Break/Fix Repair addresses issues only after equipment or systems fail, often leading to unexpected downtime and higher costs. Preventive Repair involves regular maintenance and inspections designed to identify and resolve problems before they cause failure, enhancing reliability and extending the lifespan of assets. Choosing Preventive Repair reduces emergency repairs and improves overall operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
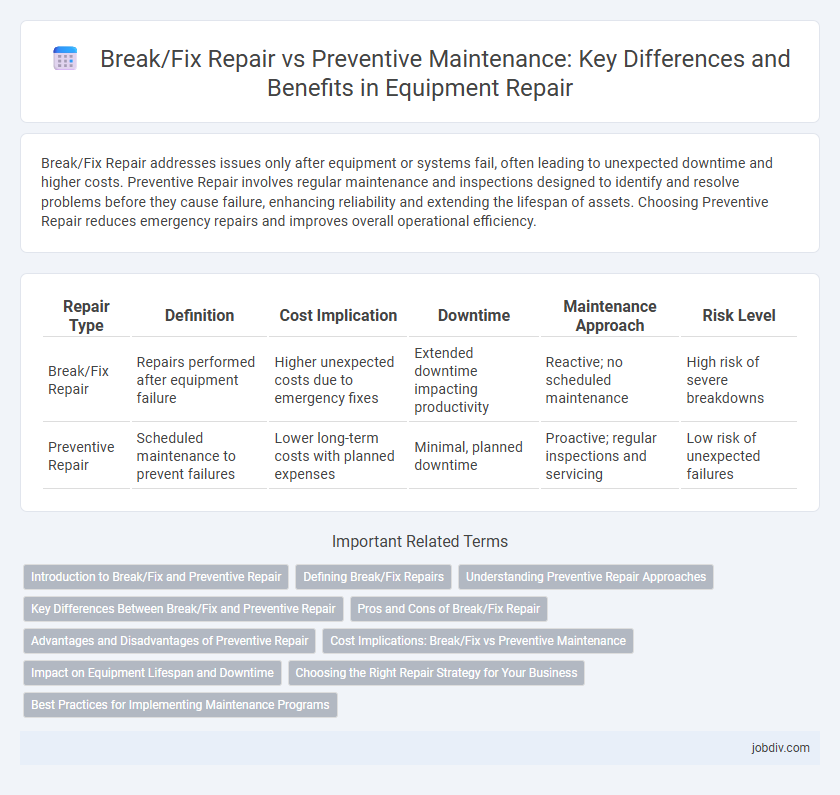
| Repair Type | Definition | Cost Implication | Downtime | Maintenance Approach | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Break/Fix Repair | Repairs performed after equipment failure | Higher unexpected costs due to emergency fixes | Extended downtime impacting productivity | Reactive; no scheduled maintenance | High risk of severe breakdowns |
| Preventive Repair | Scheduled maintenance to prevent failures | Lower long-term costs with planned expenses | Minimal, planned downtime | Proactive; regular inspections and servicing | Low risk of unexpected failures |
Introduction to Break/Fix and Preventive Repair
Break/Fix repair involves addressing equipment or system failures after they occur, focusing on fixing issues to restore functionality. Preventive repair emphasizes routine maintenance and inspections designed to identify and resolve potential problems before they lead to failures. This proactive approach reduces downtime and extends the lifespan of assets by minimizing unexpected breakdowns.
Defining Break/Fix Repairs
Break/fix repairs focus on addressing equipment or system failures only after they occur, restoring functionality by diagnosing and fixing the specific fault. This reactive repair strategy contrasts with preventive repair, which emphasizes routine maintenance to avoid breakdowns. Break/fix repairs typically incur higher downtime and unpredictable costs due to the urgent nature of fixing unexpected issues.
Understanding Preventive Repair Approaches
Preventive repair approaches focus on regular maintenance and inspections to identify potential issues before they cause equipment failure. This strategy reduces downtime and extends the lifespan of machinery by addressing wear and tear early. Emphasizing scheduled tasks and predictive analytics enhances the effectiveness of preventive repair programs.
Key Differences Between Break/Fix and Preventive Repair
Break/fix repair involves fixing equipment or systems only after a failure has occurred, leading to unplanned downtime and potentially higher emergency costs. Preventive repair focuses on regular maintenance and inspections to identify and resolve issues before they cause breakdowns, enhancing reliability and reducing unexpected interruptions. The key difference lies in the approach: break/fix is reactive, addressing problems post-failure, while preventive repair is proactive, aiming to maintain optimal performance and extend asset lifespan.
Pros and Cons of Break/Fix Repair
Break/fix repair offers immediate solutions by fixing equipment only after failure, reducing upfront maintenance costs and downtime during normal operation. However, this reactive approach can lead to unexpected breakdowns, higher emergency repair expenses, and potential extended system outages. While suitable for non-critical systems, break/fix repair risks increased total cost of ownership and decreased reliability compared to preventive maintenance strategies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Preventive Repair
Preventive repair helps extend equipment lifespan and reduce unexpected breakdowns by addressing potential issues before they escalate. It requires scheduled downtime and can involve higher upfront labor and parts costs compared to break/fix repair. However, preventive repair minimizes overall operational disruptions and costly emergency repairs, enhancing long-term reliability and safety.
Cost Implications: Break/Fix vs Preventive Maintenance
Break/Fix repair often incurs higher costs due to unexpected equipment failures, emergency service fees, and potential production downtime. Preventive maintenance reduces overall expenses by promoting regular inspections and timely repairs, which minimize the risk of costly breakdowns and extend asset lifespan. Investing in preventive repair strategies leads to more predictable budgeting and lower long-term operational costs.
Impact on Equipment Lifespan and Downtime
Break/fix repair addresses equipment failures only after they occur, often leading to increased downtime and potentially shortening equipment lifespan due to prolonged exposure to damage. Preventive repair involves regular maintenance and early detection, which significantly reduces unexpected breakdowns, extends equipment lifespan, and minimizes costly downtime. Implementing a preventive repair strategy improves operational efficiency by ensuring equipment remains in optimal condition and reduces the frequency of major repairs.
Choosing the Right Repair Strategy for Your Business
Choosing the right repair strategy for your business depends on factors like equipment criticality, budget, and downtime tolerance. Break/fix repair offers cost savings by addressing issues only when they occur, but risks unexpected failures and extended downtime. Preventive repair, involving regular maintenance schedules, reduces the likelihood of breakdowns and extends asset lifespan, making it ideal for businesses prioritizing reliability and long-term cost-efficiency.
Best Practices for Implementing Maintenance Programs
Implementing effective maintenance programs requires balancing break/fix repair strategies with preventive repair to optimize equipment lifespan and reduce downtime. Best practices include conducting regular inspections, using data-driven predictive analytics to schedule timely interventions, and training maintenance personnel to identify early signs of wear. Prioritizing a preventive repair approach lowers unexpected failures and maintenance costs while ensuring operational efficiency.
Break/Fix Repair vs Preventive Repair Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com