Operations Managers oversee the efficiency of business processes and ensure workflows align with organizational goals, focusing on strategic planning and resource management. Office Managers handle the daily administrative functions, maintaining office supplies, coordinating schedules, and supporting staff to create a productive work environment. Both roles are essential but differ in scope, with Operations Managers emphasizing broader organizational performance and Office Managers concentrating on internal office operations.
Table of Comparison
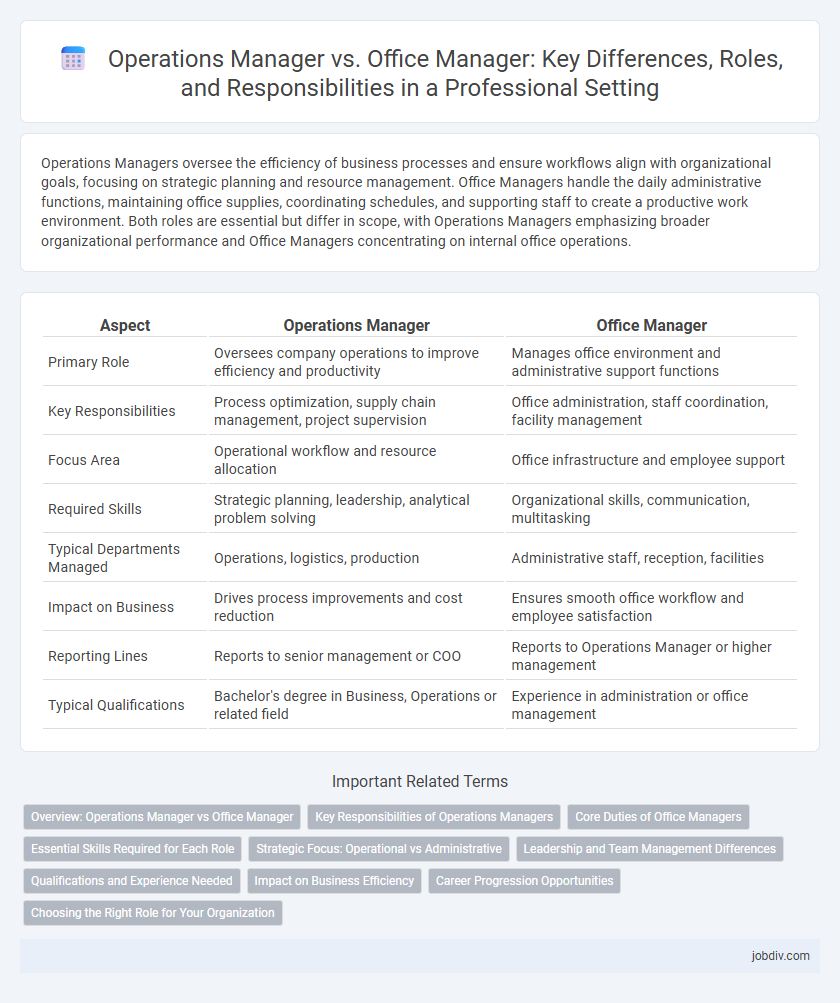
| Aspect | Operations Manager | Office Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Oversees company operations to improve efficiency and productivity | Manages office environment and administrative support functions |
| Key Responsibilities | Process optimization, supply chain management, project supervision | Office administration, staff coordination, facility management |
| Focus Area | Operational workflow and resource allocation | Office infrastructure and employee support |
| Required Skills | Strategic planning, leadership, analytical problem solving | Organizational skills, communication, multitasking |
| Typical Departments Managed | Operations, logistics, production | Administrative staff, reception, facilities |
| Impact on Business | Drives process improvements and cost reduction | Ensures smooth office workflow and employee satisfaction |
| Reporting Lines | Reports to senior management or COO | Reports to Operations Manager or higher management |
| Typical Qualifications | Bachelor's degree in Business, Operations or related field | Experience in administration or office management |
Overview: Operations Manager vs Office Manager
Operations Managers oversee core business processes, focusing on optimizing workflow, resource allocation, and strategic planning to improve overall efficiency. Office Managers handle administrative functions, including staff coordination, office maintenance, and managing daily clerical tasks to ensure smooth workplace operations. Both roles require leadership and organizational skills but differ in scope, with Operations Managers driving business performance and Office Managers supporting internal office environments.
