Electronics repair involves fixing devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops that rely on complex circuitry and microchips, requiring specialized knowledge of digital components. Electrical repair typically addresses wiring, outlets, circuit breakers, and larger electrical systems within homes or buildings, focusing on power delivery and safety standards. Understanding the distinction helps ensure the right technician is hired for either delicate gadget repairs or robust electrical system maintenance.
Table of Comparison
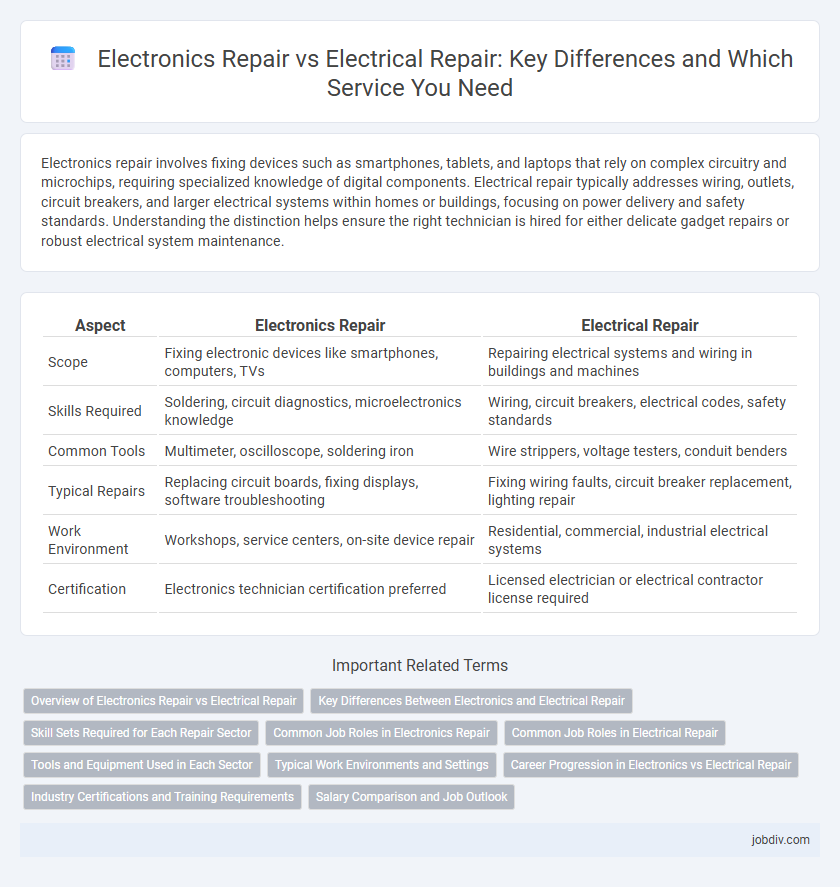
| Aspect | Electronics Repair | Electrical Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Fixing electronic devices like smartphones, computers, TVs | Repairing electrical systems and wiring in buildings and machines |
| Skills Required | Soldering, circuit diagnostics, microelectronics knowledge | Wiring, circuit breakers, electrical codes, safety standards |
| Common Tools | Multimeter, oscilloscope, soldering iron | Wire strippers, voltage testers, conduit benders |
| Typical Repairs | Replacing circuit boards, fixing displays, software troubleshooting | Fixing wiring faults, circuit breaker replacement, lighting repair |
| Work Environment | Workshops, service centers, on-site device repair | Residential, commercial, industrial electrical systems |
| Certification | Electronics technician certification preferred | Licensed electrician or electrical contractor license required |
Overview of Electronics Repair vs Electrical Repair
Electronics repair involves fixing devices with complex circuits, such as smartphones, computers, and audio equipment, focusing on microchips, circuit boards, and digital components. Electrical repair primarily deals with wiring, circuits, and electrical systems in buildings and appliances, emphasizing safety and compliance with electrical codes. Both require specialized skills but cater to different types of technology and applications within residential, commercial, and industrial environments.
