An irrigation technician specializes in installing, maintaining, and repairing irrigation systems, ensuring efficient water distribution for agricultural or landscape use. A ditch rider monitors and manages water flow in open irrigation canals or ditches, preventing leaks and ensuring equitable water delivery to farmers. Both roles are essential for optimizing water usage and supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
Table of Comparison
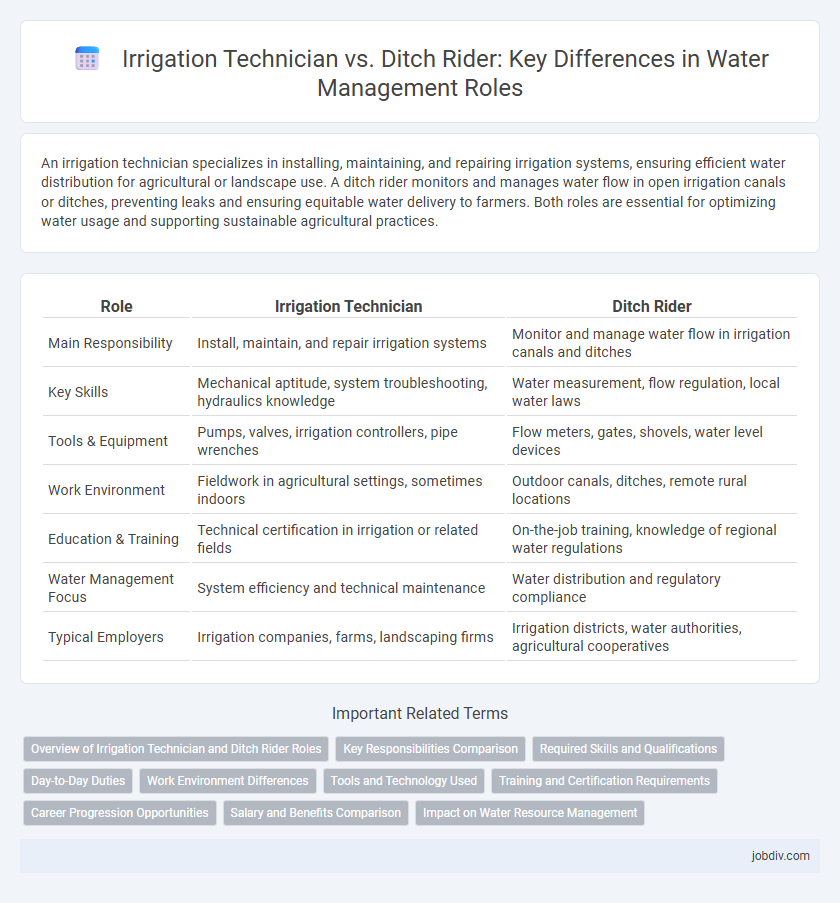
| Role | Irrigation Technician | Ditch Rider |
|---|---|---|
| Main Responsibility | Install, maintain, and repair irrigation systems | Monitor and manage water flow in irrigation canals and ditches |
| Key Skills | Mechanical aptitude, system troubleshooting, hydraulics knowledge | Water measurement, flow regulation, local water laws |
| Tools & Equipment | Pumps, valves, irrigation controllers, pipe wrenches | Flow meters, gates, shovels, water level devices |
| Work Environment | Fieldwork in agricultural settings, sometimes indoors | Outdoor canals, ditches, remote rural locations |
| Education & Training | Technical certification in irrigation or related fields | On-the-job training, knowledge of regional water regulations |
| Water Management Focus | System efficiency and technical maintenance | Water distribution and regulatory compliance |
| Typical Employers | Irrigation companies, farms, landscaping firms | Irrigation districts, water authorities, agricultural cooperatives |
Overview of Irrigation Technician and Ditch Rider Roles
Irrigation Technicians specialize in installing, maintaining, and repairing irrigation systems for agricultural and landscaping purposes, ensuring optimal water distribution and efficiency. Ditch Riders monitor and manage water flow in irrigation canals and ditches, overseeing water delivery schedules and resolving water allocation disputes among farmers. Both roles are critical for effective water management in irrigation infrastructure but differ in technical focus and operational scope.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
Irrigation Technicians specialize in maintaining and repairing irrigation systems, ensuring efficient water distribution through equipment monitoring and system troubleshooting. Ditch Riders oversee water flow management in canals and ditches, performing inspections to prevent leaks and unauthorized water use, while coordinating water deliveries to users. Both roles require knowledge of water management, but technicians focus more on mechanical and system aspects, whereas ditch riders emphasize water allocation and field-level distribution monitoring.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Irrigation technicians require strong technical skills in system installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting to ensure optimal water distribution efficiency. Ditch riders must possess in-depth knowledge of water rights, canal operations, and monitoring techniques to manage water delivery and resolve flow issues effectively. Both roles demand proficiency in equipment handling, problem-solving, and an understanding of hydrology and water management practices.
