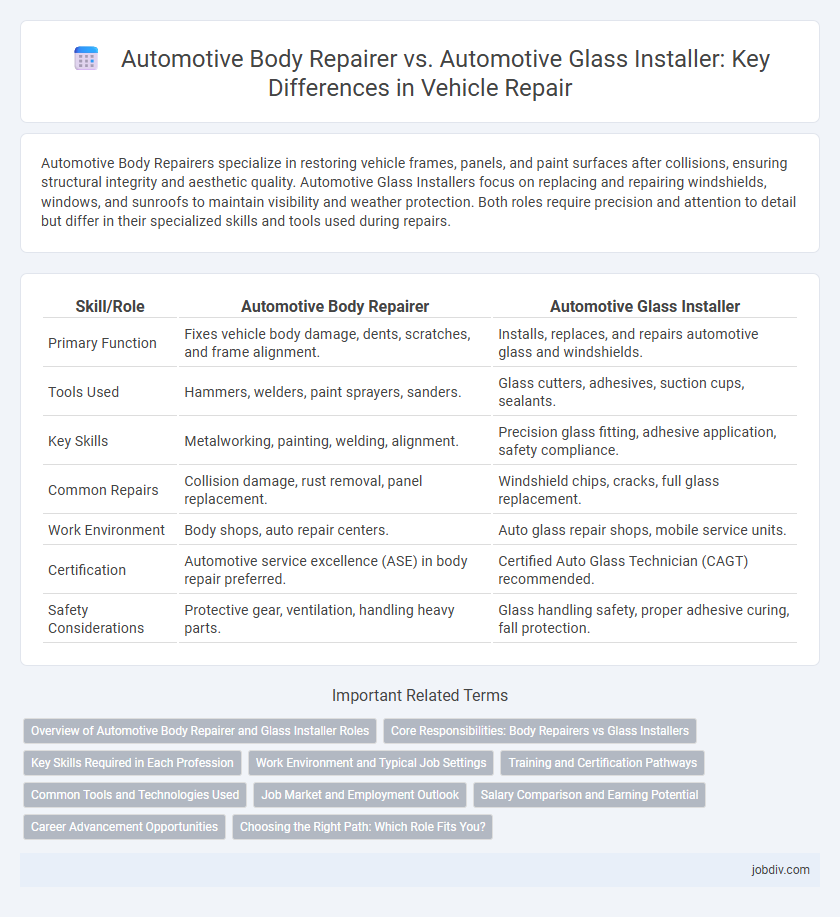
Automotive Body Repairers specialize in restoring vehicle frames, panels, and paint surfaces after collisions, ensuring structural integrity and aesthetic quality. Automotive Glass Installers focus on replacing and repairing windshields, windows, and sunroofs to maintain visibility and weather protection. Both roles require precision and attention to detail but differ in their specialized skills and tools used during repairs.
Table of Comparison
| Skill/Role | Automotive Body Repairer | Automotive Glass Installer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Fixes vehicle body damage, dents, scratches, and frame alignment. | Installs, replaces, and repairs automotive glass and windshields. |
| Tools Used | Hammers, welders, paint sprayers, sanders. | Glass cutters, adhesives, suction cups, sealants. |
| Key Skills | Metalworking, painting, welding, alignment. | Precision glass fitting, adhesive application, safety compliance. |
| Common Repairs | Collision damage, rust removal, panel replacement. | Windshield chips, cracks, full glass replacement. |
| Work Environment | Body shops, auto repair centers. | Auto glass repair shops, mobile service units. |
| Certification | Automotive service excellence (ASE) in body repair preferred. | Certified Auto Glass Technician (CAGT) recommended. |
| Safety Considerations | Protective gear, ventilation, handling heavy parts. | Glass handling safety, proper adhesive curing, fall protection. |
Overview of Automotive Body Repairer and Glass Installer Roles
Automotive body repairers specialize in restoring vehicle exteriors by fixing dents, scratches, and structural damage using techniques such as welding, sanding, and painting. Automotive glass installers focus on removing and replacing windshields, windows, and other automotive glass components, ensuring proper fit and seal to maintain safety and prevent leaks. Both roles require detailed knowledge of vehicle construction and adherence to industry safety standards but differ in their area of expertise and required technical skills.
