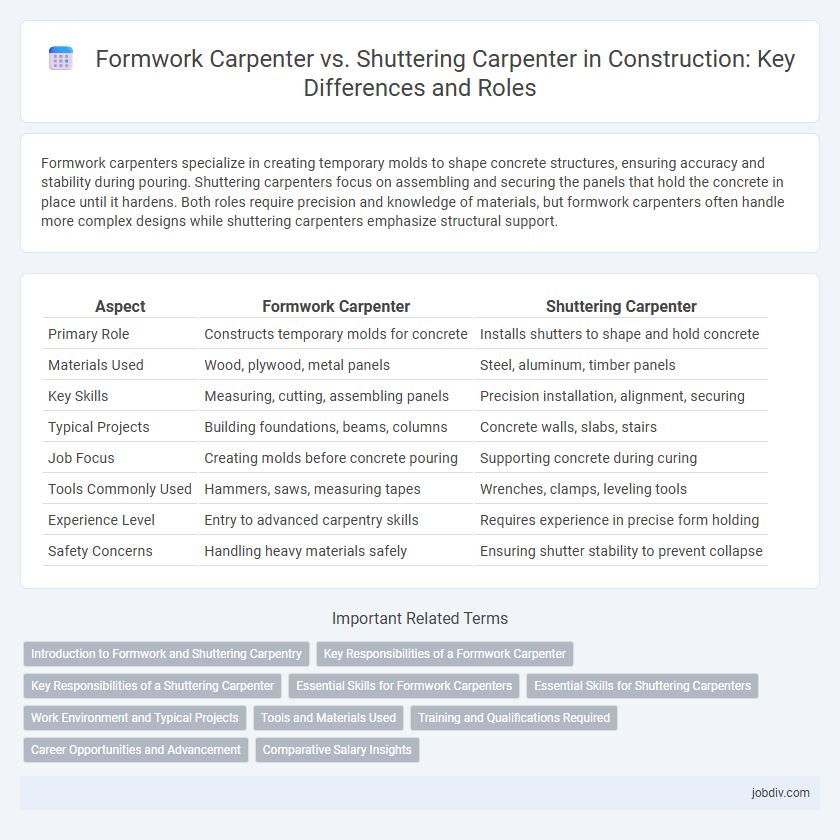
Formwork carpenters specialize in creating temporary molds to shape concrete structures, ensuring accuracy and stability during pouring. Shuttering carpenters focus on assembling and securing the panels that hold the concrete in place until it hardens. Both roles require precision and knowledge of materials, but formwork carpenters often handle more complex designs while shuttering carpenters emphasize structural support.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Formwork Carpenter | Shuttering Carpenter |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Constructs temporary molds for concrete | Installs shutters to shape and hold concrete |
| Materials Used | Wood, plywood, metal panels | Steel, aluminum, timber panels |
| Key Skills | Measuring, cutting, assembling panels | Precision installation, alignment, securing |
| Typical Projects | Building foundations, beams, columns | Concrete walls, slabs, stairs |
| Job Focus | Creating molds before concrete pouring | Supporting concrete during curing |
| Tools Commonly Used | Hammers, saws, measuring tapes | Wrenches, clamps, leveling tools |
| Experience Level | Entry to advanced carpentry skills | Requires experience in precise form holding |
| Safety Concerns | Handling heavy materials safely | Ensuring shutter stability to prevent collapse |
Introduction to Formwork and Shuttering Carpentry
Formwork carpentry involves creating temporary molds to support concrete structures until they harden, focusing on precision in constructing panels and frameworks. Shuttering carpentry specifically refers to the assembly and installation of these molds, often emphasizing reusable materials and modular designs to optimize efficiency on construction sites. Both disciplines require expertise in measuring, cutting, and assembling timber or metal components to ensure structural integrity and safety during the concrete curing process.