Key Differences Between Electronics and Electrical Repair
Electronics repair involves fixing devices with circuits, microchips, and semiconductors, such as smartphones, computers, and TVs, while electrical repair centers on systems that manage high-voltage power, including wiring, circuit breakers, and lighting installations. Electronics repair requires detailed knowledge of digital components and signal processing, whereas electrical repair demands expertise in power distribution, safety standards, and load calculations. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurately diagnosing issues and applying the correct tools and techniques in each specialized field.
Skill Sets Required for Each Repair Sector
Electronics repair demands proficiency in microelectronics, circuit analysis, and soldering techniques, focusing on small-scale components like semiconductors and printed circuit boards. Electrical repair requires expertise in wiring systems, electrical codes, and high-voltage safety procedures, often dealing with large-scale installations such as home wiring and industrial machinery. Both fields necessitate diagnostic skills but differ significantly in tools and technical knowledge due to the varying complexity and scale of devices involved.
Common Job Roles in Electronics Repair
Common job roles in electronics repair include electronics technicians, circuit board repair specialists, and device diagnosticians, each responsible for troubleshooting, repairing, and maintaining electronic devices such as smartphones, computers, and medical equipment. These professionals utilize skills in soldering, component testing, and firmware updates to restore functionality and ensure device longevity. They differ from electrical repair roles, which often focus on wiring, circuit breakers, and electrical systems within buildings or infrastructure.
Common Job Roles in Electrical Repair
Common job roles in electrical repair include electricians, electrical technicians, and maintenance engineers who specialize in diagnosing, troubleshooting, and fixing wiring, circuit breakers, and electrical systems. These professionals frequently work on residential, commercial, and industrial electrical installations to ensure safety and compliance with electrical codes. Their expertise covers tasks such as repairing faulty outlets, restoring power to malfunctioning circuits, and maintaining electrical panels to prevent system failures.
Tools and Equipment Used in Each Sector
Electronics repair relies heavily on precision tools such as soldering irons, multimeters, oscilloscopes, and anti-static mats to handle delicate circuit boards and microcomponents. Electrical repair typically requires more robust equipment like wire strippers, voltage testers, circuit breakers, and insulated screwdrivers to address high-voltage wiring and power systems. Each sector's specialized tools are essential for effective diagnosis and safe repair of their respective components.
Typical Work Environments and Settings
Electronics repair typically occurs in controlled environments such as workshops and laboratories equipped with precision tools for diagnosing and fixing circuit boards, semiconductors, and microchips. Electrical repair often takes place on-site in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, addressing wiring, circuit breakers, and power distribution systems. Both fields require specialized knowledge, but electronics repair focuses on delicate components, while electrical repair deals with higher voltage installations and safety compliance.
Career Progression in Electronics vs Electrical Repair
Career progression in electronics repair often involves advancing from entry-level technician roles to specialized fields such as circuit design, embedded systems, or robotics, benefiting from the rapid evolution of technology. Electrical repair careers typically progress through mastering residential, commercial, and industrial electrical systems, leading to licensed electrician status and opportunities in project management or electrical engineering. Both fields value certification and hands-on experience, but electronics repair tends to offer more pathways into technology-driven innovation and product development.
Industry Certifications and Training Requirements
Electronics repair technicians typically require specialized certifications such as IPC certification and training in microelectronics and circuit board diagnostics, reflecting the precision needed for devices like smartphones and computers. Electrical repair professionals often hold certifications from organizations like the National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA) or OSHA training, emphasizing safety standards and knowledge of wiring systems in residential and commercial settings. Both fields demand continual education, but electronics repair focuses more on component-level expertise, while electrical repair prioritizes compliance with electrical codes and high-voltage systems.
Salary Comparison and Job Outlook
Electronics repair technicians typically earn an average salary ranging from $40,000 to $60,000 annually, while electrical repair specialists can expect salaries between $50,000 and $75,000, reflecting higher demand for their expertise. The job outlook for electrical repair roles is projected to grow by approximately 8% over the next decade due to increased infrastructure development, whereas electronics repair jobs are anticipated to grow around 5% as consumer electronics evolve. Strong skills in circuit diagnostics and mains wiring enhance employability in both fields, with electrical repair positions offering more opportunities in industrial and commercial sectors.
Electronics Repair vs Electrical Repair Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com