Importing wholesale pet products allows businesses to access diverse and unique items not available locally, often at lower costs due to global manufacturing efficiencies. Exporting enables companies to expand their market reach by distributing pet goods internationally, increasing revenue streams and brand recognition. Both importing and exporting require compliance with international regulations and careful logistics planning to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery.
Table of Comparison
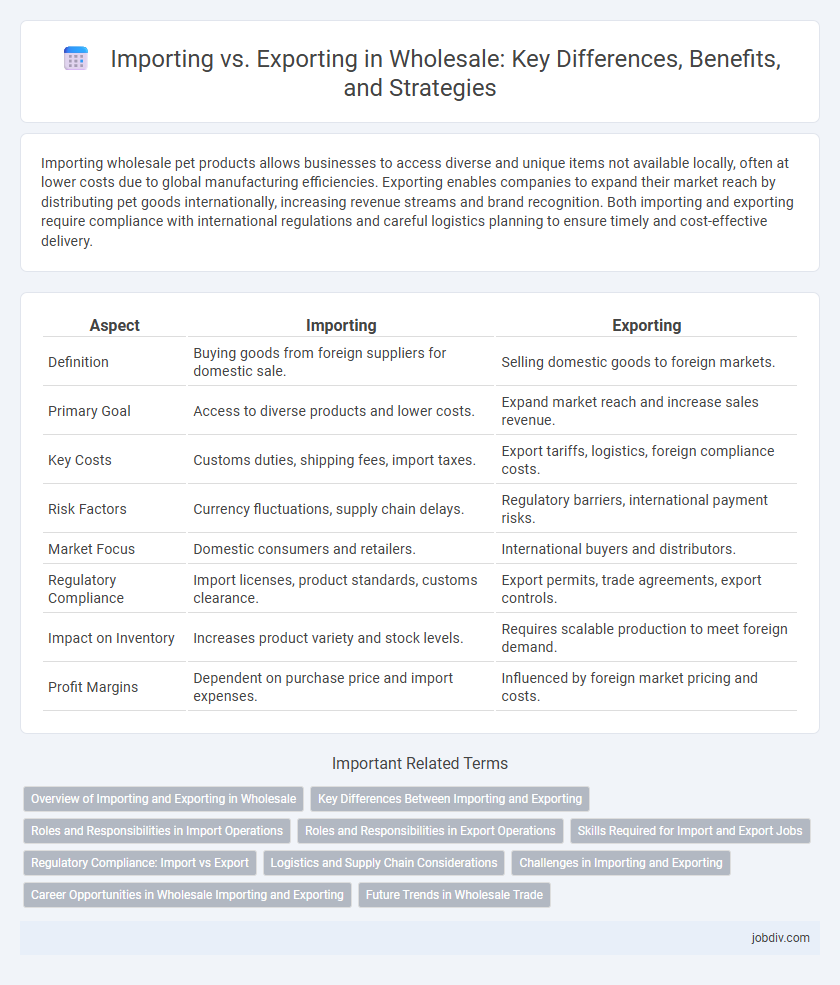
| Aspect | Importing | Exporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying goods from foreign suppliers for domestic sale. | Selling domestic goods to foreign markets. |
| Primary Goal | Access to diverse products and lower costs. | Expand market reach and increase sales revenue. |
| Key Costs | Customs duties, shipping fees, import taxes. | Export tariffs, logistics, foreign compliance costs. |
| Risk Factors | Currency fluctuations, supply chain delays. | Regulatory barriers, international payment risks. |
| Market Focus | Domestic consumers and retailers. | International buyers and distributors. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Import licenses, product standards, customs clearance. | Export permits, trade agreements, export controls. |
| Impact on Inventory | Increases product variety and stock levels. | Requires scalable production to meet foreign demand. |
| Profit Margins | Dependent on purchase price and import expenses. | Influenced by foreign market pricing and costs. |
Overview of Importing and Exporting in Wholesale
Importing in wholesale involves purchasing goods from foreign suppliers to stock and sell in domestic markets, optimizing product variety and often reducing costs. Exporting refers to selling domestically sourced products to overseas buyers, expanding market reach and increasing revenue potential. Both importing and exporting are key strategies in wholesale that drive supply chain efficiency and global trade growth.
