An HR Manager oversees employee relations, performance management, and compliance with labor laws, ensuring overall workforce stability and development. A Talent Acquisition Manager specializes in sourcing, recruiting, and onboarding top talent to meet organizational needs and support business growth. Both roles collaborate closely but differ in scope, with HR Managers focusing on ongoing employee engagement and Talent Acquisition Managers concentrating on building a strong talent pipeline.
Table of Comparison
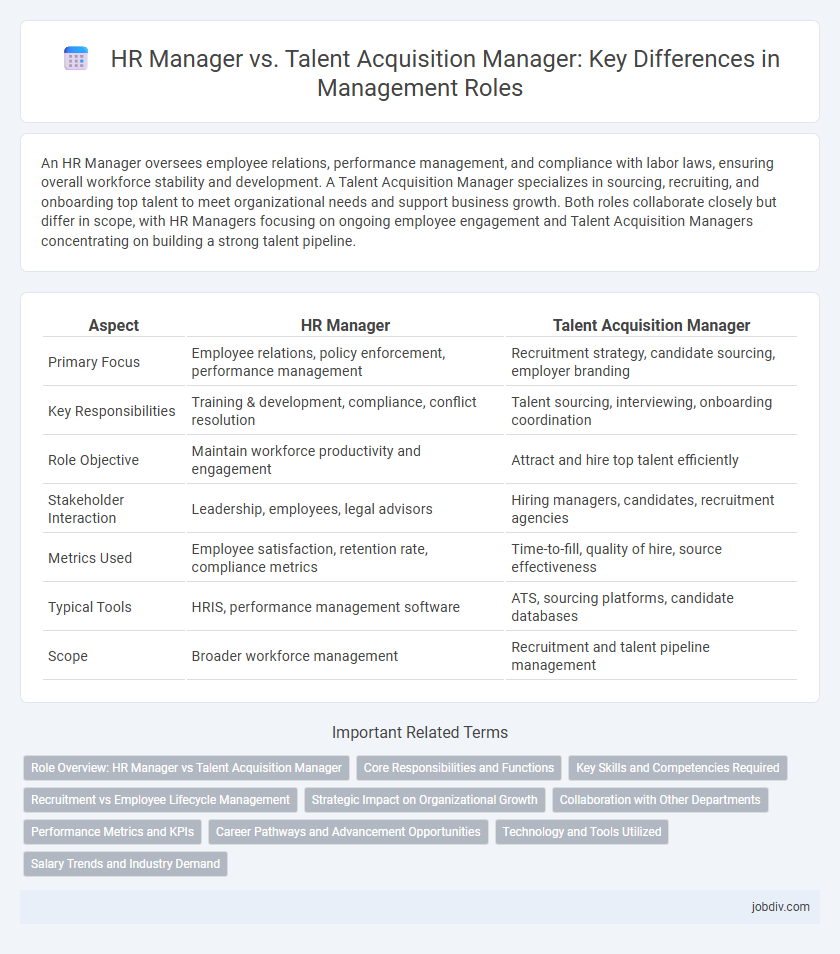
| Aspect | HR Manager | Talent Acquisition Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Employee relations, policy enforcement, performance management | Recruitment strategy, candidate sourcing, employer branding |
| Key Responsibilities | Training & development, compliance, conflict resolution | Talent sourcing, interviewing, onboarding coordination |
| Role Objective | Maintain workforce productivity and engagement | Attract and hire top talent efficiently |
| Stakeholder Interaction | Leadership, employees, legal advisors | Hiring managers, candidates, recruitment agencies |
| Metrics Used | Employee satisfaction, retention rate, compliance metrics | Time-to-fill, quality of hire, source effectiveness |
| Typical Tools | HRIS, performance management software | ATS, sourcing platforms, candidate databases |
| Scope | Broader workforce management | Recruitment and talent pipeline management |
Role Overview: HR Manager vs Talent Acquisition Manager
The HR Manager oversees employee relations, performance management, compliance, and organizational development, ensuring alignment with company policies and goals. The Talent Acquisition Manager focuses exclusively on sourcing, recruiting, and onboarding top talent to meet workforce demands. Both roles collaborate to maintain a productive and skilled workforce but differ in scope and daily responsibilities.
