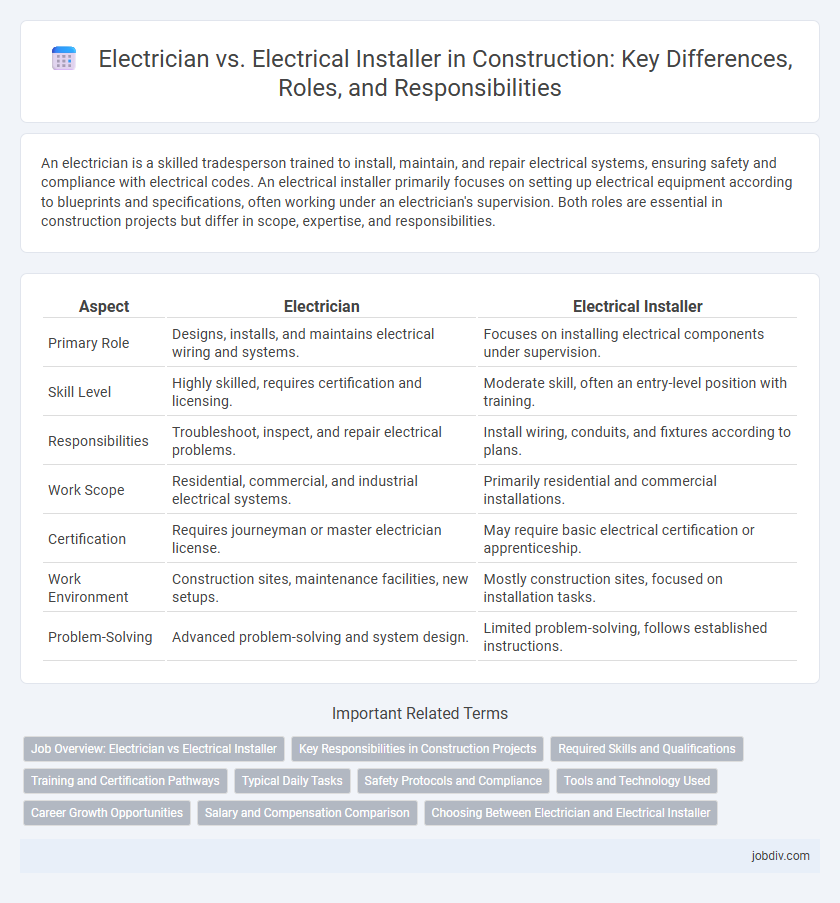
An electrician is a skilled tradesperson trained to install, maintain, and repair electrical systems, ensuring safety and compliance with electrical codes. An electrical installer primarily focuses on setting up electrical equipment according to blueprints and specifications, often working under an electrician's supervision. Both roles are essential in construction projects but differ in scope, expertise, and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Electrician | Electrical Installer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Designs, installs, and maintains electrical wiring and systems. | Focuses on installing electrical components under supervision. |
| Skill Level | Highly skilled, requires certification and licensing. | Moderate skill, often an entry-level position with training. |
| Responsibilities | Troubleshoot, inspect, and repair electrical problems. | Install wiring, conduits, and fixtures according to plans. |
| Work Scope | Residential, commercial, and industrial electrical systems. | Primarily residential and commercial installations. |
| Certification | Requires journeyman or master electrician license. | May require basic electrical certification or apprenticeship. |
| Work Environment | Construction sites, maintenance facilities, new setups. | Mostly construction sites, focused on installation tasks. |
| Problem-Solving | Advanced problem-solving and system design. | Limited problem-solving, follows established instructions. |
Job Overview: Electrician vs Electrical Installer
Electricians specialize in installing, maintaining, and repairing electrical systems in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, ensuring compliance with safety codes and standards. Electrical installers focus primarily on setting up electrical wiring, fixtures, and equipment during the construction or renovation phases, following blueprints and technical diagrams. Both roles require knowledge of electrical theory and safety protocols but differ in scope, with electricians handling more complex diagnostics and repairs than electrical installers.