Key Differences Between Importing and Exporting
Importing involves bringing goods or services into a country from abroad for sale or use, while exporting refers to sending domestic goods or services to foreign markets. Key differences include regulatory requirements, where importers deal with customs duties and compliance with local laws, while exporters focus on foreign market access and export licenses. Financially, importing requires managing currency exchange and taxes upon entry, whereas exporting emphasizes international shipping costs and potential tariffs imposed by destination countries.
Roles and Responsibilities in Import Operations
Import operations require importers to ensure compliance with customs regulations, secure necessary documentation like bills of lading and import licenses, and coordinate with freight forwarders for efficient shipment handling. Importers must also manage timely payment of duties and taxes, verify product quality and quantity upon arrival, and maintain accurate records for audit purposes. Effective communication with suppliers and customs authorities is essential to prevent delays and facilitate smooth clearance through ports.
Roles and Responsibilities in Export Operations
Export operations require precise coordination between export managers, customs brokers, and logistics providers to ensure compliance with international trade regulations. Export managers oversee documentation accuracy, shipment scheduling, and communication with foreign buyers to facilitate smooth transactions. Customs brokers handle tariff classification and duty payments, reducing risks of delays and penalties during cross-border clearance.
Skills Required for Import and Export Jobs
Importing jobs demand strong knowledge of international trade regulations, customs compliance, and supply chain management to efficiently handle inbound goods. Exporting roles require proficiency in documentation, foreign market analysis, and negotiation skills to secure and maintain overseas clients. Both positions benefit from expertise in logistics coordination, risk management, and communication across multicultural environments.
Regulatory Compliance: Import vs Export
Regulatory compliance in wholesale significantly differs between importing and exporting, with importing requiring adherence to the destination country's customs, tariffs, and product standards, while exporting demands compliance with the origin country's export controls, trade agreements, and foreign market regulations. Importers must secure necessary import licenses, clearance documents, and pay applicable duties, whereas exporters focus on export permits, declarations, and sanctions screening to avoid legal penalties. Efficient compliance management reduces shipment delays, minimizes financial risks, and ensures seamless cross-border transactions in wholesale trade.
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations
Importing requires careful coordination of inbound logistics, including customs clearance, freight forwarding, and warehousing to maintain efficient supply chain flow. Exporting demands robust outbound logistics planning, ensuring compliance with international shipping regulations and timely delivery to global customers. Both processes benefit from advanced supply chain management technologies to optimize inventory control and reduce lead times.
Challenges in Importing and Exporting
Importing challenges include navigating complex customs regulations, managing tariffs, and ensuring compliance with diverse international standards, which can lead to delays and increased costs. Exporting hurdles often involve securing reliable logistics, overcoming trade barriers, and adapting products to meet foreign market requirements. Both processes require thorough documentation, risk management strategies, and strong relationships with suppliers and regulatory authorities to optimize supply chain efficiency.
Career Opportunities in Wholesale Importing and Exporting
Wholesale importing offers career opportunities in logistics management, international compliance, and supply chain coordination, providing roles that demand expertise in global trade regulations and inventory optimization. Exporting careers focus on market analysis, export documentation, and international sales strategies, emphasizing skills in foreign market entry and cross-border customer relations. Both sectors require proficiency in trade compliance software, negotiation, and cultural communication, making them vital for professionals seeking dynamic roles in global commerce.
Future Trends in Wholesale Trade
Future trends in wholesale trade highlight a shift towards increased digital integration, with blockchain and AI enhancing transparency and efficiency in importing and exporting processes. Cross-border e-commerce platforms are expanding market reach, enabling wholesalers to streamline international transactions and reduce lead times. Sustainability and regulatory compliance are driving wholesalers to adopt eco-friendly logistics and transparent supply chain practices, shaping the competitive landscape of global trade.
Importing vs Exporting Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com