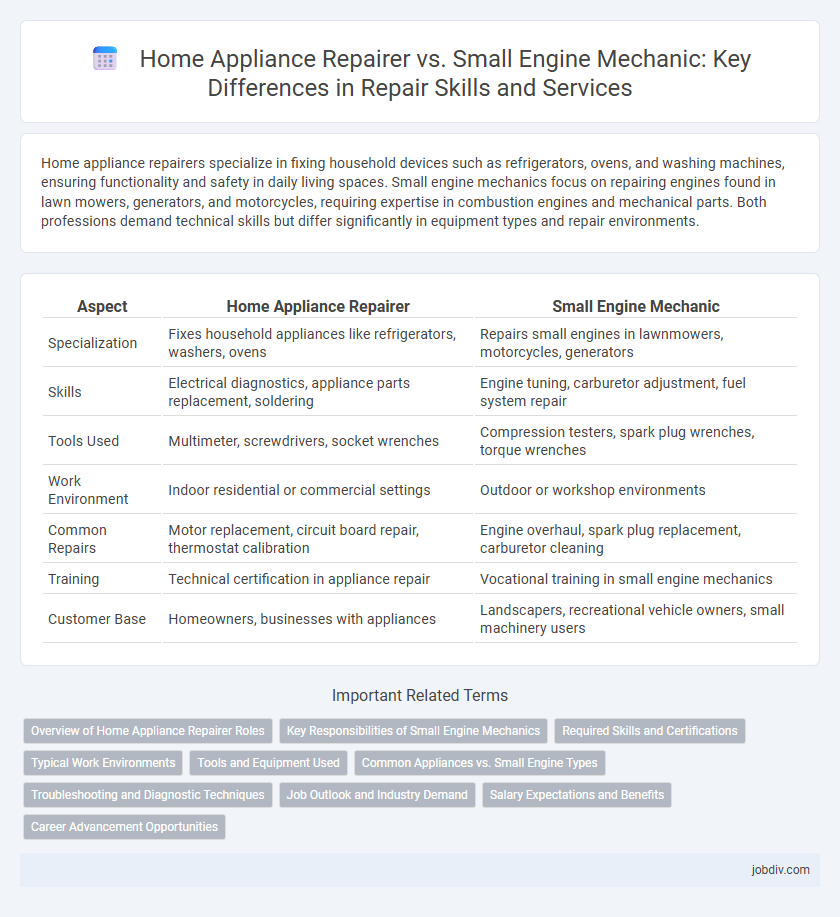
Home appliance repairers specialize in fixing household devices such as refrigerators, ovens, and washing machines, ensuring functionality and safety in daily living spaces. Small engine mechanics focus on repairing engines found in lawn mowers, generators, and motorcycles, requiring expertise in combustion engines and mechanical parts. Both professions demand technical skills but differ significantly in equipment types and repair environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Home Appliance Repairer | Small Engine Mechanic |
|---|---|---|
| Specialization | Fixes household appliances like refrigerators, washers, ovens | Repairs small engines in lawnmowers, motorcycles, generators |
| Skills | Electrical diagnostics, appliance parts replacement, soldering | Engine tuning, carburetor adjustment, fuel system repair |
| Tools Used | Multimeter, screwdrivers, socket wrenches | Compression testers, spark plug wrenches, torque wrenches |
| Work Environment | Indoor residential or commercial settings | Outdoor or workshop environments |
| Common Repairs | Motor replacement, circuit board repair, thermostat calibration | Engine overhaul, spark plug replacement, carburetor cleaning |
| Training | Technical certification in appliance repair | Vocational training in small engine mechanics |
| Customer Base | Homeowners, businesses with appliances | Landscapers, recreational vehicle owners, small machinery users |
Overview of Home Appliance Repairer Roles
Home appliance repairers specialize in diagnosing, maintaining, and fixing household devices such as refrigerators, washing machines, ovens, and microwaves, ensuring their optimal functionality. They utilize electrical and mechanical skills to troubleshoot issues, replace faulty components, and perform preventive maintenance to extend appliance lifespan. Their expertise supports residential comfort and efficiency by restoring essential home equipment promptly and reliably.
