Brake specialists focus on diagnosing and repairing issues related to a vehicle's braking system, ensuring safety and optimal stopping performance. Transmission specialists handle the repair and maintenance of the transmission, which controls gear shifting and overall vehicle movement. Choosing the right expert depends on whether the problem affects braking or gear functionality, as each requires specialized knowledge and tools.
Table of Comparison
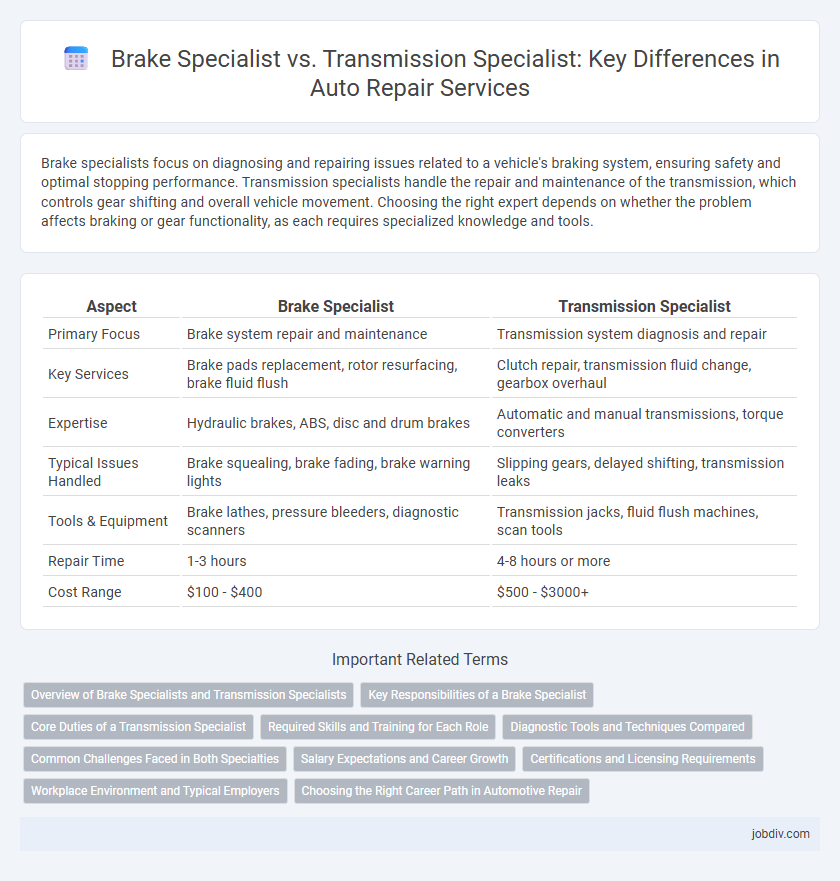
| Aspect | Brake Specialist | Transmission Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Brake system repair and maintenance | Transmission system diagnosis and repair |
| Key Services | Brake pads replacement, rotor resurfacing, brake fluid flush | Clutch repair, transmission fluid change, gearbox overhaul |
| Expertise | Hydraulic brakes, ABS, disc and drum brakes | Automatic and manual transmissions, torque converters |
| Typical Issues Handled | Brake squealing, brake fading, brake warning lights | Slipping gears, delayed shifting, transmission leaks |
| Tools & Equipment | Brake lathes, pressure bleeders, diagnostic scanners | Transmission jacks, fluid flush machines, scan tools |
| Repair Time | 1-3 hours | 4-8 hours or more |
| Cost Range | $100 - $400 | $500 - $3000+ |
Overview of Brake Specialists and Transmission Specialists
Brake specialists focus on diagnosing, repairing, and maintaining vehicle braking systems, including disc brakes, drum brakes, ABS, and brake fluid systems to ensure optimal stopping performance and safety. Transmission specialists handle the repair and maintenance of manual and automatic transmission systems, addressing issues such as gear slippage, transmission fluid leaks, and clutch problems to maintain smooth vehicle acceleration and shifting. Both specialists require advanced knowledge of automotive systems, but their expertise targets distinct components essential for vehicle control and drivability.