Core Responsibilities: Body Repairers vs Glass Installers
Automotive body repairers specialize in restoring vehicle frames, panels, and structural components to their original condition using welding, sanding, and painting techniques. In contrast, automotive glass installers focus on the precise removal and installation of windshields, side windows, and rear windows, ensuring proper sealing and fit to maintain vehicle safety and integrity. Both roles require strong attention to detail, but body repairers handle metalwork and cosmetic restoration while glass installers emphasize glass replacement and adhesive application.
Key Skills Required in Each Profession
Automotive body repairers require expertise in metalworking, welding, paint application, and dent removal to restore vehicle exteriors to factory specifications. Automotive glass installers specialize in precise measurement, glass cutting, sealing, and adherence to safety standards to ensure proper windshield and window installation. Both professions demand keen attention to detail and knowledge of vehicle anatomy, but body repairers emphasize structural restoration while glass installers focus on glass integrity and sealant application.
Work Environment and Typical Job Settings
Automotive body repairers primarily work in auto body shops or collision repair centers, often in environments with heavy machinery, paints, and physical labor involved in reshaping and repairing vehicle frames. Automotive glass installers typically operate in indoor garages, dealerships, or mobile units, focusing on precise installation and replacement of windshields and windows in controlled, clean settings to prevent damage. Both roles require adherence to safety protocols, but automotive body repairers encounter higher exposure to dust, solvents, and noise due to sanding and welding processes.
Training and Certification Pathways
Automotive body repairers require extensive training in metalwork, painting, and structural repair, often completing apprenticeships and obtaining certifications like I-CAR or ASE Collision Repair Specialist. Automotive glass installers focus on specialized training in windshield and window replacement, with certifications from organizations such as the National Glass Association (NGA) or the Auto Glass Safety Council (AGSC). Both pathways emphasize hands-on experience and ongoing education to maintain industry standards and ensure safety compliance.
Common Tools and Technologies Used
Automotive body repairers primarily use tools such as dent pullers, welding machines, spray guns, and frame straightening equipment to restore vehicle exteriors, while automotive glass installers rely on specialized adhesives, suction cups, and precision cutting tools to fit and replace windshields and windows. Both professions utilize diagnostic software and safety gear to ensure quality repairs and compliance with industry standards. Advanced technologies like laser measuring systems and UV curing lamps are becoming common in both fields to enhance accuracy and durability of repairs.
Job Market and Employment Outlook
Automotive body repairers face steady demand driven by vehicle collision rates and the need for restoring structural integrity, with a projected employment growth of 4% over the next decade according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Automotive glass installers experience increasing job opportunities due to rising vehicle safety standards and advancements in windshield technology, with a faster-than-average growth rate of 8%. Both professions require specialized skills, but automotive glass installers may benefit from greater employment expansion in regions emphasizing advanced automotive safety features.
Salary Comparison and Earning Potential
Automotive Body Repairers earn a median salary around $45,000 per year, with experienced technicians in specialized shops reaching up to $60,000 annually. Automotive Glass Installers typically earn slightly less, averaging about $40,000 per year, though those working in high-demand urban areas or for large dealerships can exceed $50,000. The earning potential for body repairers often grows with advanced skills in frame straightening and paint matching, while glass installers benefit from certifications in safety regulations and complex windshield technologies.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Automotive body repairers can advance their careers by specializing in collision repair techniques, mastering paint technologies, or moving into supervisory and estimator roles, which often lead to higher salaries and greater job security. Automotive glass installers have opportunities to progress by gaining certifications in advanced glass technologies, such as ADAS calibration, or by opening their own installation businesses, which can increase earning potential. Both careers benefit from continuous training and industry certifications to stay competitive and enhance career advancement prospects.
Choosing the Right Path: Which Role Fits You?
Automotive Body Repairers specialize in restoring vehicle frames and panels after collisions, using techniques like welding and sanding to ensure structural integrity and aesthetic quality. Automotive Glass Installers focus on fitting, replacing, and sealing windshields and windows, requiring precise measurement skills and knowledge of adhesives to maintain safety standards. Choosing between these roles depends on whether you prefer hands-on metalwork and structural repair or detailed glass installation and finishing within the automotive repair industry.
Automotive Body Repairer vs Automotive Glass Installer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com