Refurbishers focus on restoring pets' equipment or accessories to like-new condition by cleaning, repairing minor damages, and replacing worn parts, ensuring safe and functional use. Rebuilders take a more comprehensive approach, often disassembling and reconstructing products from the ground up to extend lifespan or improve performance. Choosing between a refurbisher and a rebuilder depends on the extent of damage and the desired quality of repair for pet-related items.
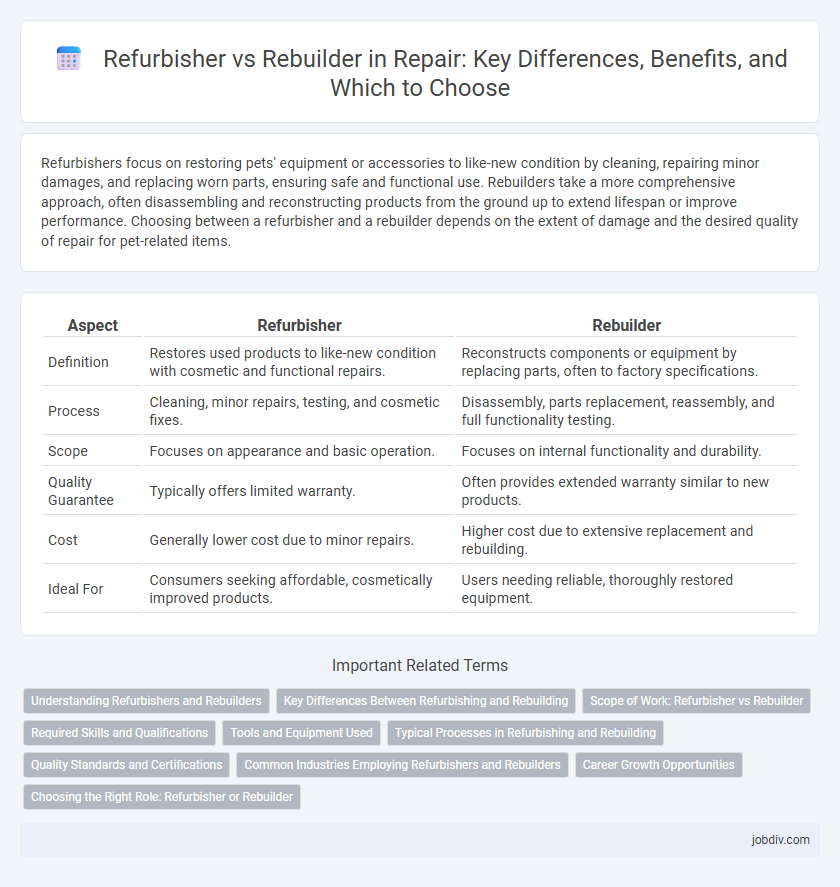
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Refurbisher | Rebuilder |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Restores used products to like-new condition with cosmetic and functional repairs. | Reconstructs components or equipment by replacing parts, often to factory specifications. |
| Process | Cleaning, minor repairs, testing, and cosmetic fixes. | Disassembly, parts replacement, reassembly, and full functionality testing. |
| Scope | Focuses on appearance and basic operation. | Focuses on internal functionality and durability. |
| Quality Guarantee | Typically offers limited warranty. | Often provides extended warranty similar to new products. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to minor repairs. | Higher cost due to extensive replacement and rebuilding. |
| Ideal For | Consumers seeking affordable, cosmetically improved products. | Users needing reliable, thoroughly restored equipment. |
Understanding Refurbishers and Rebuilders
Refurbishers primarily restore used products to a like-new condition by thoroughly inspecting, repairing, and replacing faulty parts to ensure functionality and appearance meet high standards. Rebuilders focus on reconstructing complex systems or equipment, often disassembling, repairing, and reassembling components to restore operational integrity and extend lifecycle performance. Both roles require expert technical skills and quality control processes but differ in scope and depth of restoration efforts.
