HVAC technicians specialize in installing, maintaining, and repairing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to ensure indoor comfort. Refrigeration mechanics focus on the repair and maintenance of refrigeration units, which are essential for preserving perishable goods in both commercial and industrial settings. Both professionals require a strong understanding of thermodynamics and electrical systems to effectively troubleshoot and fix cooling-related equipment.
Table of Comparison
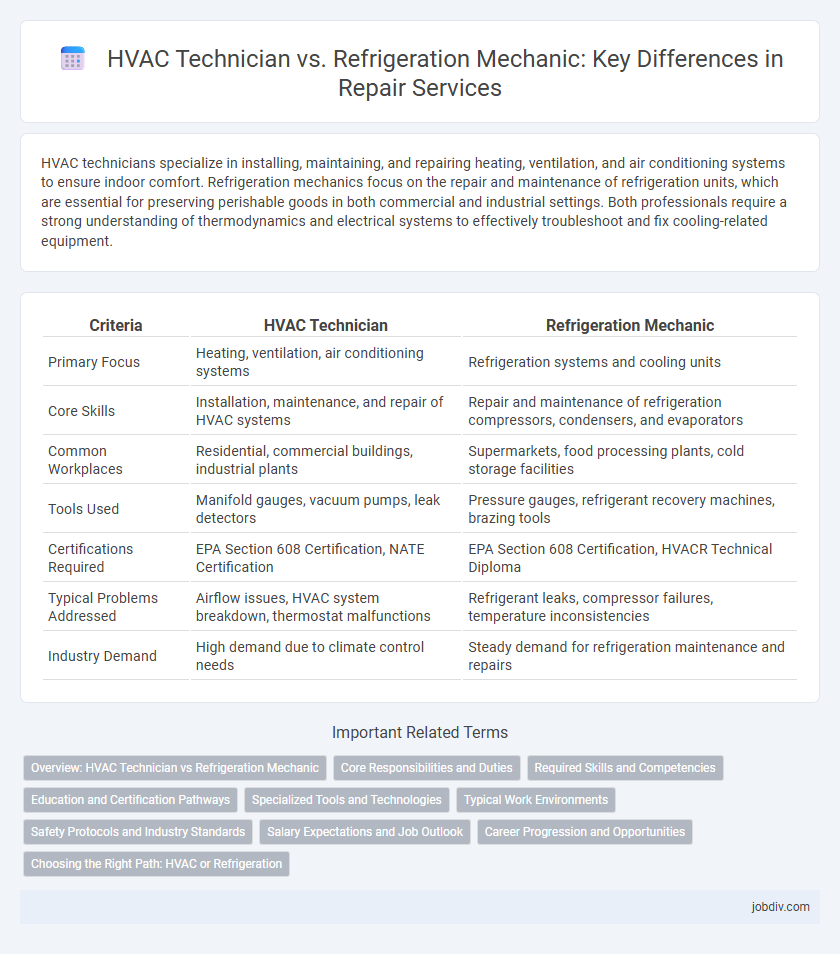
| Criteria | HVAC Technician | Refrigeration Mechanic |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Heating, ventilation, air conditioning systems | Refrigeration systems and cooling units |
| Core Skills | Installation, maintenance, and repair of HVAC systems | Repair and maintenance of refrigeration compressors, condensers, and evaporators |
| Common Workplaces | Residential, commercial buildings, industrial plants | Supermarkets, food processing plants, cold storage facilities |
| Tools Used | Manifold gauges, vacuum pumps, leak detectors | Pressure gauges, refrigerant recovery machines, brazing tools |
| Certifications Required | EPA Section 608 Certification, NATE Certification | EPA Section 608 Certification, HVACR Technical Diploma |
| Typical Problems Addressed | Airflow issues, HVAC system breakdown, thermostat malfunctions | Refrigerant leaks, compressor failures, temperature inconsistencies |
| Industry Demand | High demand due to climate control needs | Steady demand for refrigeration maintenance and repairs |
Overview: HVAC Technician vs Refrigeration Mechanic
HVAC technicians specialize in installing, repairing, and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, ensuring optimal indoor air quality and climate control. Refrigeration mechanics focus specifically on cooling systems, such as commercial refrigerators and freezers, repairing compressors, condensers, and evaporators. Both professions require knowledge of electrical systems and refrigerants but differ in their scope, with HVAC technicians covering broader climate control systems and refrigeration mechanics specializing in low-temperature applications.
