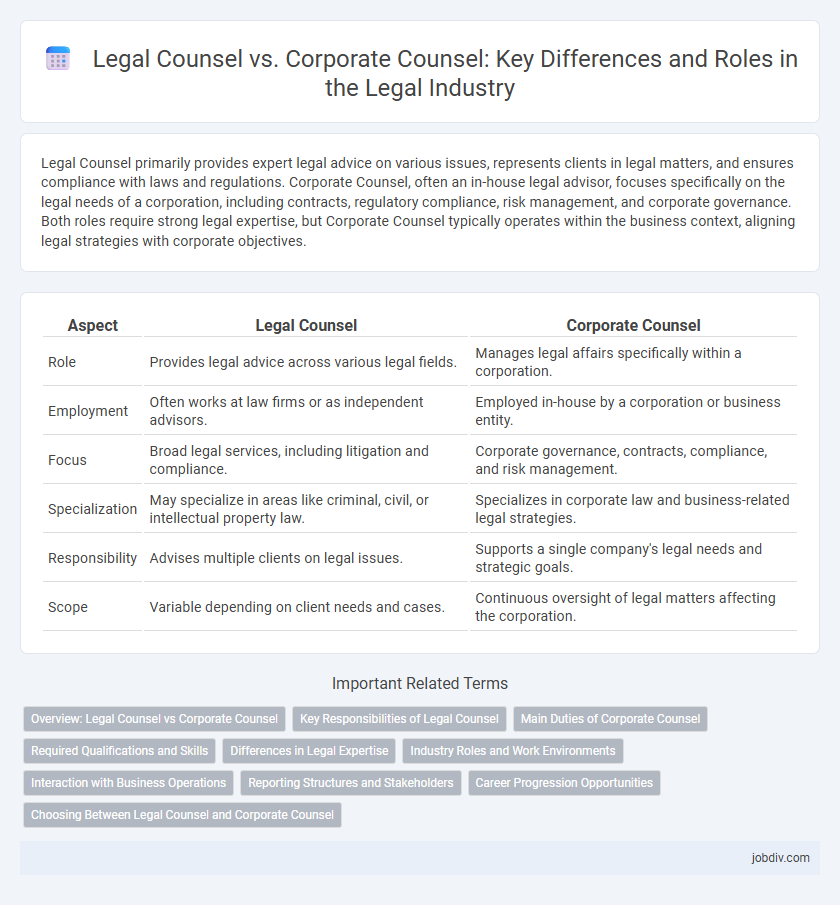
Legal Counsel primarily provides expert legal advice on various issues, represents clients in legal matters, and ensures compliance with laws and regulations. Corporate Counsel, often an in-house legal advisor, focuses specifically on the legal needs of a corporation, including contracts, regulatory compliance, risk management, and corporate governance. Both roles require strong legal expertise, but Corporate Counsel typically operates within the business context, aligning legal strategies with corporate objectives.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Legal Counsel | Corporate Counsel |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Provides legal advice across various legal fields. | Manages legal affairs specifically within a corporation. |
| Employment | Often works at law firms or as independent advisors. | Employed in-house by a corporation or business entity. |
| Focus | Broad legal services, including litigation and compliance. | Corporate governance, contracts, compliance, and risk management. |
| Specialization | May specialize in areas like criminal, civil, or intellectual property law. | Specializes in corporate law and business-related legal strategies. |
| Responsibility | Advises multiple clients on legal issues. | Supports a single company's legal needs and strategic goals. |
| Scope | Variable depending on client needs and cases. | Continuous oversight of legal matters affecting the corporation. |
Overview: Legal Counsel vs Corporate Counsel
Legal Counsel typically provides specialized advice on compliance, litigation, and regulatory matters across various industries, focusing on risk management and legal strategy. Corporate Counsel, often embedded within a company, handles a broad range of legal issues related to corporate governance, contracts, mergers and acquisitions, and employment law. Both roles require expertise in corporate law but differ in scope and organizational integration, with Corporate Counsel acting as in-house advisors aligned with business operations.
