Drop shippers operate without holding inventory, forwarding customer orders directly to manufacturers or suppliers, which reduces upfront costs and storage needs. Stocking wholesalers maintain inventory, allowing for faster shipping times and greater control over stock availability, but require higher investment in warehousing and logistics. Choosing between drop shipping and stocking wholesaler models depends on your business priorities, such as cash flow management and delivery speed.
Table of Comparison
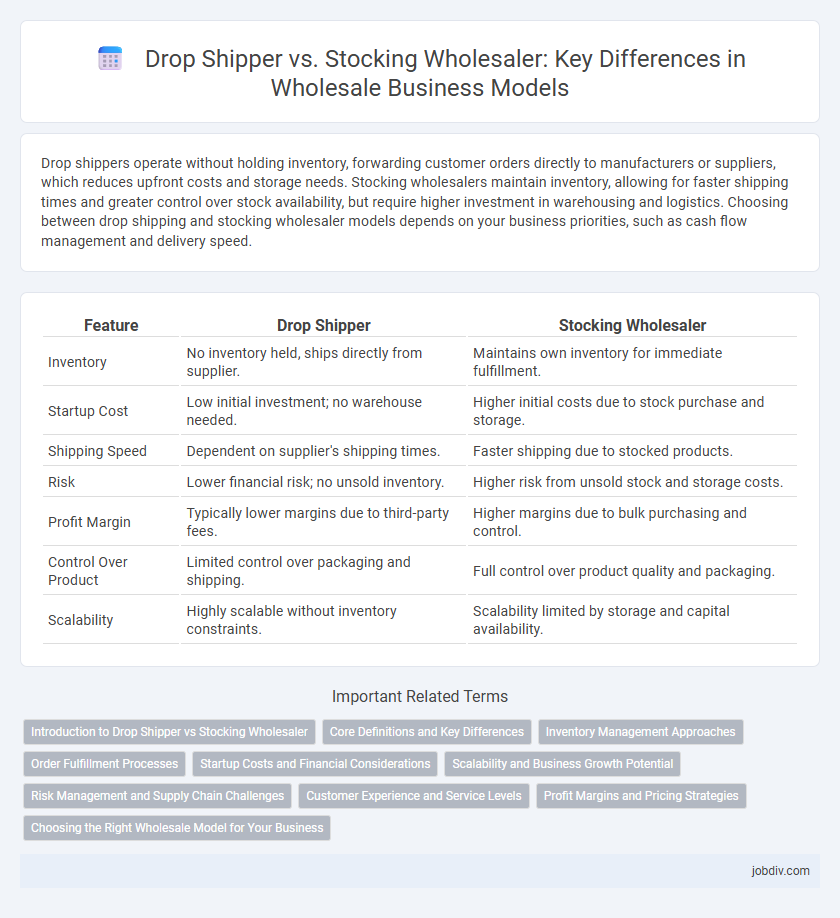
| Feature | Drop Shipper | Stocking Wholesaler |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory | No inventory held, ships directly from supplier. | Maintains own inventory for immediate fulfillment. |
| Startup Cost | Low initial investment; no warehouse needed. | Higher initial costs due to stock purchase and storage. |
| Shipping Speed | Dependent on supplier's shipping times. | Faster shipping due to stocked products. |
| Risk | Lower financial risk; no unsold inventory. | Higher risk from unsold stock and storage costs. |
| Profit Margin | Typically lower margins due to third-party fees. | Higher margins due to bulk purchasing and control. |
| Control Over Product | Limited control over packaging and shipping. | Full control over product quality and packaging. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable without inventory constraints. | Scalability limited by storage and capital availability. |
Introduction to Drop Shipper vs Stocking Wholesaler
Drop shippers fulfill orders directly from suppliers without holding inventory, minimizing upfront costs and reducing storage risks. Stocking wholesalers maintain large inventories, enabling faster order fulfillment and bulk purchasing advantages for retailers. Understanding these distinct operational models helps businesses choose the best supply chain strategy based on cost, speed, and storage capabilities.