Core Responsibilities and Functions
HR Managers oversee comprehensive employee relations, benefits administration, performance management, and compliance with labor laws to maintain a productive workforce. Talent Acquisition Managers specialize in sourcing, recruiting, and onboarding top talent, focusing on employer branding, candidate experience, and workforce planning strategies. Both roles collaborate to align human resources initiatives with organizational goals but focus on distinct stages of the employee lifecycle.
Key Skills and Competencies Required
HR Managers require strong organizational leadership, employee relations expertise, and proficiency in performance management systems to effectively oversee workforce policies and maintain a productive work environment. Talent Acquisition Managers must excel in strategic sourcing, candidate assessment, and employer branding to attract top talent and optimize recruitment processes. Both roles demand excellent communication skills, data-driven decision-making, and adaptability to align human resource strategies with dynamic business goals.
Recruitment vs Employee Lifecycle Management
HR Managers oversee the entire employee lifecycle, including recruitment, onboarding, development, and retention, ensuring alignment with organizational goals. Talent Acquisition Managers specialize in the recruitment process, focusing on sourcing, attracting, and hiring top talent to meet company workforce needs. Recruitment is a key subset of talent acquisition, whereas employee lifecycle management encompasses broader human resource functions beyond hiring.
Strategic Impact on Organizational Growth
HR Managers drive organizational growth by developing comprehensive workforce strategies, managing employee relations, and enhancing performance management systems, which collectively improve productivity and retention. Talent Acquisition Managers contribute strategically by identifying and securing high-potential candidates, reducing time-to-hire, and aligning recruitment with long-term business objectives to build a competitive talent pipeline. Both roles are critical; HR Managers focus on optimizing existing human capital, while Talent Acquisition Managers ensure continuous infusion of fresh skills essential for sustainable growth.
Collaboration with Other Departments
HR Managers collaborate closely with department heads to align workforce planning and employee development strategies with organizational goals. Talent Acquisition Managers work alongside hiring managers and department teams to understand specific role requirements and ensure the recruitment process meets those needs effectively. Both roles coordinate with finance and operations to manage budgets and streamline onboarding processes.
Performance Metrics and KPIs
HR Managers primarily focus on employee performance metrics such as retention rates, employee engagement scores, and training effectiveness, which directly impact overall organizational productivity. Talent Acquisition Managers emphasize KPIs like time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, quality of hire, and candidate experience to optimize recruitment efficiency and workforce quality. Measuring these distinct yet complementary metrics allows companies to align talent management strategies with business goals and improve both employee development and strategic hiring outcomes.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
HR Managers often progress into senior leadership roles such as HR Director or Chief Human Resources Officer (CHRO) due to their comprehensive oversight of employee relations, compliance, and organizational development. Talent Acquisition Managers typically advance by specializing further, moving into roles like Recruitment Director or Head of Talent Strategy, leveraging expertise in sourcing, employer branding, and workforce planning. Career pathways in HR management emphasize broad strategic responsibilities, while talent acquisition focuses on building high-impact recruitment capabilities for organizational growth.
Technology and Tools Utilized
HR Managers utilize comprehensive human resource information systems (HRIS) like Workday and SAP SuccessFactors to manage employee records, payroll, and performance evaluations, ensuring streamlined HR operations. Talent Acquisition Managers rely heavily on applicant tracking systems (ATS) such as Greenhouse and Lever, alongside AI-powered recruitment platforms like HireVue, to identify, engage, and evaluate top candidates efficiently. Both roles leverage data analytics tools to enhance decision-making, but Talent Acquisition Managers prioritize sourcing technologies and candidate experience platforms to optimize hiring workflows.
Salary Trends and Industry Demand
HR Managers typically command higher average salaries, ranging from $75,000 to $110,000 annually, due to their broad responsibilities in employee relations, compliance, and organizational development. Talent Acquisition Managers, with a specialized focus on recruiting and workforce planning, earn between $65,000 and $95,000, reflecting growing demand in competitive industries like tech and healthcare. Both roles are experiencing robust industry demand, but Talent Acquisition Managers benefit from rapid salary growth linked to talent shortages and strategic hiring needs.
HR Manager vs Talent Acquisition Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com