Key Responsibilities of Legal Counsel
Legal Counsel primarily manages a company's legal risks by providing expert advice on contracts, compliance, and regulatory issues, ensuring adherence to laws and mitigating potential litigation. They draft and review legal documents, negotiate with external parties, and represent the organization in legal proceedings. Their role is crucial in safeguarding corporate interests through proactive legal strategies and thorough risk assessments.
Main Duties of Corporate Counsel
Corporate Counsel primarily manages legal risks within a corporation by providing ongoing advice on business transactions, regulatory compliance, and internal policies to ensure alignment with legal standards. They draft, review, and negotiate contracts, handle corporate governance matters, and oversee litigation and dispute resolution when the company is involved. Their role integrates legal expertise with strategic business objectives to protect the company's interests and support operational decisions.
Required Qualifications and Skills
Legal Counsel typically requires a Juris Doctor (JD) degree, admission to the state bar, and experience in litigation or regulatory compliance, emphasizing strong analytical and negotiation skills. Corporate Counsel often demands expertise in corporate law, contract management, and business strategy, along with proficiency in risk assessment and internal advising. Both roles necessitate excellent communication, problem-solving abilities, and ethical judgment tailored to their specific organizational environments.
Differences in Legal Expertise
Legal Counsel typically provides specialized legal advice in specific areas such as litigation, intellectual property, or regulatory compliance, often working externally or on a case-by-case basis. Corporate Counsel, also known as in-house counsel, offers broad legal expertise tailored to the company's overall business needs, including contract negotiation, corporate governance, and risk management. The primary difference lies in the scope and integration of legal services, where Legal Counsel focuses on specialized issues and Corporate Counsel manages ongoing legal support within the corporate structure.
Industry Roles and Work Environments
Legal Counsel primarily operates within law firms or as external advisors, specializing in litigation, compliance, and contract negotiation across various industries. Corporate Counsel, also known as in-house counsel, works internally within a corporation, focusing on managing legal risks, corporate governance, regulatory compliance, and strategic business decisions specific to the company's industry. The work environment for Corporate Counsel is typically more integrated with the business operations, while Legal Counsel often handles a broader range of clients and legal issues from a more advisory or advocacy standpoint.
Interaction with Business Operations
Legal Counsel typically provides external advice to businesses on compliance, contracts, and risk management, maintaining a broader perspective across multiple clients and industries. Corporate Counsel operates internally within a company, collaborating closely with business units to align legal strategies with corporate objectives and facilitate day-to-day operational decisions. Their interaction with business operations is more integrated, ensuring legal considerations are embedded in corporate policies, transactions, and strategic initiatives.
Reporting Structures and Stakeholders
Legal Counsel typically reports to the General Counsel or Chief Legal Officer, providing legal advice to internal business units and external clients, while Corporate Counsel is embedded within a corporation, reporting directly to senior executives such as the CEO or CFO. Legal Counsel's stakeholders include law firms, regulatory bodies, and external clients, whereas Corporate Counsel primarily engages with internal stakeholders like department heads, compliance officers, and board members. The distinction in reporting structures influences how each role prioritizes communication and legal risk management strategies within their respective organizations.
Career Progression Opportunities
Legal Counsel roles typically offer diverse career progression opportunities within law firms, involving specialization in litigation, compliance, or advisory services, leading to senior partner or managing attorney positions. Corporate Counsel positions emphasize in-house expertise, with career growth often advancing toward chief legal officer or general counsel roles, integrating legal strategy with business operations. Both career paths require continuous skill development, but Corporate Counsel careers demand a deeper alignment with corporate governance and risk management for top executive advancement.
Choosing Between Legal Counsel and Corporate Counsel
Choosing between legal counsel and corporate counsel depends on the specific needs of a business. Legal counsel typically provides specialized expertise in litigation, compliance, and regulatory issues, often working as external advisors. Corporate counsel, on the other hand, are in-house lawyers focused on managing daily legal matters, contracts, and corporate governance to ensure alignment with the company's strategic goals.
Legal Counsel vs Corporate Counsel Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com