Key Responsibilities of Operations Managers
Operations Managers oversee the organization's daily operations, focusing on improving efficiency, managing supply chains, and optimizing workflows to meet business goals. They are responsible for strategic planning, resource allocation, budgeting, and performance analysis to drive operational excellence. Operations Managers coordinate cross-departmental activities to ensure seamless processes and enhance overall productivity.
Core Duties of Office Managers
Office Managers oversee administrative functions, facility management, and staff coordination, ensuring smooth daily operations within an office environment. They handle schedules, manage office supplies, and implement company policies to maintain organizational efficiency. Their role focuses on supporting operational infrastructure rather than strategic business decisions.
Essential Skills Required for Each Role
Operations Managers require strong strategic planning, analytical thinking, and leadership skills to optimize processes and drive organizational efficiency. Office Managers must excel in communication, multitasking, and organizational abilities to ensure smooth daily administrative functions and team support. Both roles demand problem-solving capabilities, but Operations Managers emphasize operational execution, while Office Managers focus on office environment management.
Strategic Focus: Operational vs Administrative
Operations Managers prioritize strategic planning and process improvements to enhance operational efficiency and drive business growth. Office Managers focus on administrative tasks such as managing schedules, coordinating office resources, and maintaining workplace organization to support daily business functions. The distinction lies in Operations Managers aligning activities with long-term organizational goals while Office Managers ensure smooth day-to-day office operations.
Leadership and Team Management Differences
Operations Managers oversee strategic leadership, driving cross-functional team alignment and performance to optimize organizational processes and achieve business objectives. Office Managers focus on supervisory leadership within administrative teams, ensuring efficient office operations and supporting staff productivity through day-to-day task management. The distinction lies in Operations Managers managing broader operational scope and decision-making, while Office Managers lead tactical implementation within office environments.
Qualifications and Experience Needed
Operations Managers typically require a bachelor's degree in business administration, management, or a related field, with 5-7 years of experience in operations or project management demonstrating strong leadership and strategic planning skills. Office Managers often hold an associate or bachelor's degree in business administration or office management, supported by 3-5 years of experience in administrative roles emphasizing organizational skills and office coordination. Both roles benefit from proficiency in enterprise resource planning (ERP) software and excellent communication abilities, but Operations Managers demand deeper expertise in process optimization and cross-functional team management.
Impact on Business Efficiency
Operations Managers drive business efficiency by streamlining processes, optimizing resource allocation, and implementing performance metrics that enhance productivity across departments. Office Managers maintain organizational flow by managing administrative tasks, coordinating office activities, and ensuring effective communication among staff, which supports a smooth working environment. The combined efforts of both roles significantly improve operational workflows, reduce downtime, and contribute to sustained business growth.
Career Progression Opportunities
Operations Managers often have broader career progression opportunities due to their strategic involvement in optimizing business processes, supply chain management, and cross-departmental leadership. Office Managers typically advance within administrative and support-focused roles, such as Senior Office Manager or Executive Assistant, but may face limited growth beyond organizational administration. Career pathways for Operations Managers frequently lead to executive roles like Director of Operations or Chief Operating Officer (COO), reflecting higher responsibility and influence within the company.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Organization
Operations Managers oversee company-wide processes to enhance efficiency and productivity, focusing on strategic planning, resource allocation, and performance optimization. Office Managers handle administrative tasks, facility management, and employee coordination to ensure smooth daily operations within the office environment. Choosing the right role depends on your organization's scale and needs--Operations Managers suit larger, process-driven companies, while Office Managers fit businesses requiring dedicated office administration.
Operations Manager vs Office Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com