An appliance repairman specializes in fixing household devices like refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens, ensuring everyday convenience and functionality. Equipment repairmen typically handle industrial or commercial machinery, focusing on heavy-duty tools and complex mechanical systems. Understanding the distinction helps homeowners and businesses seek the right expert for efficient and reliable repair services.
Table of Comparison
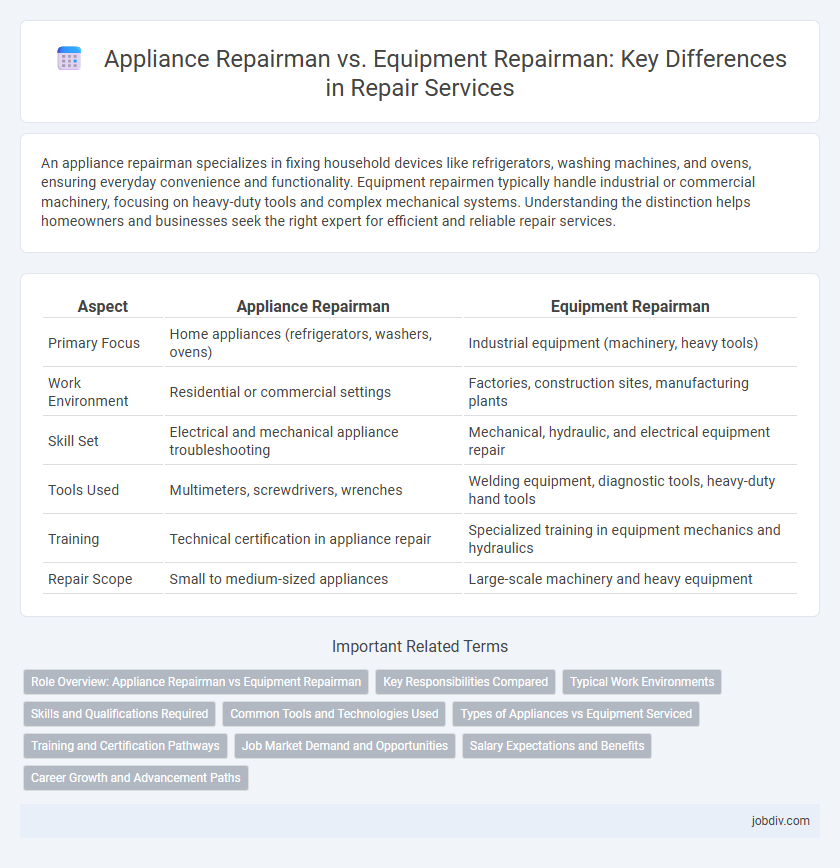
| Aspect | Appliance Repairman | Equipment Repairman |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Home appliances (refrigerators, washers, ovens) | Industrial equipment (machinery, heavy tools) |
| Work Environment | Residential or commercial settings | Factories, construction sites, manufacturing plants |
| Skill Set | Electrical and mechanical appliance troubleshooting | Mechanical, hydraulic, and electrical equipment repair |
| Tools Used | Multimeters, screwdrivers, wrenches | Welding equipment, diagnostic tools, heavy-duty hand tools |
| Training | Technical certification in appliance repair | Specialized training in equipment mechanics and hydraulics |
| Repair Scope | Small to medium-sized appliances | Large-scale machinery and heavy equipment |
Role Overview: Appliance Repairman vs Equipment Repairman
An appliance repairman specializes in diagnosing and fixing household devices such as refrigerators, washers, and ovens, ensuring residential functionality and safety. Equipment repairmen focus on industrial machinery maintenance and repairs, often working with heavy-duty engines, manufacturing tools, and specialized mechanical systems to minimize operational downtime. Both roles require technical expertise but differ in scale and environment, with appliance repairmen serving consumer needs and equipment repairmen supporting industrial production.
