Waste Management Technicians handle the operational aspects of waste collection, sorting, and disposal, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and safety standards. Solid Waste Engineers design and optimize waste treatment facilities, develop sustainable waste management systems, and analyze the environmental impact of various disposal methods. Both roles contribute to efficient waste reduction and environmental protection but differ in their focus on hands-on operations versus strategic planning and engineering solutions.
Table of Comparison
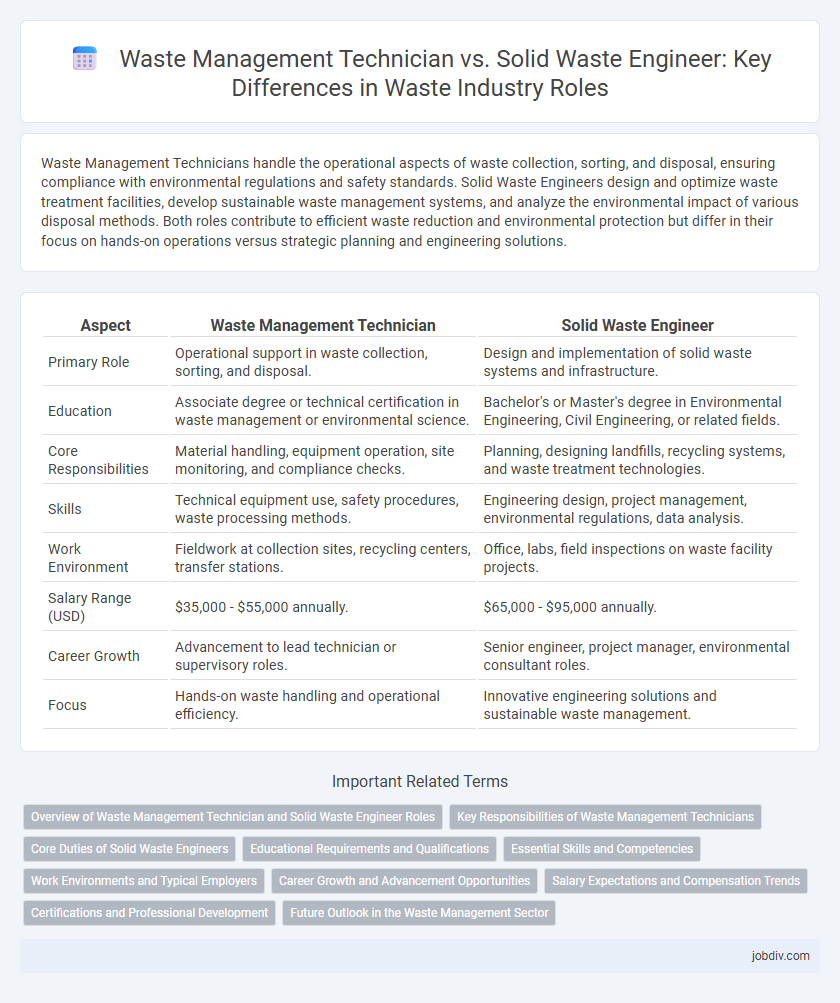
| Aspect | Waste Management Technician | Solid Waste Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Operational support in waste collection, sorting, and disposal. | Design and implementation of solid waste systems and infrastructure. |
| Education | Associate degree or technical certification in waste management or environmental science. | Bachelor's or Master's degree in Environmental Engineering, Civil Engineering, or related fields. |
| Core Responsibilities | Material handling, equipment operation, site monitoring, and compliance checks. | Planning, designing landfills, recycling systems, and waste treatment technologies. |
| Skills | Technical equipment use, safety procedures, waste processing methods. | Engineering design, project management, environmental regulations, data analysis. |
| Work Environment | Fieldwork at collection sites, recycling centers, transfer stations. | Office, labs, field inspections on waste facility projects. |
| Salary Range (USD) | $35,000 - $55,000 annually. | $65,000 - $95,000 annually. |
| Career Growth | Advancement to lead technician or supervisory roles. | Senior engineer, project manager, environmental consultant roles. |
| Focus | Hands-on waste handling and operational efficiency. | Innovative engineering solutions and sustainable waste management. |
Overview of Waste Management Technician and Solid Waste Engineer Roles
Waste Management Technicians specialize in the operational aspects of waste collection, sorting, and disposal, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and promoting efficient waste handling processes. Solid Waste Engineers focus on designing and implementing systems for waste treatment, recycling, and landfill management, utilizing engineering principles to optimize waste reduction and environmental protection. Both roles are critical in the waste management sector, combining practical skills and technical expertise to address sustainable waste solutions.