Core Definitions and Key Differences
A drop shipper acts as an intermediary who sells products directly from suppliers to customers without holding inventory, while a stocking wholesaler maintains physical stock to fulfill orders promptly. Drop shippers minimize upfront investment and storage costs but rely on third-party suppliers for fulfillment, resulting in longer delivery times. Stocking wholesalers offer faster shipping and greater control over inventory but require significant capital for warehousing and stock management.
Inventory Management Approaches
Drop shippers manage inventory by relying on suppliers to hold and ship products directly to customers, minimizing their own warehousing needs and reducing upfront investment. Stocking wholesalers maintain physical inventory, enabling faster order fulfillment and tighter control over stock levels, but requiring significant storage space and capital. Efficient inventory management for drop shippers involves real-time supplier coordination, while stocking wholesalers emphasize accurate demand forecasting and warehouse optimization.
Order Fulfillment Processes
Drop shippers process orders by forwarding customer purchases directly to manufacturers or suppliers, eliminating the need for inventory storage and reducing upfront costs. Stocking wholesalers manage inventory in warehouses, enabling faster order fulfillment and greater control over stock levels but requiring significant capital investment in storage and handling. Efficient order fulfillment for drop shippers relies on seamless communication with suppliers, while stocking wholesalers benefit from streamlined logistics and quicker shipment times.
Startup Costs and Financial Considerations
Drop shippers incur lower startup costs as they avoid inventory expenses, while stocking wholesalers require substantial capital investment for purchasing and storing products. Financial considerations for drop shippers include relying on supplier reliability and potentially lower profit margins, whereas stocking wholesalers benefit from higher control over inventory and pricing but face risks associated with unsold stock. Effective cash flow management is crucial for stocking wholesalers due to upfront inventory costs and warehousing expenses.
Scalability and Business Growth Potential
Drop shippers offer high scalability by eliminating inventory costs and allowing quick expansion into diverse product lines, making them ideal for businesses prioritizing flexible growth. Stocking wholesalers provide greater control over inventory and fulfillment speed, supporting steady, sustainable growth with larger order volumes and consistent supply reliability. Scalability in drop shipping hinges on supplier partnerships and platform efficiency, while stocking wholesalers benefit from established warehousing and bulk purchasing economies to fuel long-term business expansion.
Risk Management and Supply Chain Challenges
Drop shippers minimize inventory risk by not holding stock, relying on suppliers to fulfill orders directly, which reduces upfront capital but introduces dependency on third-party reliability. Stocking wholesalers face higher inventory risks due to purchasing and storing large quantities, yet maintain greater control over supply chain speed and product availability. Effective risk management requires balancing inventory investment against supplier dependability while navigating challenges such as lead time variability and demand forecasting accuracy.
Customer Experience and Service Levels
Drop shippers often provide faster access to a wider product range without inventory holding, enhancing customer experience through diverse choices and lower prices. Stocking wholesalers maintain physical inventory, enabling quicker order fulfillment and reliable service levels by reducing delays and stockouts. Customers benefit from drop shippers' extensive selections and cost savings, while stocking wholesalers excel in speed, consistency, and personalized support.
Profit Margins and Pricing Strategies
Drop shippers often benefit from lower upfront costs as they don't hold inventory, resulting in thinner profit margins but reduced financial risk. Stocking wholesalers invest in inventory, allowing them to negotiate better bulk pricing and achieve higher profit margins through volume discounts. Pricing strategies for drop shippers focus on competitive retail markups, while stocking wholesalers leverage economies of scale to optimize pricing and maximize profitability.
Choosing the Right Wholesale Model for Your Business
Choosing the right wholesale model depends on inventory management and cash flow preferences; drop shippers avoid inventory costs by shipping products directly from suppliers, reducing upfront investment and risk. Stocking wholesalers maintain inventory, offering faster order fulfillment and greater control over product quality but require higher storage costs and capital. Evaluating your business's scale, target market demands, and operational capacity ensures optimal alignment between supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Drop Shipper vs Stocking Wholesaler Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com