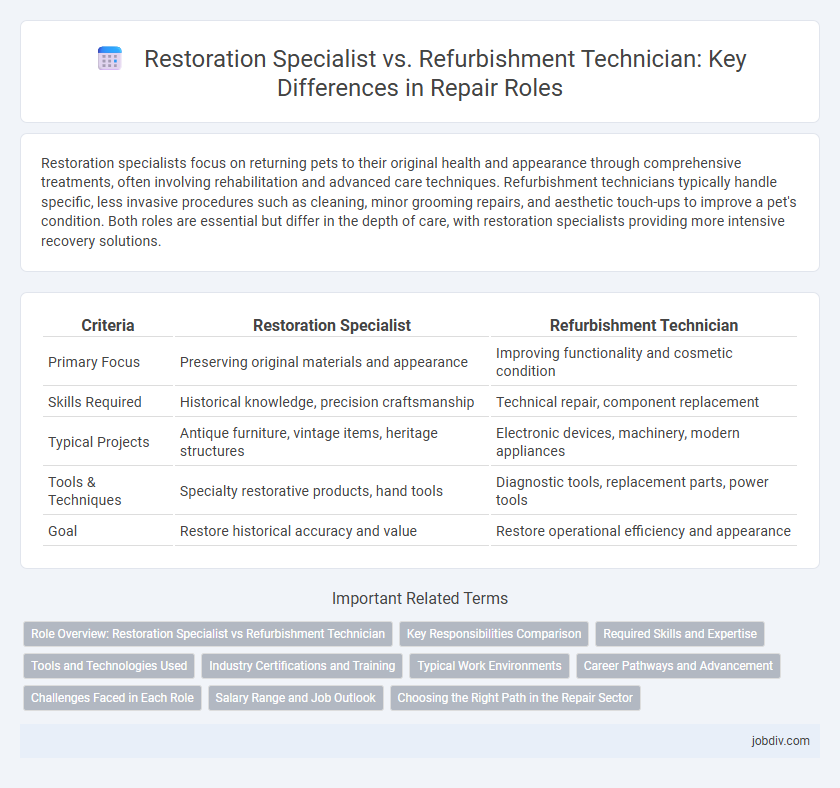
Restoration specialists focus on returning pets to their original health and appearance through comprehensive treatments, often involving rehabilitation and advanced care techniques. Refurbishment technicians typically handle specific, less invasive procedures such as cleaning, minor grooming repairs, and aesthetic touch-ups to improve a pet's condition. Both roles are essential but differ in the depth of care, with restoration specialists providing more intensive recovery solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Restoration Specialist | Refurbishment Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Preserving original materials and appearance | Improving functionality and cosmetic condition |
| Skills Required | Historical knowledge, precision craftsmanship | Technical repair, component replacement |
| Typical Projects | Antique furniture, vintage items, heritage structures | Electronic devices, machinery, modern appliances |
| Tools & Techniques | Specialty restorative products, hand tools | Diagnostic tools, replacement parts, power tools |
| Goal | Restore historical accuracy and value | Restore operational efficiency and appearance |
Role Overview: Restoration Specialist vs Refurbishment Technician
Restoration Specialists focus on returning damaged or aged items to their original condition using specialized techniques and materials, often dealing with historical or valuable objects. Refurbishment Technicians handle the process of inspecting, repairing, and upgrading products to improve functionality and appearance, typically in a commercial or industrial context. Both roles require precise repair skills, but Restoration Specialists emphasize preservation, while Refurbishment Technicians prioritize modernization and efficiency.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
Restoration Specialists focus on recovering damaged property to its original condition by assessing structural integrity, removing contaminants, and applying specialized cleaning techniques. Refurbishment Technicians primarily handle upgrading and renewing equipment or surfaces, including sanding, painting, and replacing hardware to enhance appearance and functionality. Both roles require strong knowledge of materials and tools, but Restoration Specialists emphasize damage mitigation, while Refurbishment Technicians prioritize aesthetic and operational improvements.
