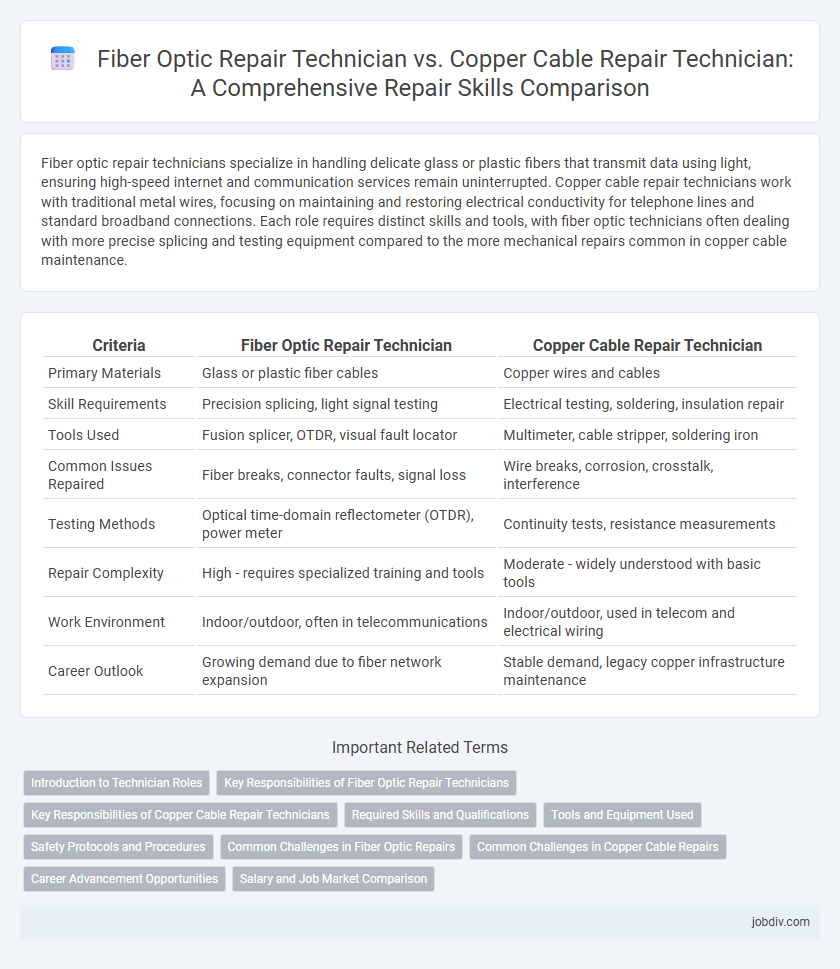
Fiber optic repair technicians specialize in handling delicate glass or plastic fibers that transmit data using light, ensuring high-speed internet and communication services remain uninterrupted. Copper cable repair technicians work with traditional metal wires, focusing on maintaining and restoring electrical conductivity for telephone lines and standard broadband connections. Each role requires distinct skills and tools, with fiber optic technicians often dealing with more precise splicing and testing equipment compared to the more mechanical repairs common in copper cable maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Fiber Optic Repair Technician | Copper Cable Repair Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Materials | Glass or plastic fiber cables | Copper wires and cables |
| Skill Requirements | Precision splicing, light signal testing | Electrical testing, soldering, insulation repair |
| Tools Used | Fusion splicer, OTDR, visual fault locator | Multimeter, cable stripper, soldering iron |
| Common Issues Repaired | Fiber breaks, connector faults, signal loss | Wire breaks, corrosion, crosstalk, interference |
| Testing Methods | Optical time-domain reflectometer (OTDR), power meter | Continuity tests, resistance measurements |
| Repair Complexity | High - requires specialized training and tools | Moderate - widely understood with basic tools |
| Work Environment | Indoor/outdoor, often in telecommunications | Indoor/outdoor, used in telecom and electrical wiring |
| Career Outlook | Growing demand due to fiber network expansion | Stable demand, legacy copper infrastructure maintenance |
Introduction to Technician Roles
Fiber Optic Repair Technicians specialize in diagnosing and fixing issues in fiber optic networks, using advanced tools to handle delicate glass fibers that transmit data at high speeds. Copper Cable Repair Technicians focus on maintaining and repairing traditional copper wiring systems, addressing signal interference and physical damage that affects voice and data communication. Both roles require specific technical knowledge and hands-on skills tailored to their respective transmission mediums, ensuring reliable network performance.
