A librarian primarily manages and curates physical and digital collections of books and related resources, ensuring easy access for students and educators. A media specialist, however, integrates technology and multimedia tools into learning environments, supporting digital literacy and innovative instructional methods. Both roles are essential in modern education, complementing each other to enhance student engagement and resource accessibility.
Table of Comparison
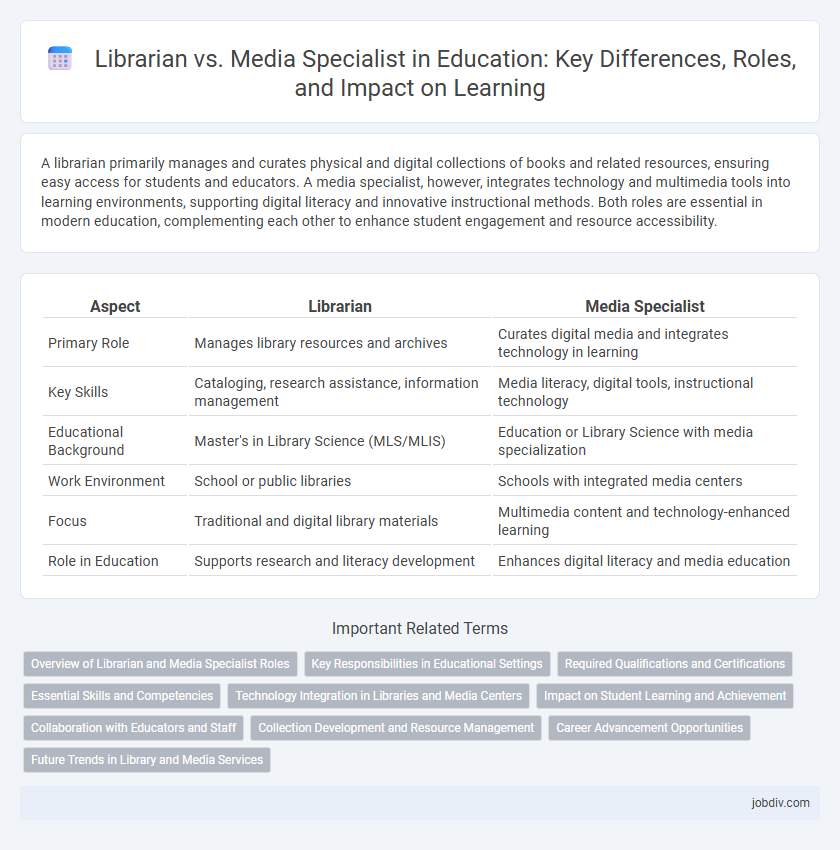
| Aspect | Librarian | Media Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manages library resources and archives | Curates digital media and integrates technology in learning |
| Key Skills | Cataloging, research assistance, information management | Media literacy, digital tools, instructional technology |
| Educational Background | Master's in Library Science (MLS/MLIS) | Education or Library Science with media specialization |
| Work Environment | School or public libraries | Schools with integrated media centers |
| Focus | Traditional and digital library materials | Multimedia content and technology-enhanced learning |
| Role in Education | Supports research and literacy development | Enhances digital literacy and media education |
Overview of Librarian and Media Specialist Roles
Librarians manage library resources, organize information, and assist users with research and information literacy, ensuring access to physical and digital collections. Media specialists focus on integrating technology and multimedia resources into educational environments, supporting curriculum development with digital tools and media content. Both roles enhance learning by promoting information access and literacy, but librarians emphasize resource management while media specialists prioritize technological integration.
Key Responsibilities in Educational Settings
Librarians in educational settings primarily manage physical and digital library resources, ensuring students and staff have access to books, journals, and research databases while teaching information literacy skills. Media Specialists focus on integrating multimedia technology and digital content into the curriculum, facilitating technology training for educators, and supporting the use of audio-visual tools for enhanced learning experiences. Both roles collaborate to create resource-rich environments that promote effective research, critical thinking, and technology proficiency among learners.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Librarians typically require a Master's degree in Library Science (MLS) or Library and Information Science (MLIS) along with state certification for school librarianship. Media Specialists often need similar qualifications but may also require specific endorsements in educational technology or media management. Both roles demand knowledge of digital resources, information literacy, and instructional collaboration to support curriculum development effectively.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Librarians excel in cataloging, research assistance, and information organization, ensuring easy access to physical and digital resources. Media specialists bring expertise in multimedia technology, digital content creation, and integrating technology into curriculum to enhance student engagement. Both roles require strong communication, information literacy, and instructional skills to support educational outcomes effectively.
Technology Integration in Libraries and Media Centers
Librarians primarily focus on managing physical collections and traditional resources, while media specialists emphasize integrating digital technologies and multimedia tools to enhance learning experiences. Media specialists play a critical role in facilitating access to digital content, promoting information literacy, and training students and staff in technology use. Effective collaboration between librarians and media specialists ensures seamless technology integration, supporting innovative instruction and resource accessibility in libraries and media centers.
Impact on Student Learning and Achievement
Librarians enhance student learning by curating diverse resources and teaching information literacy skills that foster critical thinking and research abilities. Media specialists integrate technology and multimedia tools into the curriculum, promoting digital literacy and engagement with interactive educational content. Both roles significantly contribute to improved academic achievement by supporting personalized learning and encouraging lifelong learning habits.
Collaboration with Educators and Staff
Librarians collaborate with educators and staff by curating resources that align with curriculum standards, enhancing literacy development and research skills across grade levels. Media specialists integrate technology and multimedia tools to support instructional goals, providing training and resources to promote digital literacy. Both roles foster a collaborative environment that strengthens teaching strategies and improves student learning outcomes.
Collection Development and Resource Management
Librarians focus on traditional collection development by curating physical books, journals, and archival materials to support curriculum needs and promote literacy. Media specialists expand resource management by integrating digital media, interactive learning tools, and multimedia resources that enhance student engagement and technological fluency. Both roles require strategic acquisition, organization, and evaluation of materials to align with educational standards and evolving instructional methods.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Librarians typically advance into roles such as library directors, archivists, or information resource managers, often requiring knowledge of cataloging systems and library science credentials. Media specialists, on the other hand, leverage skills in digital literacy and multimedia resource management to progress toward instructional coordinator or educational technology specialist positions. Both careers benefit from continuous professional development but diverge in focus, with librarians emphasizing traditional information management and media specialists prioritizing innovative educational technologies.
Future Trends in Library and Media Services
Emerging trends in education highlight the evolving roles of librarians and media specialists, driven by rapid digital transformation and increasing demand for multimedia literacy. Libraries are integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and immersive digital content to enhance information retrieval and interactive learning experiences. Media specialists are expanding their expertise in digital content curation, virtual collaboration tools, and data privacy management to support 21st-century educational environments and foster critical digital citizenship skills.
Librarian vs Media Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com