Day-to-Day Duties
Irrigation Technicians manage the installation, maintenance, and repair of irrigation systems, ensuring optimal water distribution for agricultural fields. Ditch Riders monitor water flow through canals and ditches, regulate gates and valves, and inspect infrastructure to prevent leaks and ensure equitable water delivery. Both roles are critical in water resource management, with technicians focusing on system functionality while ditch riders oversee water distribution logistics.
Work Environment Differences
Irrigation technicians typically work in diverse agricultural settings, managing and maintaining complex irrigation systems to optimize water distribution. Ditch riders operate primarily in outdoor environments, patrolling canals and ditches to monitor water flow and ensure efficient delivery to farmland. While irrigation technicians often use advanced technology and equipment, ditch riders rely more on hands-on inspection and water management skills in variable weather conditions.
Tools and Technology Used
Irrigation technicians utilize advanced tools such as flow meters, soil moisture sensors, and automated control systems to ensure precise water distribution and system efficiency. Ditch riders primarily rely on manual tools like gates, wrenches, and valves to monitor and manage open canal systems, conducting physical inspections to maintain water flow. The integration of real-time monitoring technology is more prevalent among irrigation technicians, enhancing their ability to optimize water use in agricultural settings.
Training and Certification Requirements
Irrigation technicians typically require formal training through specialized agricultural or technical programs and certification such as the Certified Irrigation Contractor (CIC) credential. Ditch riders often gain expertise through on-the-job experience and may need certification from local water management authorities, emphasizing knowledge of water rights and canal operations. Both roles prioritize practical skills, but irrigation technicians generally hold more formalized certifications related to system design and maintenance.
Career Progression Opportunities
Irrigation technicians often have broader career progression opportunities, advancing into roles such as irrigation system designers, project managers, or water resource specialists due to their technical expertise and knowledge of modern irrigation technologies. Ditch riders typically gain experience in water management and canal operation, with potential career growth leading to supervisory positions or water district management, emphasizing operational oversight and regulatory compliance. Both career paths offer specialized skills, but irrigation technicians tend to have more opportunities for advancement in engineering and technology-driven sectors within water management.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
Irrigation technicians typically earn an average salary ranging from $40,000 to $60,000 annually, often including benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. Ditch riders generally have a salary range closer to $35,000 to $55,000, with benefits that may include hazard pay, overtime compensation, and seasonal job security. Both roles demand specialized skills in water management and offer financial packages influenced by geographic location, employer size, and experience level.
Impact on Water Resource Management
Irrigation technicians focus on maintaining and optimizing mechanical systems to improve water efficiency, significantly reducing water waste through precise control of flow and timing. Ditch riders monitor canal and ditch operations directly, ensuring water distribution aligns with legal allocations and preventing water theft or loss during conveyance. Both roles are crucial for sustainable water resource management, balancing technological efficiency with real-time field oversight to enhance overall irrigation system performance.
Irrigation Technician vs Ditch Rider Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com