Recruiters typically manage the entire hiring process for an organization, sourcing candidates for a variety of roles and maintaining long-term relationships with clients. Headhunters specialize in identifying and approaching top-level or niche talent, often for executive or highly specialized positions. Both roles require strong networking skills, but headhunters are more proactive in targeting passive candidates.
Table of Comparison
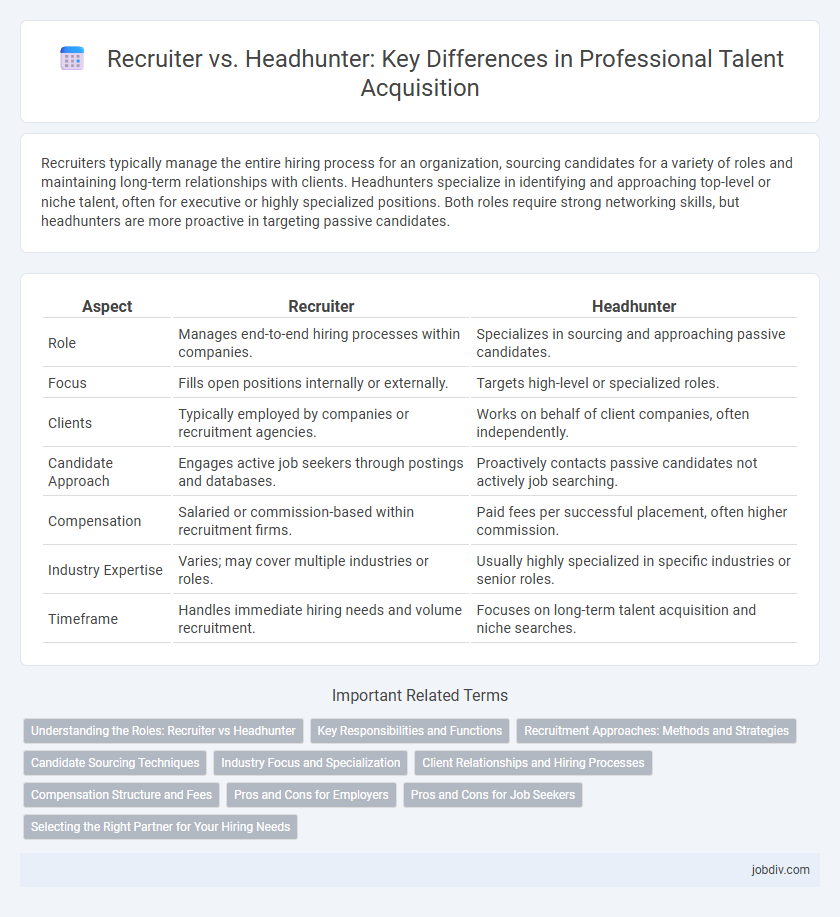
| Aspect | Recruiter | Headhunter |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Manages end-to-end hiring processes within companies. | Specializes in sourcing and approaching passive candidates. |
| Focus | Fills open positions internally or externally. | Targets high-level or specialized roles. |
| Clients | Typically employed by companies or recruitment agencies. | Works on behalf of client companies, often independently. |
| Candidate Approach | Engages active job seekers through postings and databases. | Proactively contacts passive candidates not actively job searching. |
| Compensation | Salaried or commission-based within recruitment firms. | Paid fees per successful placement, often higher commission. |
| Industry Expertise | Varies; may cover multiple industries or roles. | Usually highly specialized in specific industries or senior roles. |
| Timeframe | Handles immediate hiring needs and volume recruitment. | Focuses on long-term talent acquisition and niche searches. |
Understanding the Roles: Recruiter vs Headhunter
Recruiters manage the entire hiring process, sourcing candidates for various positions within an organization, often focusing on volume and organizational fit. Headhunters specialize in identifying and attracting top-tier talent for specific, high-level roles, frequently targeting passive candidates not actively seeking employment. Understanding these distinctions enables companies to select the appropriate talent acquisition strategy aligned with their recruitment needs and objectives.
