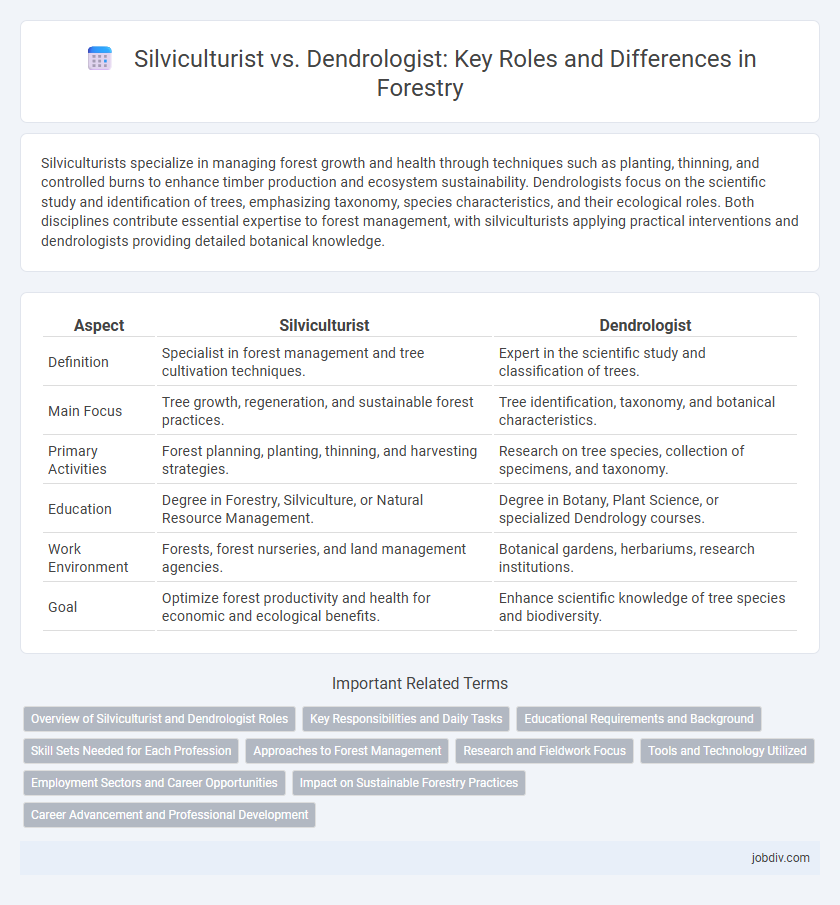
Silviculturists specialize in managing forest growth and health through techniques such as planting, thinning, and controlled burns to enhance timber production and ecosystem sustainability. Dendrologists focus on the scientific study and identification of trees, emphasizing taxonomy, species characteristics, and their ecological roles. Both disciplines contribute essential expertise to forest management, with silviculturists applying practical interventions and dendrologists providing detailed botanical knowledge.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Silviculturist | Dendrologist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialist in forest management and tree cultivation techniques. | Expert in the scientific study and classification of trees. |
| Main Focus | Tree growth, regeneration, and sustainable forest practices. | Tree identification, taxonomy, and botanical characteristics. |
| Primary Activities | Forest planning, planting, thinning, and harvesting strategies. | Research on tree species, collection of specimens, and taxonomy. |
| Education | Degree in Forestry, Silviculture, or Natural Resource Management. | Degree in Botany, Plant Science, or specialized Dendrology courses. |
| Work Environment | Forests, forest nurseries, and land management agencies. | Botanical gardens, herbariums, research institutions. |
| Goal | Optimize forest productivity and health for economic and ecological benefits. | Enhance scientific knowledge of tree species and biodiversity. |
Overview of Silviculturist and Dendrologist Roles
Silviculturists manage forest growth, health, and quality through practices like planting, thinning, and controlled burns to ensure sustainable timber production and ecosystem balance. Dendrologists specialize in the identification, classification, and study of trees, focusing on tree species characteristics, distributions, and taxonomy. Both roles are vital for forest management: silviculturists apply practical techniques for forest development, while dendrologists provide essential knowledge of tree species necessary for informed decision-making.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Silviculturists focus on managing forest regeneration, growth, and health through activities like planting, thinning, and controlled burns to ensure sustainable timber production and ecosystem balance. Dendrologists specialize in identifying and studying tree species, analyzing their characteristics, distribution, and ecological roles to support biodiversity and forest conservation efforts. Both professionals collaborate to optimize forest management by combining practical silvicultural techniques with scientific knowledge of tree taxonomy and biology.
