An Infection Control Nurse specializes in preventing and managing infections within healthcare settings through surveillance, education, and implementing protocols. A Quality Improvement Nurse focuses on enhancing overall patient care quality by analyzing processes, identifying areas for improvement, and promoting best practices across clinical workflows. Both roles are essential for patient safety but differ in scope and key responsibilities, with infection control targeting specific pathogens and quality improvement addressing broader healthcare outcomes.
Table of Comparison
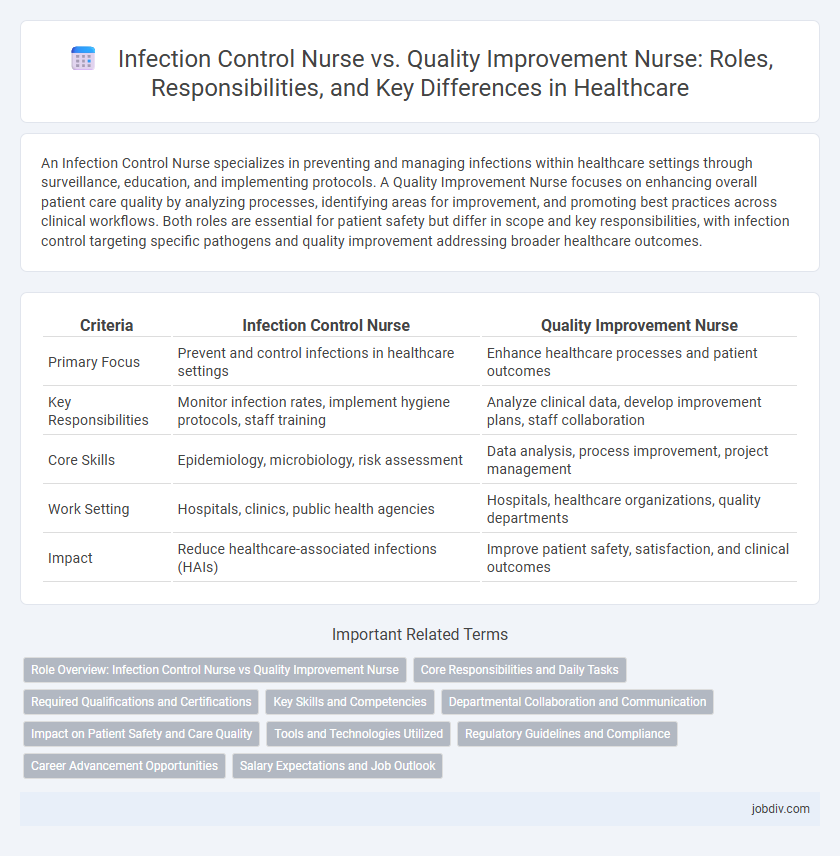
| Criteria | Infection Control Nurse | Quality Improvement Nurse |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Prevent and control infections in healthcare settings | Enhance healthcare processes and patient outcomes |
| Key Responsibilities | Monitor infection rates, implement hygiene protocols, staff training | Analyze clinical data, develop improvement plans, staff collaboration |
| Core Skills | Epidemiology, microbiology, risk assessment | Data analysis, process improvement, project management |
| Work Setting | Hospitals, clinics, public health agencies | Hospitals, healthcare organizations, quality departments |
| Impact | Reduce healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) | Improve patient safety, satisfaction, and clinical outcomes |
Role Overview: Infection Control Nurse vs Quality Improvement Nurse
Infection Control Nurses specialize in preventing and managing healthcare-associated infections through surveillance, staff education, and implementation of infection control protocols. Quality Improvement Nurses focus on enhancing patient care processes by analyzing clinical outcomes, developing improvement strategies, and ensuring compliance with healthcare standards. Both roles collaborate to promote patient safety but differ in their primary focus areas: infection prevention versus comprehensive quality enhancement.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
An Infection Control Nurse monitors infection rates, implements protocols to prevent healthcare-associated infections, and educates staff on hygiene practices to ensure patient safety. A Quality Improvement Nurse analyzes clinical data, develops strategies to enhance patient care outcomes, and coordinates interdisciplinary teams to implement process improvements. Both roles focus on patient safety but differ in scope, with Infection Control Nurses concentrating on infection prevention and Quality Improvement Nurses driving overall healthcare quality enhancements.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Infection Control Nurses typically require a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) and certification such as Certified Infection Control (CIC) to specialize in preventing and managing healthcare-associated infections. Quality Improvement Nurses often hold a BSN or higher and benefit from certifications like Certified Professional in Healthcare Quality (CPHQ) to drive patient care enhancements and process optimization. Both roles demand strong clinical experience and ongoing education to meet healthcare safety standards and regulatory requirements.