Core Responsibilities and Duties
HVAC technicians specialize in installing, maintaining, and repairing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, ensuring optimal indoor climate control and energy efficiency. Refrigeration mechanics focus on the servicing and repair of cooling systems used in commercial and industrial refrigeration units, including cold storage and transportation refrigeration. Both roles require strong troubleshooting skills, but HVAC technicians handle a broader range of climate control systems, while refrigeration mechanics concentrate on refrigeration-specific components and refrigerants.
Required Skills and Competencies
HVAC Technicians require proficiency in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, electrical wiring, and diagnostic tools to ensure optimal climate control and energy efficiency. Refrigeration Mechanics specialize in repairing and maintaining refrigeration equipment, demanding strong knowledge of refrigerants, pressure systems, and mechanical components. Both roles necessitate problem-solving skills, adherence to safety standards, and familiarity with industry regulations such as EPA certification for handling refrigerants.
Education and Certification Pathways
HVAC technicians typically complete postsecondary training programs in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, earning certifications such as EPA Section 608 to handle refrigerants safely. Refrigeration mechanics often pursue apprenticeship programs or technical diplomas specializing in commercial and industrial refrigeration systems, obtaining certifications like the Certified Refrigeration Technician credential. Both careers require ongoing education to stay current with evolving technologies and regulatory standards in building systems repair.
Specialized Tools and Technologies
HVAC technicians utilize advanced diagnostic tools like multimeters, refrigerant analyzers, and thermal imaging cameras to service heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems efficiently. Refrigeration mechanics specialize in tools such as vacuum pumps, recovery machines, and manifold gauges specifically designed for maintaining and repairing refrigeration units. Both professionals rely on cutting-edge technologies like microprocessor-based controls and eco-friendly refrigerants to ensure precise and environmentally compliant repairs.
Typical Work Environments
HVAC technicians commonly operate in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, maintaining and repairing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to ensure optimal indoor air quality and comfort. Refrigeration mechanics primarily work in commercial kitchens, supermarkets, and food processing plants, specializing in the installation, maintenance, and repair of refrigeration systems critical for food preservation. Both roles demand proficiency with diagnostic tools and compliance with safety regulations, though HVAC technicians often face broader environmental conditions compared to the specialized, temperature-sensitive environments of refrigeration mechanics.
Safety Protocols and Industry Standards
HVAC technicians and refrigeration mechanics adhere to strict safety protocols and industry standards, including OSHA regulations and EPA guidelines for handling refrigerants. HVAC technicians focus on maintaining ventilation systems, requiring knowledge of electrical safety and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), while refrigeration mechanics emphasize safe leak detection and refrigerant recovery to prevent environmental hazards. Both roles require certification on refrigerant handling, such as EPA Section 608, ensuring compliance with federal laws and minimizing workplace risks.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
HVAC technicians earn an average salary ranging from $45,000 to $65,000 annually, with strong demand driven by residential and commercial climate control needs. Refrigeration mechanics typically command salaries between $40,000 and $60,000, benefiting from steady job growth linked to industrial and food preservation sectors. Both careers offer positive job outlooks, but HVAC technicians often experience broader employment opportunities due to diverse system installations and maintenance services.
Career Progression and Opportunities
HVAC technicians often start with fundamental heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems and can advance to specialized roles like system design or project management, benefiting from a broad skill set applicable across residential and commercial sectors. Refrigeration mechanics typically focus on industrial and commercial refrigeration systems, with career progression leading to senior technician roles or supervisory positions in large-scale facilities such as food processing plants or supermarkets. Both careers offer opportunities for certification and specialization, but HVAC technicians generally have a wider range of employment options and versatility across multiple industries.
Choosing the Right Path: HVAC or Refrigeration
HVAC technicians specialize in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, focusing on climate control and air quality in residential and commercial settings, while refrigeration mechanics primarily work on cooling systems crucial for food storage and industrial applications. Choosing the right path depends on career goals, with HVAC offering broader opportunities in building comfort and refrigeration providing niche expertise in temperature-sensitive environments. Both professions require technical skills, but refrigeration mechanics often deal with complex compressor and coolant technologies, whereas HVAC technicians must understand diverse systems including heating and ventilation controls.
HVAC Technician vs Refrigeration Mechanic Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com