Key Responsibilities of a Brake Specialist
A Brake Specialist is responsible for diagnosing, repairing, and maintaining vehicle brake systems to ensure optimal safety and performance. Their key tasks include inspecting brake pads, rotors, calipers, and hydraulic lines, as well as replacing worn components and performing brake fluid flushes. Expertise in ABS systems and brake system diagnostics sets them apart from Transmission Specialists, who focus on gearbox repair and maintenance.
Core Duties of a Transmission Specialist
A transmission specialist primarily focuses on diagnosing, repairing, and maintaining automotive transmission systems, including manual, automatic, and CVT types. Their core duties involve fluid replacement, clutch adjustments, and rebuilding or replacing transmission components to ensure smooth gear shifting and overall vehicle performance. Unlike brake specialists who concentrate on brake pads, rotors, and calipers, transmission specialists address complex drivetrain mechanisms critical for power transfer and vehicle mobility.
Required Skills and Training for Each Role
Brake specialists require in-depth knowledge of hydraulic and pneumatic systems, expertise in diagnosing issues with brake pads, rotors, and calipers, and proficiency in using diagnostic tools like brake fluid testers and pressure gauges. Transmission specialists must possess advanced understanding of manual and automatic transmission systems, including torque converters and clutch assemblies, along with skills in electronic control module diagnostics and precision assembly techniques. Both roles demand formal automotive training and certification, though transmission specialists typically undergo more extensive technical education due to the complexity of transmission repairs.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques Compared
Brake specialists utilize advanced tools such as brake fluid testers, electronic brake force gauges, and ultrasonic brake pad thickness sensors to identify issues like worn brake pads or fluid contamination. Transmission specialists rely on scan tools with transmission-specific software, pressure gauges, and clutch friction testers to diagnose problems including slipping gears or hydraulic faults. Both experts employ computerized diagnostic systems but tailor their techniques to the unique mechanical and electronic components of brakes or transmissions.
Common Challenges Faced in Both Specialties
Brake specialists and transmission specialists often encounter challenges related to diagnosing complex mechanical failures that require advanced diagnostic tools and expertise. Both face issues with worn or damaged components leading to inconsistent vehicle performance, demanding precise repair techniques to ensure safety and reliability. Effective communication with customers about repair necessity and cost is a shared challenge, critical for maintaining trust and satisfaction.
Salary Expectations and Career Growth
Brake specialists typically earn an average annual salary ranging from $40,000 to $60,000, with opportunities for growth as they gain certifications and experience in automotive brake systems. Transmission specialists command higher salaries, often between $50,000 and $75,000 annually, due to the complexity and technical expertise required in diagnosing and repairing transmission systems. Career advancement for transmission specialists frequently includes roles such as lead technician or service manager, supported by specialized training and industry demand for skilled transmission repair professionals.
Certifications and Licensing Requirements
Brake specialists typically hold certifications such as ASE Brake Specialist certification, ensuring expertise in brake system diagnostics and repairs. Transmission specialists often require more advanced certifications like ASE Automatic Transmission/Transaxle certification due to the complexity of transmission systems. Both fields demand adherence to state licensing requirements and continuous education to maintain up-to-date skills and compliance with safety standards.
Workplace Environment and Typical Employers
Brake specialists often work in auto repair shops, brake service centers, or dealerships, focusing on vehicle safety and stopping systems. Transmission specialists are typically employed by transmission repair shops, specialized automotive service centers, or large dealerships with advanced drivetrain service facilities. Both roles demand hands-on mechanical skills, but brake specialists usually operate in faster-paced environments with frequent customer interactions, while transmission specialists handle more complex repairs in specialized workshop settings.
Choosing the Right Career Path in Automotive Repair
Brake specialists concentrate on diagnosing and repairing braking systems, ensuring vehicle safety through expertise in hydraulic components, brake pads, rotors, and ABS technology. Transmission specialists focus on the complex mechanics of manual and automatic transmissions, mastering gear systems, clutches, and torque converters to maintain smooth vehicle operation. Choosing the right career path in automotive repair depends on an individual's interest in either vehicle safety systems or drivetrain functionality, along with the willingness to develop specialized diagnostic and repair skills.
Brake Specialist vs Transmission Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com