Key Responsibilities of Waste Management Technicians
Waste Management Technicians primarily focus on the operational aspects of waste collection, sorting, and disposal, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and safety protocols. They monitor equipment functionality, perform routine inspections, and assist in the maintenance of waste processing facilities to optimize efficiency. Their role emphasizes hands-on management of waste streams, supporting Solid Waste Engineers who design and oversee broader waste management systems and sustainability initiatives.
Core Duties of Solid Waste Engineers
Solid Waste Engineers design and implement systems for effective waste handling, focusing on sustainable landfill development, waste treatment technologies, and environmental compliance. They conduct site assessments, develop waste reduction strategies, and ensure adherence to health and safety regulations. Their expertise supports long-term waste management planning and resource recovery initiatives.
Educational Requirements and Qualifications
A Waste Management Technician typically requires an associate degree or a technical diploma in environmental science or waste management, emphasizing hands-on skills in waste collection, sorting, and basic facility operations. In contrast, a Solid Waste Engineer must hold a bachelor's degree in environmental engineering, civil engineering, or a related field, with expertise in designing waste treatment systems, landfill management, and compliance with environmental regulations. Professional certifications such as Certified Solid Waste Manager (CSWM) or Engineer-in-Training (EIT) further enhance qualifications for Solid Waste Engineers.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Waste Management Technicians require hands-on skills in hazardous material handling, equipment operation, and regulatory compliance to effectively manage collection and disposal processes. Solid Waste Engineers must demonstrate competency in designing waste treatment systems, conducting environmental impact assessments, and applying principles of sustainable resource management. Both roles demand a strong understanding of local waste management policies and proficient problem-solving abilities to optimize waste reduction and recycling efforts.
Work Environments and Typical Employers
Waste Management Technicians typically work in field settings such as recycling centers, landfills, and waste collection sites, where they manage day-to-day operations and ensure compliance with safety protocols. Solid Waste Engineers are often employed by municipal governments, environmental consulting firms, or waste management companies, working in office environments and project sites to design and implement waste disposal systems and sustainable solutions. Both roles require collaboration with environmental agencies and public utilities to optimize waste processing and minimize environmental impact.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Waste Management Technicians typically engage in operational tasks such as collection, processing, and disposal of waste, providing entry-level experience with opportunities for certification and skill development. Solid Waste Engineers focus on designing systems and strategies for waste reduction, recycling, and environmental compliance, offering advanced career growth through engineering degrees and specialized training. Career advancement for technicians often leads to supervisory roles, while engineers can progress into management, project leadership, or consultancy positions in environmental and public sectors.
Salary Expectations and Compensation Trends
Waste Management Technicians typically earn median salaries ranging from $35,000 to $50,000 annually, reflecting entry to mid-level positions focused on operational tasks such as waste collection and sorting. Solid Waste Engineers command higher compensation, often between $70,000 to $100,000 per year, driven by their specialized expertise in designing waste treatment systems and managing large-scale solid waste projects. Compensation trends indicate rising demand for engineers due to increasing environmental regulations and sustainable waste management initiatives, resulting in competitive salary growth within the solid waste engineering sector.
Certifications and Professional Development
Waste Management Technicians typically hold certifications such as OSHA hazardous waste operations training (HAZWOPER) and Certified Solid Waste Manager (CSWM) credentials, emphasizing hands-on skills in waste collection and site operations. Solid Waste Engineers often require advanced certifications like Professional Engineer (PE) licensure and LEED Accreditation, focusing on environmental compliance, system design, and sustainable waste solutions. Both roles demand ongoing professional development through specialized workshops and industry seminars to stay current with evolving waste management technologies and regulations.
Future Outlook in the Waste Management Sector
The future outlook for Waste Management Technicians is strong due to increasing demand for skilled personnel in waste collection, sorting, and recycling processes, driven by stricter environmental regulations and growing sustainability initiatives. Solid Waste Engineers face expanding opportunities as advances in technology and infrastructure require specialized expertise in designing efficient waste treatment systems, landfill management, and resource recovery. Both roles are critical for advancing circular economy goals, with growth fueled by urbanization and global commitments to reducing landfill use and greenhouse gas emissions.
Waste Management Technician vs Solid Waste Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com