Consultancy offers tailored advice and strategic solutions to optimize business performance, while audit focuses on systematically reviewing financial records to ensure accuracy and compliance. Consultancy emphasizes proactive improvement and innovation, whereas audit provides an objective assessment of existing operations. Both services are essential, with consultancy driving growth and audits ensuring regulatory adherence.
Table of Comparison
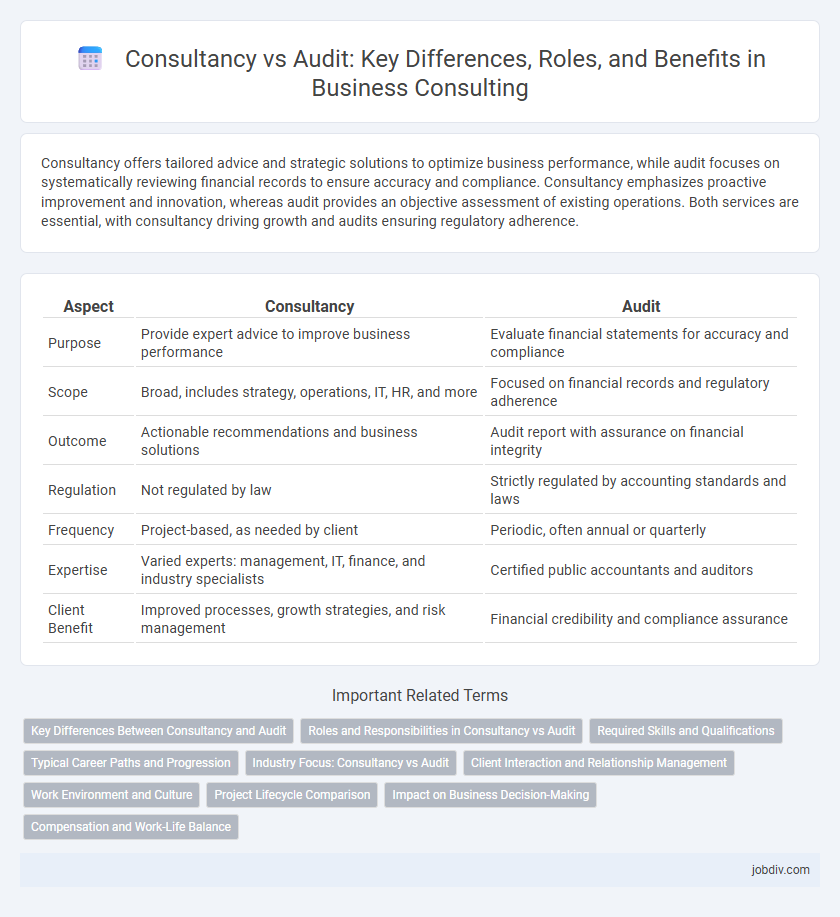
| Aspect | Consultancy | Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provide expert advice to improve business performance | Evaluate financial statements for accuracy and compliance |
| Scope | Broad, includes strategy, operations, IT, HR, and more | Focused on financial records and regulatory adherence |
| Outcome | Actionable recommendations and business solutions | Audit report with assurance on financial integrity |
| Regulation | Not regulated by law | Strictly regulated by accounting standards and laws |
| Frequency | Project-based, as needed by client | Periodic, often annual or quarterly |
| Expertise | Varied experts: management, IT, finance, and industry specialists | Certified public accountants and auditors |
| Client Benefit | Improved processes, growth strategies, and risk management | Financial credibility and compliance assurance |
Key Differences Between Consultancy and Audit
Consultancy focuses on providing strategic advice to improve business performance, while audit involves evaluating financial statements for accuracy and compliance. Consultancy delivers tailored solutions to address organizational challenges, whereas audit ensures regulatory adherence and identifies risks through systematic examination. The key differences lie in consultancy's proactive, advisory nature versus audit's retrospective, verification-based approach.