Key Responsibilities of Fiber Optic Repair Technicians
Fiber optic repair technicians specialize in installing, splicing, and troubleshooting fiber optic cables to ensure high-speed data transmission and minimal signal loss. Their key responsibilities include identifying cable faults using optical time-domain reflectometers (OTDR), performing precise cable splicing to restore connectivity, and maintaining network integrity by testing and certifying fiber optic links. Proficiency in handling delicate glass fibers and adhering to strict safety and industry standards distinguishes their role from copper cable repair technicians.
Key Responsibilities of Copper Cable Repair Technicians
Copper Cable Repair Technicians specialize in diagnosing and repairing faults in copper wiring systems used in telecommunications and networking infrastructure. Their key responsibilities include splicing, testing, and maintaining copper cables to ensure signal integrity, as well as troubleshooting issues such as line noise, interference, and physical damage. They perform routine inspections and collaborate with network engineers to maintain optimal system performance and reduce downtime caused by cable failures.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Fiber Optic Repair Technicians require expertise in splicing, testing with OTDR equipment, and knowledge of light signal transmission, while Copper Cable Repair Technicians specialize in pair bonding, continuity testing, and understanding of electrical signal interference. Both roles demand proficiency in troubleshooting, adherence to safety standards, and familiarity with cable installation tools, but fiber optic technicians often need certification in fiber handling and fusion splicing. Copper cable technicians generally require skills in crimping, soldering, and analog signal diagnostics to ensure optimal performance.
Tools and Equipment Used
Fiber optic repair technicians rely on precision tools such as fusion splicers, optical power meters, and fiber strippers to handle delicate glass fibers and ensure high-quality signal transmission. Copper cable repair technicians commonly use wire strippers, crimping tools, and multimeters designed to test electrical continuity and diagnose faults in copper wiring systems. Both roles require specialized equipment tailored to the physical properties and signal types of their respective cabling materials to maintain network integrity.
Safety Protocols and Procedures
Fiber optic repair technicians adhere to strict safety protocols involving laser safety, use of personal protective equipment (PPE) like safety goggles, and proper handling of fiber shards to prevent eye and skin injuries. Copper cable repair technicians follow procedures that emphasize electrical safety, including de-energizing circuits, using insulated tools, and grounding to avoid electric shock and arc flash hazards. Both roles require compliance with industry standards such as OSHA regulations and regular safety training to minimize workplace risks.
Common Challenges in Fiber Optic Repairs
Fiber optic repair technicians frequently face challenges such as precise splicing requirements, sensitivity to microbends and macrobends, and the need for specialized equipment like fusion splicers and optical time-domain reflectometers (OTDR). Unlike copper cable repairs, fiber optic repairs demand strict cleanliness protocols to prevent signal loss caused by contamination or connector damage. Environmental factors, such as temperature fluctuations and physical stress on delicate fibers, further complicate fiber optic restoration efforts compared to the more robust copper cable repairs.
Common Challenges in Copper Cable Repairs
Copper cable repair technicians often face challenges such as signal degradation caused by corrosion, physical damage to the cables, and interference from electromagnetic sources. Diagnosing faults requires specialized tools to detect issues like shorts, opens, and impedance mismatches within the cable infrastructure. Maintaining network reliability involves frequent testing and careful handling to prevent further deterioration of copper cable connections.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Fiber optic repair technicians benefit from rapid career advancement due to increasing demand for high-speed internet infrastructure and specialized skills in advanced technologies like DWDM and GPON. Copper cable repair technicians face slower growth prospects as legacy systems are gradually phased out, though they maintain relevance in certain rural and older urban networks. Mastery of fiber optic installation, splicing, and network troubleshooting offers stronger long-term career stability and access to higher-paying roles.
Salary and Job Market Comparison
Fiber optic repair technicians typically earn higher salaries than copper cable repair technicians due to the specialized skills required in handling advanced optical technology and growing demand in telecommunications infrastructure. The job market for fiber optic technicians is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing adoption of high-speed internet and 5G networks, whereas copper cable repair roles are gradually declining as legacy infrastructure is phased out. Salary ranges for fiber optic technicians often fall between $50,000 and $80,000 annually, while copper cable technicians generally earn between $40,000 and $60,000, reflecting differences in market demand and technical complexity.
Fiber Optic Repair Technician vs Copper Cable Repair Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com