40,000 to $60,000 range, influenced by their knowledge in organic waste management and soil enhancement techniques. Both roles may include benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, with variations depending on industry and geographic location.
Choosing the Right Waste Management Career
Recycling specialists focus on processing materials like plastics, metals, and paper to reduce landfill waste, requiring knowledge in sorting technologies and resource recovery. Composting specialists manage organic waste decomposing processes, promoting soil health and reducing methane emissions through expertise in microbial activity and nutrient cycling. Selecting between these careers depends on your interest in either advancing circular economy practices or enhancing sustainable organic waste solutions.
Recycling Specialist vs Composting Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com