Key Responsibilities and Functions
Recruiters manage the end-to-end hiring process by sourcing, screening, and interviewing candidates to fill open roles within an organization. Headhunters specialize in identifying and approaching high-level or niche talent, often targeting passive candidates for executive or hard-to-fill positions. Both focus on talent acquisition, but recruiters typically handle volume hiring while headhunters concentrate on strategic placements.
Recruitment Approaches: Methods and Strategies
Recruiters primarily focus on managing the entire hiring process by sourcing candidates through job postings, networking, and applicant tracking systems, aiming to fill positions efficiently within a company's internal talent acquisition framework. Headhunters employ proactive, targeted strategies such as direct outreach and market mapping to identify and engage passive candidates with specialized skills or executive experience often not actively seeking new roles. These recruitment approaches differ in scope and intensity, with recruiters handling volume-based hiring needs and headhunters concentrating on high-level or niche talent acquisition using personalized search tactics.
Candidate Sourcing Techniques
Recruiters leverage in-house databases, job boards, and social media platforms like LinkedIn to source active candidates aligned with company requirements. Headhunters employ advanced sourcing methods including direct outreach, networking within niche industries, and utilizing proprietary talent pools to identify passive candidates. Both utilize applicant tracking systems (ATS) and data analytics to optimize candidate sourcing efficiency and precision.
Industry Focus and Specialization
Recruiters often work across a broad range of industries and handle multiple roles, providing general talent acquisition services, while headhunters specialize deeply within specific sectors and focus on high-level or niche positions. Industry focus allows headhunters to develop extensive networks and insights, enabling precise matches for specialized roles such as executive, technical, or strategic hires. This specialization gives headhunters a competitive edge in understanding market trends, salary benchmarks, and candidate availability within their niche, compared to recruiters with a wider but less targeted scope.
Client Relationships and Hiring Processes
Recruiters maintain long-term client relationships by working exclusively with organizations to understand their culture and ongoing talent needs, ensuring tailored hiring processes that align with company objectives. Headhunters engage in targeted, high-level talent searches for specific roles, often operating on a project basis with multiple clients simultaneously, which demands rapid identification and vetting of specialized candidates. Both roles require strategic communication and candidate assessment, but recruiters emphasize continuous partnership while headhunters prioritize swift, expert matchmaking for critical positions.
Compensation Structure and Fees
Recruiters typically earn a salary or hourly wage and may receive bonuses based on performance, while headhunters operate on a contingency or retainer fee basis, charging a percentage of the candidate's first-year salary upon successful placement. Recruitment agencies often set headhunter fees between 20% and 30% of annual compensation, reflecting the specialized search and industry expertise provided. Unlike recruiters, headhunters bear more financial risk upfront and invest significant resources in sourcing high-level candidates for executive or niche roles.
Pros and Cons for Employers
Recruiters provide a broader talent pool and maintain ongoing relationships with candidates, offering cost-effective and continuous hiring support, but may lack specialization in niche industries. Headhunters excel in targeting highly specialized or executive-level candidates quickly, delivering high-quality matches through intensive market research, though their services often come at a higher price and focus on single, urgent hires. Employers benefit from recruiters for volume hiring and long-term talent acquisition strategies, while headhunters are ideal for critical roles requiring top-tier expertise and discretion.
Pros and Cons for Job Seekers
Recruiters offer a broader range of job opportunities across various industries, but their focus on filling multiple roles might limit personalized attention for job seekers; headhunters specialize in targeted, high-level positions, providing tailored support and insider industry knowledge, though their narrow focus can reduce overall job options. Job seekers benefit from recruiters' extensive networks and ongoing industry connections, while headhunters provide strategic career advice and exclusive access to unadvertised vacancies. The choice depends on the candidate's career level and desired job specificity, balancing volume of opportunities with depth of expertise.
Selecting the Right Partner for Your Hiring Needs
Choosing between a recruiter and a headhunter depends on your specific hiring needs and industry requirements. Recruiters typically manage a broad range of positions through direct sourcing and nurturing talent pools, while headhunters specialize in filling high-level or niche roles by actively targeting passive candidates. Evaluating their expertise, network reach, and recruitment approach ensures alignment with your company's culture and long-term talent strategy.
Recruiter vs Headhunter Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com