Key Differences Between Refurbishing and Rebuilding
Refurbishing involves restoring a product to a like-new condition by cleaning, repairing minor faults, and replacing easily replaceable parts without altering the fundamental structure. Rebuilding entails a comprehensive process of disassembling, inspecting, replacing major components, and reassembling to restore full functionality, often used for complex machinery or vehicles. Key differences include the scope of work, with refurbishing focusing on cosmetic and minor functional fixes, while rebuilding addresses deep structural repairs and long-term reliability.
Scope of Work: Refurbisher vs Rebuilder
A refurbisher typically restores products to a like-new condition by repairing cosmetic damage and replacing minor components, ensuring functionality and appearance meet quality standards. In contrast, a rebuilder undertakes more extensive repairs, often disassembling and overhauling major parts or systems to restore structural integrity and full operational capacity. The scope of work for rebuilders demands higher technical expertise and involves comprehensive diagnostics, structural repairs, and component replacement beyond surface-level fixes.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Refurbishers require strong skills in cosmetic repairs, surface finishing, and quality control to restore products to near-new condition. Rebuilders need advanced technical knowledge in disassembly, diagnostics, mechanical repairs, and reassembly, often requiring certifications in specific machinery or electronics. Both roles demand attention to detail and problem-solving abilities, but rebuilders typically hold more specialized qualifications related to engineering or technical trades.
Tools and Equipment Used
Refurbishers primarily use diagnostic tools, cleaning equipment, and specialized software to restore products to like-new condition, emphasizing precision in cosmetic and functional repairs. Rebuilders rely more heavily on heavy machinery, welding tools, and mechanical equipment to disassemble, replace, and reconstruct major components for full operational restoration. Both use industry-standard calibration devices to ensure safety and quality standards are met after repair.
Typical Processes in Refurbishing and Rebuilding
Refurbishers typically focus on restoring products to like-new condition through cleaning, repairing minor defects, replacing worn parts, and thorough testing to ensure functionality. Rebuilders, however, undertake a more extensive process by disassembling the entire product, overhauling or replacing major components, and reassembling the system to meet original equipment specifications. Both processes emphasize quality control, but rebuilding often involves a deeper level of technical expertise and component-level restoration.
Quality Standards and Certifications
Refurbishers follow stringent quality standards like ISO 9001 to ensure devices meet manufacturer specifications and undergo thorough testing and cosmetic restoration. Rebuilders focus on structural integrity and function, often certified to standards such as SAE J2530 for rebuilt automotive components, guaranteeing safety and performance compliance. Both emphasize certifications but differ in scope: refurbishers prioritize full product quality renewal, while rebuilders concentrate on restoring core functionality to meet regulatory requirements.
Common Industries Employing Refurbishers and Rebuilders
Refurbishers and rebuilders are essential in industries such as automotive, electronics, and heavy machinery, where restoring used equipment to functional or near-new condition extends product lifespan and reduces costs. Automotive shops commonly employ rebuilders to restore engines and transmissions, while electronics companies rely on refurbishers to repair and upgrade consumer devices like smartphones and laptops. Heavy equipment manufacturers and construction firms utilize both roles to maintain and revitalize machinery, ensuring operational efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Career Growth Opportunities
Refurbishers primarily focus on restoring used products to a like-new condition, honing skills in quality control, cosmetic repairs, and component replacement, which builds expertise in product lifecycle management. Rebuilders engage in more complex repairs involving disassembly, diagnosis, and full system restoration, offering deeper technical knowledge and opportunities to specialize in advanced mechanical or electronic systems. Career growth in rebuilding typically leads to higher-level roles such as system engineers or technical supervisors, while refurbishing can provide a strong foundation for quality assurance or supply chain management positions.
Choosing the Right Role: Refurbisher or Rebuilder
Choosing between a refurbisher and a rebuilder depends on the extent of repair needed and the desired outcome quality. Refurbishers focus on restoring cosmetic appearance and basic functionality, making them ideal for minor repairs or improving aesthetic value. Rebuilders perform extensive structural or mechanical repairs, suited for severely damaged items requiring complete restoration to original or near-original condition.
Refurbisher vs Rebuilder Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com