Key Responsibilities of a Formwork Carpenter
A Formwork Carpenter specializes in constructing and assembling temporary molds made from wood, metal, or plastic to hold concrete in place until it sets and gains strength. Key responsibilities include measuring, cutting, and assembling formwork components to precise specifications, ensuring structural integrity and alignment, and collaborating with engineers to interpret blueprints accurately. Their expertise ensures the safety and quality of concrete structures by preventing deformation and facilitating efficient removal after curing.
Key Responsibilities of a Shuttering Carpenter
Shuttering carpenters specialize in assembling and dismantling temporary molds made of wood, metal, or plastic to support concrete structures during curing. Their key responsibilities include measuring, cutting, and installing formwork components accurately to ensure structural integrity and alignment. They also collaborate closely with engineers and construction teams to modify molds for complex designs and ensure safety standards on-site.
Essential Skills for Formwork Carpenters
Formwork carpenters require precise measurement and cutting skills to create accurate molds for concrete structures, ensuring structural integrity. Mastery in assembling and dismantling formwork systems using materials like timber, plywood, and metal is crucial to meeting project specifications and timelines. Expertise in reading blueprints and understanding load-bearing requirements distinguishes formwork carpenters from shuttering carpenters, emphasizing the importance of technical knowledge in construction safety and quality.
Essential Skills for Shuttering Carpenters
Shuttering carpenters must excel in precise measuring and cutting techniques to ensure the durability and accuracy of concrete molds. Proficiency in interpreting technical drawings and blueprints is crucial for constructing complex formwork structures. Strong knowledge of material properties, including timber and metal, enables shuttering carpenters to create safe and efficient frameworks essential for modern construction projects.
Work Environment and Typical Projects
Formwork carpenters primarily work on large-scale construction sites such as commercial buildings and infrastructure projects, assembling and dismantling molds that shape concrete structures. Shuttering carpenters often operate in similar environments but tend to specialize in precise, complex form installations for bridges, tunnels, and intricate architectural elements. Both roles demand adaptability to outdoor conditions and collaboration with concrete finishers and structural engineers to ensure safety and quality.
Tools and Materials Used
Formwork carpenters primarily use plywood, timber, and metal panels to create molds for concrete structures, relying on tools such as nail guns, hammers, and measuring tapes to ensure precise assembly. Shuttering carpenters focus on reusable metal or plastic shutters with modular components, utilizing clamps, wrenches, and scaffolding equipment for efficient form installation and removal. Both roles require expertise in handling levels, braces, and concrete release agents to achieve durable and accurate concrete finishes.
Training and Qualifications Required
Formwork carpenters typically require specialized training in constructing temporary molds for poured concrete, often involving apprenticeships and certification in carpentry or concrete formwork techniques. Shuttering carpenters focus on assembling and dismantling shutter systems and usually gain qualifications through vocational courses emphasizing structural support and safety standards. Both roles demand knowledge of construction blueprints, material handling, and adherence to building regulations, with formal training tailored to the complexity of the formwork or shuttering system used.
Career Opportunities and Advancement
Formwork carpenters specialize in constructing temporary molds for concrete structures, offering diverse career paths in commercial, residential, and infrastructure projects with potential to advance into site supervisor or project manager roles. Shuttering carpenters focus specifically on assembling and dismantling metal or wooden shutters, often leading to opportunities in specialized concrete forming companies or large-scale construction firms with prospects for technical specialist or foreman positions. Both careers demand strong skills in blueprint reading, precision, and safety, and advancement often depends on gaining certifications and experience in increasingly complex projects.
Comparative Salary Insights
Formwork carpenters typically earn slightly higher salaries than shuttering carpenters due to their specialized skills in creating complex molds for concrete structures. Industry data indicates that formwork carpenters can expect average annual earnings ranging from $45,000 to $60,000, whereas shuttering carpenters usually receive between $40,000 and $55,000. Geographic location, project complexity, and experience significantly influence salary variations in both roles within the construction sector.
Formwork Carpenter vs Shuttering Carpenter Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com