Key Responsibilities of Small Engine Mechanics
Small engine mechanics specialize in diagnosing, repairing, and maintaining small internal combustion engines used in lawn mowers, chainsaws, and generators. Their key responsibilities include inspecting engines for mechanical issues, replacing worn-out parts such as spark plugs and carburetors, and performing routine maintenance like oil changes and tuning. They must also ensure engines operate efficiently and meet safety standards, often collaborating with customers to explain problems and recommend solutions.
Required Skills and Certifications
Home appliance repairers require expertise in diagnosing and fixing electrical and mechanical issues in household devices, often needing certifications like EPA Section 608 for refrigerants and familiarity with multimeters and circuit boards. Small engine mechanics specialize in repairing engines under 25 horsepower, such as lawnmowers and generators, requiring skills in carburetor tuning, fuel system repair, and certifications such as ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) or manufacturer-specific training. Both professions demand strong troubleshooting abilities and knowledge of safety protocols, but their certifications and technical skills vary according to the types of equipment they service.
Typical Work Environments
Home appliance repairers primarily work in residential settings, repair shops, or in-store service centers, frequently handling microwaves, refrigerators, and washing machines. Small engine mechanics operate mostly in outdoor environments, repair garages, or equipment rental businesses, focusing on lawn mowers, chainsaws, and generators. Both professions require diagnostic tools and hands-on technical skills, but the typical work environment varies significantly based on the type of machinery serviced.
Tools and Equipment Used
Home appliance repairers utilize specialized diagnostic tools such as multimeters, voltage testers, and thermal imaging cameras to troubleshoot electronic components of refrigerators, washers, and ovens. Small engine mechanics rely heavily on equipment including spark plug testers, compression gauges, and carburetor cleaner tools to maintain and repair lawnmowers, chainsaws, and generators. Both professions require wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers, but their toolkits are tailored to address the specific mechanical or electrical systems of their respective equipment.
Common Appliances vs. Small Engine Types
Home appliance repairers specialize in fixing common household devices such as refrigerators, washing machines, and microwaves, ensuring efficient operation of everyday appliances. Small engine mechanics focus on repairing engines found in lawn mowers, chainsaws, and generators, which require knowledge of internal combustion engines and fuel systems. Both fields demand technical expertise but cater to distinctly different equipment categories, with home appliance repair emphasizing electrical components and small engine mechanics prioritizing mechanical engine parts.
Troubleshooting and Diagnostic Techniques
Home appliance repairers utilize specialized diagnostic tools and software to identify electrical faults, component failures, and system malfunctions in household devices such as refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens. Small engine mechanics focus on troubleshooting combustion engines by performing compression tests, fuel system inspections, and ignition system diagnostics to pinpoint performance issues in lawn mowers, generators, and motorbikes. Proficiency in interpreting technical manuals and utilizing multimeters, oscilloscopes, and diagnostic scanners is essential for accurate fault detection in both professions.
Job Outlook and Industry Demand
Job outlook for home appliance repairers is steady, driven by increasing reliance on household electronics and a trend toward repairing rather than replacing appliances. Small engine mechanics face rising demand in agricultural, construction, and recreational sectors, fueled by equipment maintenance needs and growing outdoor activities. Industry projections indicate both fields will experience moderate growth, with small engine mechanics benefiting from expanding markets and home appliance repairers supported by sustainable consumer practices.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Home appliance repairers typically earn an average salary ranging from $35,000 to $50,000 annually, with benefits that often include health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, reflecting the steady demand for household appliance maintenance. Small engine mechanics usually have a salary range between $30,000 and $45,000 per year, with benefits that may vary widely but often include health coverage and overtime pay due to seasonal fluctuations in repair work. Salary expectations for both roles depend on experience, location, and certification, with home appliance repairers generally experiencing more consistent income due to regular residential demand.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Home appliance repairers often advance to supervisory roles or specialize in high-tech appliance systems, gaining certifications in smart technology integration to enhance career prospects. Small engine mechanics can progress by obtaining technical certifications and moving into roles such as service managers or equipment sales specialists, with opportunities in agricultural or construction equipment sectors. Both careers benefit from continuous education and specialization, but home appliance repair offers faster advancement in residential and commercial markets.
Home Appliance Repairer vs Small Engine Mechanic Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com