Key Responsibilities Compared
Appliance repairmen specialize in diagnosing and fixing household devices such as refrigerators, ovens, and washing machines, ensuring proper functionality and safety compliance. Equipment repairmen focus on industrial or commercial machinery, performing maintenance, troubleshooting mechanical issues, and restoring operational efficiency in manufacturing or construction settings. Both roles require technical skills and knowledge of electrical and mechanical systems, but appliance repairmen work predominantly with consumer goods while equipment repairmen handle heavy-duty equipment.
Typical Work Environments
Appliance repairmen typically work in residential settings, repairing household items such as refrigerators, ovens, and washers, often entering customers' homes to perform on-site repairs. Equipment repairmen usually operate in industrial or commercial environments, maintaining and fixing machinery used in manufacturing plants, construction sites, or large facilities. Both professions require adaptability to various work conditions but differ significantly in the scale and type of equipment handled.
Skills and Qualifications Required
An appliance repairman requires expertise in diagnosing and fixing household devices such as refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens, with skills in electrical systems, plumbing, and user interface technology. Equipment repairmen specialize in maintaining and repairing industrial machines and tools, demanding proficiency in mechanical systems, hydraulics, and heavy machinery diagnostics. Both roles necessitate technical certifications, hands-on experience, and strong troubleshooting abilities tailored to their specific repair environments.
Common Tools and Technologies Used
Appliance repairmen commonly use multimeters, screwdrivers, and thermal cameras to diagnose and fix household devices like refrigerators and washing machines. Equipment repairmen often rely on hydraulic presses, torque wrenches, and computerized diagnostic systems to service heavy machinery and industrial equipment. Both professions utilize advanced software for troubleshooting, but their toolsets are tailored to the scale and complexity of the appliances or equipment they maintain.
Types of Appliances vs Equipment Serviced
Appliance repairmen specialize in household devices such as refrigerators, ovens, washing machines, and dishwashers, ensuring these common appliances function efficiently for daily use. Equipment repairmen focus on industrial or commercial machinery, including HVAC systems, manufacturing tools, and heavy-duty generators, addressing maintenance and breakdowns in larger-scale operations. Understanding these distinctions helps in selecting the right professional for either domestic appliance fixes or complex equipment servicing.
Training and Certification Pathways
Appliance repairmen typically undergo training through technical schools or vocational programs that focus on household devices, earning certifications such as EPA 608 for refrigerant handling or from organizations like the Professional Service Association. Equipment repairmen often receive specialized education in industrial machinery, with certifications that may include Certified Maintenance & Reliability Professional (CMRP) or manufacturer-specific credentials reflecting expertise in heavy-duty equipment. Both pathways emphasize hands-on experience combined with formal training to ensure proficiency in troubleshooting and repairing complex mechanical and electrical systems.
Job Market Demand and Opportunities
The demand for appliance repairmen is driven by the widespread use of household devices like refrigerators, washers, and ovens, creating consistent job opportunities in residential and commercial sectors. Equipment repairmen, specializing in industrial machinery and heavy equipment, face growing opportunities due to increased manufacturing activities and infrastructure projects. Both fields require technical expertise, but equipment repairman roles often offer higher wages and advancement potential due to the complexity and scale of the machinery involved.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Appliance repairmen typically earn between $35,000 and $55,000 annually, with benefits including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. Equipment repairmen often command higher salaries ranging from $45,000 to $70,000 per year due to specialized skills, alongside comprehensive benefits such as hazard pay, overtime compensation, and advanced training opportunities. Both roles offer job stability but equipment repairmen generally experience greater earning potential and benefits packages.
Career Growth and Advancement Paths
Appliance repairmen typically specialize in household devices like refrigerators, washers, and ovens, offering a clear career progression from junior technician roles to senior technician or supervisory positions within residential service companies. Equipment repairmen focus on industrial machinery, often advancing into maintenance management, equipment engineering, or specialized technical support roles due to the complexity and scale of industrial systems. Both careers benefit from certifications and continued education, but equipment repair often provides more opportunities for advancement in large manufacturing or construction firms because of the technical expertise required.
Appliance Repairman vs Equipment Repairman Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com