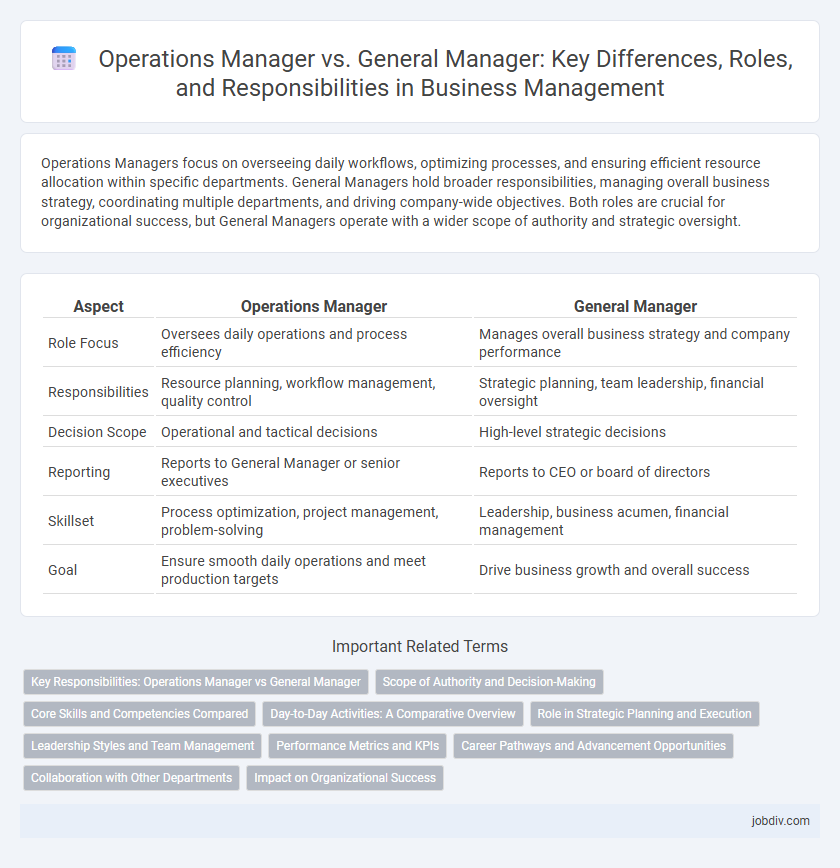
Operations Managers focus on overseeing daily workflows, optimizing processes, and ensuring efficient resource allocation within specific departments. General Managers hold broader responsibilities, managing overall business strategy, coordinating multiple departments, and driving company-wide objectives. Both roles are crucial for organizational success, but General Managers operate with a wider scope of authority and strategic oversight.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Operations Manager | General Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Oversees daily operations and process efficiency | Manages overall business strategy and company performance |
| Responsibilities | Resource planning, workflow management, quality control | Strategic planning, team leadership, financial oversight |
| Decision Scope | Operational and tactical decisions | High-level strategic decisions |
| Reporting | Reports to General Manager or senior executives | Reports to CEO or board of directors |
| Skillset | Process optimization, project management, problem-solving | Leadership, business acumen, financial management |
| Goal | Ensure smooth daily operations and meet production targets | Drive business growth and overall success |
Key Responsibilities: Operations Manager vs General Manager
Operations Managers concentrate on optimizing day-to-day processes, managing workflow efficiency, and supervising production or service delivery teams. General Managers hold broader authority, overseeing multiple departments, setting strategic goals, and coordinating cross-functional activities to achieve organizational objectives. Both roles require strong leadership, but Operations Managers focus on execution and process improvement, while General Managers emphasize overall business performance and growth.
Scope of Authority and Decision-Making
An Operations Manager primarily oversees daily business functions, focusing on managing production, quality control, and logistics to ensure operational efficiency. In contrast, a General Manager holds broader authority, encompassing strategic planning, financial performance, and overall organizational leadership across multiple departments. Decision-making for Operations Managers centers on tactical execution within established guidelines, while General Managers engage in high-level, cross-functional decisions impacting the company's direction and long-term success.
Core Skills and Competencies Compared
Operations Managers excel in process optimization, supply chain management, and quality control, ensuring efficient day-to-day operations. General Managers demonstrate broad leadership, strategic planning, financial acumen, and cross-departmental coordination, overseeing overall business performance. Both roles require strong communication, problem-solving, and decision-making skills, but Operations Managers emphasize operational efficiency while General Managers prioritize organizational growth and resource alignment.
Day-to-Day Activities: A Comparative Overview
Operations Managers concentrate on optimizing daily workflows, supervising production processes, and ensuring efficient resource allocation to meet operational targets. General Managers oversee broader business functions, including strategy implementation, cross-department coordination, and overall organizational performance. While Operations Managers focus on process efficiency and team supervision within specific units, General Managers drive company-wide objectives and long-term growth strategies.
Role in Strategic Planning and Execution
Operations Managers concentrate on implementing daily processes and optimizing efficiency to achieve short-term objectives within the company's strategic framework. General Managers oversee broader business functions, integrating strategic planning with execution to drive long-term growth and organizational goals. The General Manager's role encompasses cross-departmental coordination, while the Operations Manager focuses on operational tactics aligned with strategic priorities.
Leadership Styles and Team Management
Operations Managers typically employ a task-oriented leadership style, prioritizing process efficiency, resource allocation, and day-to-day team management to meet short-term objectives. General Managers adopt a broader transformational leadership approach, focusing on strategic vision, organizational culture, and motivating diverse teams across multiple departments for long-term growth. Both roles require strong communication skills, but General Managers place greater emphasis on influencing cross-functional collaboration and employee development initiatives.
Performance Metrics and KPIs
Operations Managers primarily focus on performance metrics related to process efficiency, such as production output, quality control, and operational cost reduction, ensuring day-to-day activities align with strategic goals. General Managers oversee broader KPIs including overall profitability, market share growth, employee satisfaction, and cross-departmental performance, integrating operational results to drive long-term business success. Effective management requires aligning Operations Manager metrics with General Manager KPIs to enhance organizational performance and achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Operations Managers typically advance by specializing in process optimization, supply chain management, and team leadership, often moving into roles such as Senior Operations Manager or Director of Operations. General Managers have a broader scope, overseeing multiple departments and driving overall business strategy, which positions them for executive roles like Vice President or Chief Operating Officer. Career progression for both roles depends heavily on developing strong leadership skills, strategic thinking, and cross-functional experience to unlock higher management opportunities.
Collaboration with Other Departments
Operations Managers collaborate closely with departments such as production, logistics, and quality control to ensure efficient workflow and meet organizational goals. General Managers maintain a broader collaboration scope, engaging with finance, marketing, HR, and operations to align diverse departmental strategies with overall business objectives. Effective interdepartmental communication facilitated by both roles drives operational excellence and strategic growth.
Impact on Organizational Success
Operations Managers drive organizational success by optimizing daily workflows, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring quality control, directly influencing cost management and customer satisfaction. General Managers shape the broader strategic vision, align cross-departmental goals, and lead company-wide initiatives that foster long-term growth and competitive advantage. Both roles are critical, with Operations Managers focusing on tactical execution and General Managers on strategic leadership to maximize overall business performance.
Operations Manager vs General Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com