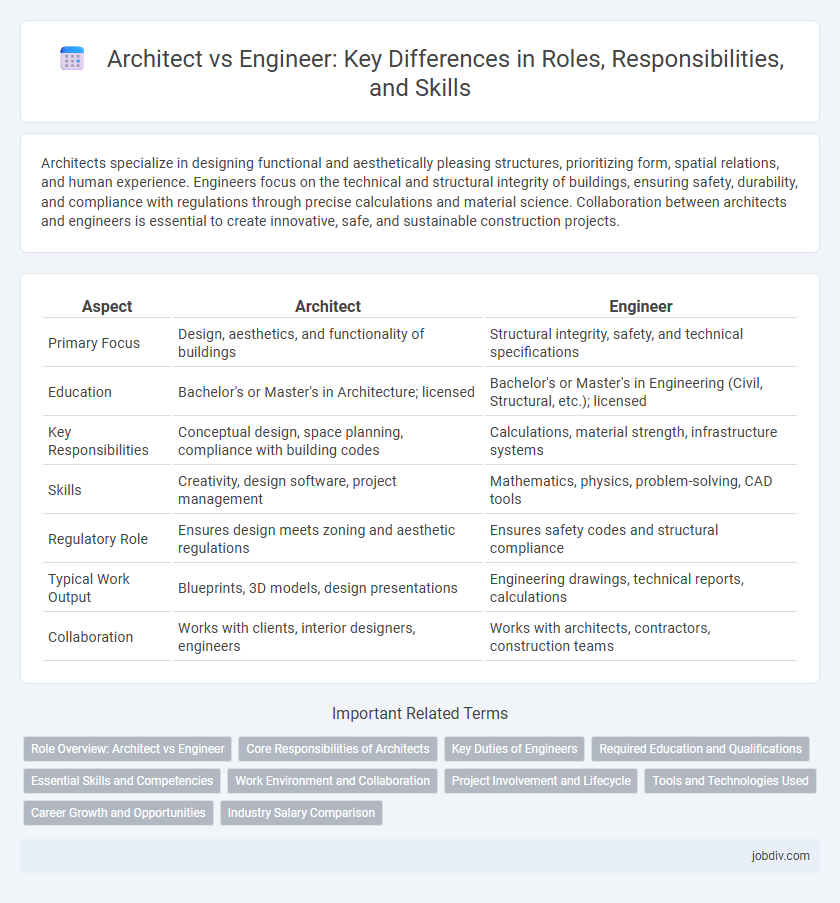
Architects specialize in designing functional and aesthetically pleasing structures, prioritizing form, spatial relations, and human experience. Engineers focus on the technical and structural integrity of buildings, ensuring safety, durability, and compliance with regulations through precise calculations and material science. Collaboration between architects and engineers is essential to create innovative, safe, and sustainable construction projects.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Architect | Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Design, aesthetics, and functionality of buildings | Structural integrity, safety, and technical specifications |
| Education | Bachelor's or Master's in Architecture; licensed | Bachelor's or Master's in Engineering (Civil, Structural, etc.); licensed |
| Key Responsibilities | Conceptual design, space planning, compliance with building codes | Calculations, material strength, infrastructure systems |
| Skills | Creativity, design software, project management | Mathematics, physics, problem-solving, CAD tools |
| Regulatory Role | Ensures design meets zoning and aesthetic regulations | Ensures safety codes and structural compliance |
| Typical Work Output | Blueprints, 3D models, design presentations | Engineering drawings, technical reports, calculations |
| Collaboration | Works with clients, interior designers, engineers | Works with architects, contractors, construction teams |
Role Overview: Architect vs Engineer
Architects focus on the creative design and aesthetic aspects of buildings, ensuring functionality, safety, and compliance with zoning laws. Engineers specialize in the technical and structural integrity of construction projects, applying principles of physics and mathematics to develop solutions for stability and efficiency. Both roles collaborate to balance innovation with practical feasibility in the built environment.
Core Responsibilities of Architects
Architects primarily focus on designing functional, aesthetic, and safe building environments, integrating spatial design with regulatory compliance to ensure usability and innovation. They develop detailed blueprints, collaborate with clients to understand project requirements, and oversee construction phases to maintain design integrity. Architects balance creativity with technical knowledge, addressing environmental impact and urban planning within their core responsibilities.
Key Duties of Engineers
Engineers are responsible for designing, analyzing, and overseeing the construction of structures, systems, or products to ensure functionality, safety, and efficiency. Their key duties include conducting technical research, creating detailed project plans, performing calculations and simulations, and managing compliance with industry standards and regulations. Engineers collaborate with multidisciplinary teams to troubleshoot problems, optimize performance, and innovate within fields such as civil, mechanical, electrical, or software engineering.
Required Education and Qualifications
Architects must obtain a professional degree in architecture, typically a Bachelor or Master of Architecture, and complete an accredited internship before passing the Architect Registration Examination (ARE). Engineers generally require a bachelor's degree in engineering from an accredited program, followed by earning the Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) certification, gaining work experience, and passing the Professional Engineer (PE) exam. Both professions demand continuous education to maintain licensure and stay updated with industry standards.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Architects require strong design thinking, creativity, and spatial awareness to conceptualize functional and aesthetically pleasing structures, while engineers emphasize analytical skills, mathematics, and technical problem-solving for structural integrity and safety. Proficiency in software tools like AutoCAD and BIM is crucial for architects, whereas engineers rely heavily on simulations, calculations, and materials science knowledge. Effective communication and project management skills are vital for both professions to collaborate with clients, contractors, and multidisciplinary teams efficiently.
Work Environment and Collaboration
Architects typically work in design studios or offices, focusing on creative planning and conceptual development, while engineers often operate in technical settings including labs, construction sites, and offices, emphasizing detailed calculations and structural integrity. Collaboration between architects and engineers is essential to harmonize aesthetic vision with technical feasibility, ensuring project success from initial sketches to final construction. Effective communication and mutual respect for each discipline's expertise enhance teamwork and optimize outcomes in complex building projects.
Project Involvement and Lifecycle
Architects lead the conceptual design phase, focusing on aesthetics, functionality, and user experience throughout the entire project lifecycle. Engineers engage primarily during the development, technical detailing, and construction phases, ensuring structural integrity, feasibility, and compliance with engineering standards. Both roles collaborate closely during project review, execution, and commissioning to deliver a cohesive and structurally sound final product.
Tools and Technologies Used
Architects primarily use design software like AutoCAD, Revit, and SketchUp to create detailed building plans and 3D models, emphasizing aesthetics and spatial functionality. Engineers rely on tools such as MATLAB, Civil 3D, and structural analysis software to ensure structural integrity, load calculations, and compliance with safety standards. Both professionals integrate Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology to enhance collaboration and streamline project workflows.
Career Growth and Opportunities
Architects primarily advance through design leadership and project management roles, leveraging creativity and technical knowledge to shape building aesthetics and functionality. Engineers often experience rapid career growth via specialization in fields like civil, mechanical, or software engineering, enabling positions in research, development, and executive management. Both careers offer robust opportunities in construction, infrastructure, and technology sectors, with engineers generally commanding higher starting salaries and architects gaining increased market demand in sustainable design.
Industry Salary Comparison
Architects typically earn a median annual salary of around $80,000, while engineers, depending on specialization, often command higher wages, with median salaries ranging from $85,000 to $120,000. Civil, mechanical, and electrical engineers tend to have salaries on the higher end of the spectrum, influenced by industry demand and technical expertise. Salary growth potential also varies, with engineers generally experiencing faster increases due to technological advancements and project complexity.
Architect vs Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com