Educational Requirements and Background
Silviculturists typically require a bachelor's degree in forestry, natural resources, or environmental science with coursework emphasizing forest management, ecology, and soil science to effectively plan and implement sustainable forest practices. Dendrologists usually hold degrees in botany, plant sciences, or forestry, with specialized education in tree identification, taxonomy, and physiology, focusing on the scientific study of woody plants. Both professions benefit from field experience and advanced studies, but silviculturists prioritize forest management skills while dendrologists emphasize botanical research and species classification.
Skill Sets Needed for Each Profession
Silviculturists require expertise in forest management techniques, ecological principles, and fire management, coupled with skills in tree growth assessment and forest regeneration practices. Dendrologists focus on deep botanical knowledge, species identification, and taxonomy, emphasizing skills in plant physiology and genetic analysis of trees. Both professions benefit from proficiency in GIS technology and data analysis for sustainable forest resource management.
Approaches to Forest Management
Silviculturists emphasize practical forest management techniques, focusing on tree cultivation, regeneration, and stand dynamics to optimize timber production and ecosystem health. Dendrologists concentrate on the scientific study and identification of tree species, providing critical data on species characteristics and distribution to inform management decisions. Integrating silvicultural practices with dendrological knowledge enhances adaptive forest management strategies that balance ecological sustainability and economic objectives.
Research and Fieldwork Focus
Silviculturists specialize in the research and management of forest growth, regeneration, and health, conducting fieldwork to develop sustainable practices for timber production and ecosystem balance. Dendrologists focus on the identification, classification, and study of tree species, analyzing tree morphology and genetics in natural habitats to support biodiversity conservation and forest ecology. Both professions conduct extensive fieldwork, but silviculturists prioritize forest management techniques, while dendrologists emphasize botanical research and species-specific studies.
Tools and Technology Utilized
Silviculturists employ tools such as GPS mapping devices, growth modeling software, and remote sensing technologies to monitor forest development and manage tree planting effectively. Dendrologists focus on identifying tree species using hand lenses, microscopes, and DNA sequencing tools to analyze leaf, bark, and seed characteristics accurately. Both professionals increasingly utilize geographic information systems (GIS) and drone technology to enhance data collection and forest assessment precision.
Employment Sectors and Career Opportunities
Silviculturists primarily find employment in forest management agencies, environmental consulting firms, and timber production companies where they focus on sustainable forest growth and health. Dendrologists work extensively in academic research institutions, botanical gardens, and conservation organizations, specializing in tree species identification and taxonomy. Career opportunities for silviculturists often involve fieldwork and forest planning, while dendrologists engage in scientific studies that support biodiversity and ecological preservation.
Impact on Sustainable Forestry Practices
Silviculturists design and implement forest management techniques that promote tree growth, health, and regeneration, directly influencing sustainable yield and ecosystem balance. Dendrologists contribute by identifying tree species and understanding their ecological roles, aiding in biodiversity conservation and habitat preservation. Together, their expertise ensures sustainable forestry practices that maintain forest productivity while protecting environmental integrity.
Career Advancement and Professional Development
Silviculturists advance their careers by specializing in forest management techniques, enhancing skills in regeneration, growth, and harvesting practices, often pursuing certifications like Certified Silviculturist. Dendrologists focus on tree identification and taxonomy, expanding expertise through botanical research and advanced degrees in plant sciences, which open opportunities in academic and conservation roles. Both professions benefit from continuous education and professional development through workshops, seminars, and memberships in organizations such as the Society of American Foresters.
Silviculturist vs Dendrologist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com