Required Skills and Expertise
Restoration specialists require advanced knowledge of historical materials and techniques to preserve the original integrity of objects, often focusing on delicate and culturally significant items. Refurbishment technicians need strong mechanical and technical skills to repair, upgrade, and modernize equipment or products efficiently, emphasizing functionality over originality. Both roles demand attention to detail and precision, but restoration specialists prioritize authenticity while refurbishment technicians emphasize practical enhancement.
Tools and Technologies Used
Restoration specialists utilize advanced techniques such as moisture meters, thermal imaging cameras, and industrial dehumidifiers to detect and eliminate damage caused by water, fire, or mold. Refurbishment technicians often rely on tools like sanders, grinders, and automated spray systems to restore and upgrade surfaces, focusing on cosmetic and functional improvements. Both roles require proficiency with specialized software for estimating costs and managing projects, but restoration emphasizes environmental hazard detection while refurbishment centers on surface refinement technologies.
Industry Certifications and Training
Restoration specialists typically hold industry certifications such as IICRC (Institute of Inspection Cleaning and Restoration Certification) which emphasize water damage, fire, and mold remediation expertise, ensuring thorough and compliant restoration processes. Refurbishment technicians often acquire certifications related to specific equipment or machinery, focusing on skills like mechanical repairs, electrical rewiring, and component replacement to extend product lifespan. Both roles require ongoing training, but restoration specialists prioritize environmental safety and damage assessment, while refurbishment technicians center on technical proficiency and system optimization.
Typical Work Environments
Restoration specialists typically work in environments affected by damage such as fire, water, or mold, including residential homes, commercial buildings, and disaster sites, where they assess and mitigate damage to return structures to pre-loss conditions. Refurbishment technicians usually operate in controlled workshop settings or manufacturing facilities, focusing on repairing, upgrading, and reconditioning equipment, machinery, or consumer goods to extend their lifespan and restore functionality. Both roles demand specialized tools and protective gear tailored to their specific work environments, ensuring safety and efficiency during repair processes.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Restoration specialists focus on recovering and preserving damaged structures or items, often requiring expertise in historical materials and advanced cleaning techniques, leading to career advancement opportunities in heritage conservation and project management. Refurbishment technicians specialize in repairing and upgrading equipment or facilities to improve functionality and appearance, with pathways often progressing toward supervisory roles in maintenance or quality control departments. Both careers offer specialized skill development, but restoration specialists typically advance into roles involving detailed assessments and preservation strategies, while refurbishment technicians move toward operational management and technical oversight.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Restoration specialists often encounter challenges involving extensive damage assessment and the need for precise techniques to preserve original materials, especially in historical or valuable items. Refurbishment technicians primarily face obstacles related to updating or upgrading equipment efficiently while ensuring functionality and aesthetics meet current standards. Both roles demand keen attention to detail but differ in the complexity of material conservation versus modernization processes.
Salary Range and Job Outlook
Restoration Specialists typically earn between $40,000 and $65,000 annually, with job growth projected at 5% over the next decade due to increasing demand in disaster recovery and historical preservation. Refurbishment Technicians usually have a salary range of $35,000 to $55,000, driven by steady demand in manufacturing and electronic equipment maintenance sectors. Both roles offer solid employment opportunities, but Restoration Specialists may experience higher salary potential and faster job outlook growth linked to environmental and property restoration projects.
Choosing the Right Path in the Repair Sector
Restoration specialists focus on preserving and returning items to their original condition, often working with antiques, art, and historical artifacts to maintain authenticity and value. Refurbishment technicians primarily concentrate on updating and improving functionality, repairing wear and tear to extend an item's usability in modern settings. Selecting the right path depends on one's interest in meticulous preservation versus practical enhancements in the repair sector.
Restoration Specialist vs Refurbishment Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com