Key Responsibilities in Construction Projects
Electricians specialize in wiring, troubleshooting, and ensuring electrical systems comply with safety codes throughout construction projects. Electrical installers focus on installing electrical equipment and components according to blueprints and technical diagrams. Both roles collaborate to ensure electrical systems are efficiently integrated and operational in buildings.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Electricians require comprehensive knowledge of electrical theory, blueprint reading, and strict adherence to safety codes, along with certifications such as a journeyman or master electrician license. Electrical installers focus on installing and maintaining wiring systems, necessitating skills in physical dexterity, troubleshooting, and familiarity with electrical tools, often requiring an apprenticeship and basic electrical certification. Both roles demand strong problem-solving abilities, but electricians typically need advanced technical training and licensing to handle complex tasks and inspections.
Training and Certification Pathways
Electricians undergo extensive training involving apprenticeship programs and must obtain licenses through state certification exams to ensure compliance with electrical codes and safety standards. Electrical installers typically complete specialized vocational courses focusing on the installation and maintenance of electrical systems, often earning certifications like the National Center for Construction Education and Research (NCCER) credentials. Both roles require continuous education to keep up with evolving technology and regulatory requirements in the construction industry.
Typical Daily Tasks
Electricians typically troubleshoot and repair electrical systems, install wiring, outlets, and circuit breakers, and ensure compliance with safety codes in residential, commercial, or industrial settings. Electrical installers focus on assembling, installing, and testing electrical components such as lighting fixtures, control panels, and wiring systems, often following pre-designed plans or blueprints. Both roles require proficiency in reading electrical diagrams, but electricians engage more in diagnostics and system maintenance, while electrical installers emphasize setup and initial configuration.
Safety Protocols and Compliance
Electricians and electrical installers both adhere to strict safety protocols and compliance standards, but electricians typically perform more complex wiring and system troubleshooting, requiring in-depth knowledge of National Electrical Code (NEC) regulations. Electrical installers focus on the safe installation of electrical components, ensuring devices meet industry safety certifications such as UL listing and local building codes. Compliance with OSHA standards is mandatory for both roles to minimize electrical hazards and maintain workplace safety.
Tools and Technology Used
Electricians utilize advanced diagnostic tools such as multimeters, oscilloscopes, and thermal imaging cameras to accurately assess electrical systems and ensure safety compliance. Electrical installers primarily rely on power drills, conduit benders, and cable pullers to efficiently install wiring infrastructure and electrical components. Both professionals adapt to evolving smart technologies, incorporating programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and automation systems to meet modern construction demands.
Career Growth Opportunities
Electricians typically have broader career growth opportunities due to their extensive training and licensing requirements, enabling them to work on complex wiring systems in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Electrical installers often focus on specific system setups like solar panels or telecommunications, offering specialization but with more limited advancement paths compared to licensed electricians. Pursuing certifications, gaining experience in advanced electrical systems, and expanding skill sets into renewable energy technologies significantly enhance career prospects in both fields.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Electricians typically earn an average annual salary ranging from $50,000 to $70,000 depending on experience, while electrical installers may earn slightly less, around $40,000 to $60,000 per year due to the varying scope of work and required certifications. Compensation packages for electricians often include benefits such as overtime pay, union membership perks, and apprenticeships that can boost earnings. Electrical installers might receive standard benefits but usually have fewer opportunities for overtime and specialized pay premiums compared to licensed electricians.
Choosing Between Electrician and Electrical Installer
Choosing between an electrician and an electrical installer depends largely on the project's complexity and scope. Electricians are licensed professionals skilled in wiring, troubleshooting, and ensuring compliance with electrical codes, making them ideal for repairs, maintenance, and intricate installations. Electrical installers typically focus on basic installation tasks under supervision, suited for standard setups and less complex electrical work.
Electrician vs Electrical Installer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com