Roles and Responsibilities in Consultancy vs Audit
Consultancy primarily involves providing expert advice, strategic planning, and problem-solving tailored to improve business performance, innovation, and efficiency, while audit focuses on systematically examining financial records and operational processes to ensure compliance, accuracy, and risk management. Consultants collaborate closely with management to recommend improvements and implement changes, whereas auditors maintain a more independent role to objectively assess and verify organizational practices according to regulatory standards. The consultancy role emphasizes forward-looking solutions and value creation, whereas audit centers on historical data validation and accountability.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Consultancy requires strong problem-solving skills, strategic thinking, and industry-specific expertise to provide tailored solutions and drive business growth. Essential qualifications often include advanced degrees in business or relevant fields, certifications such as PMP or Six Sigma, and proficiency in data analysis and communication. In contrast, audit demands a deep understanding of accounting principles, attention to detail, and certifications like CPA or ACCA to ensure compliance and accurate financial reporting.
Typical Career Paths and Progression
Consultancy career paths often begin with roles such as Analyst or Junior Consultant, progressing to Senior Consultant, Manager, and eventually Partner, emphasizing strategic problem-solving and client relationship management. Audit careers typically start as Audit Associates or Junior Auditors, advancing through Senior Auditor, Audit Manager, and eventually Audit Partner, focusing on financial compliance, risk assessment, and regulatory reporting. Career progression in consultancy generally offers broader industry exposure and varied project experiences, while audit provides deep expertise in accounting standards and financial control frameworks.
Industry Focus: Consultancy vs Audit
Consultancy services prioritize industry-specific strategies to drive innovation, operational efficiency, and tailored business solutions, leveraging deep sector expertise across technology, healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. Audit firms focus on compliance, financial accuracy, and regulatory adherence, ensuring transparent reporting and risk management within industries such as banking, insurance, and public sector entities. The distinct industry focus enables consultancy to deliver strategic growth insights, while audits provide assurance and credibility to stakeholders.
Client Interaction and Relationship Management
Consultancy emphasizes proactive client interaction, fostering collaborative problem-solving and tailored strategic advice to drive business growth. Audit centers on independent assessment and verification of financial records with limited client engagement, focusing on compliance and accuracy. Effective relationship management in consultancy builds trust and long-term partnerships, enhancing client satisfaction and value creation beyond transactional audit engagements.
Work Environment and Culture
Consultancy fosters a dynamic, collaborative work environment emphasizing innovation and adaptability, often involving diverse client interactions and project variety. Audit environments prioritize structured, regulatory compliance with a focus on accuracy, consistency, and adherence to strict deadlines within a standardized process. Consultancy culture values flexibility and creativity, while audit culture emphasizes precision, risk management, and formal reporting standards.
Project Lifecycle Comparison
Consultancy services guide organizations through the entire project lifecycle by offering strategic planning, risk management, and continuous performance evaluation. Audits primarily involve independent assessments at specific milestones to ensure compliance, accuracy, and adherence to standards. While consultancy drives proactive decision-making and project optimization, audits provide retrospective verification and validation within the project timeline.
Impact on Business Decision-Making
Consultancy provides tailored strategies and actionable insights that drive proactive business decisions and foster innovation. Audit focuses on historical financial accuracy and regulatory compliance, ensuring transparency but offering limited forward-looking guidance. The impact of consultancy on business decision-making is more dynamic, enabling organizations to adapt quickly to market changes and optimize growth opportunities.
Compensation and Work-Life Balance
Consultancy roles typically offer higher compensation packages compared to audit positions, driven by their demand for specialized expertise and strategic advisory skills. Work-life balance in consultancy varies widely but often involves longer hours and frequent travel, contrasting with audit roles that generally maintain more structured schedules aligned with fiscal calendars. Firms investing in consultancy services prioritize flexibility and performance-based rewards to attract top talent, while audit departments emphasize stability and predictable routines.
Consultancy vs Audit Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com