Key Skills and Competencies
Infection Control Nurses excel in epidemiology, aseptic techniques, and outbreak management, ensuring adherence to infection prevention protocols and conducting surveillance to minimize healthcare-associated infections. Quality Improvement Nurses specialize in data analysis, process redesign, and performance measurement, driving evidence-based initiatives to enhance patient safety and clinical outcomes. Both roles require strong communication, critical thinking, and interdisciplinary collaboration to effectively implement healthcare best practices.
Departmental Collaboration and Communication
Infection Control Nurses collaborate closely with clinical staff and environmental services to monitor and reduce hospital-acquired infections through effective communication and data sharing. Quality Improvement Nurses engage multidisciplinary teams by facilitating regular meetings and using evidence-based feedback processes to enhance patient safety and care standards. Both roles emphasize seamless departmental collaboration to drive continuous health outcomes improvement and foster a culture of safety.
Impact on Patient Safety and Care Quality
Infection Control Nurses play a critical role in reducing healthcare-associated infections by implementing evidence-based protocols and monitoring compliance, directly enhancing patient safety and care quality. Quality Improvement Nurses focus on analyzing clinical processes and leading initiatives to improve overall healthcare delivery systems, resulting in improved patient outcomes and reduced errors. Both roles synergistically contribute to a safer healthcare environment through targeted interventions and ongoing performance evaluation.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Infection Control Nurses utilize surveillance software, electronic health records (EHRs), and diagnostic microbiology tools to monitor and prevent healthcare-associated infections. Quality Improvement Nurses employ data analytics platforms, process mapping software, and patient feedback systems to enhance clinical workflows and patient outcomes. Both roles leverage mobile health technologies and decision support systems to ensure evidence-based practices and real-time interventions.
Regulatory Guidelines and Compliance
Infection Control Nurses specialize in implementing and monitoring adherence to regulatory guidelines from agencies such as the CDC and WHO to prevent healthcare-associated infections. Quality Improvement Nurses focus on compliance with broader healthcare regulations like The Joint Commission standards, driving systematic improvements in patient safety and care quality. Both roles require detailed documentation and continuous education to ensure regulatory compliance and optimize healthcare outcomes.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Infection Control Nurses specialize in preventing healthcare-associated infections, enhancing patient safety through surveillance and staff education, which opens pathways to leadership roles in epidemiology and public health. Quality Improvement Nurses focus on optimizing healthcare processes and patient outcomes by implementing evidence-based practices, leading to career advancement in hospital administration and quality management. Both roles offer strategic development opportunities, with Infection Control Nurses often progressing into roles such as Infection Prevention Director, while Quality Improvement Nurses may advance to Quality Assurance Director or Clinical Quality Manager positions.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Infection Control Nurses typically earn an average annual salary ranging from $65,000 to $85,000 due to their specialized role in preventing healthcare-associated infections. Quality Improvement Nurses command salaries between $70,000 and $90,000, reflecting their responsibility in enhancing patient care processes and outcomes. Job outlook for both positions is strong, driven by increasing healthcare regulations and emphasis on patient safety, with a projected growth rate of about 9% for Infection Control Nurses and 11% for Quality Improvement Nurses over the next decade.
Infection Control Nurse vs Quality Improvement Nurse Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com