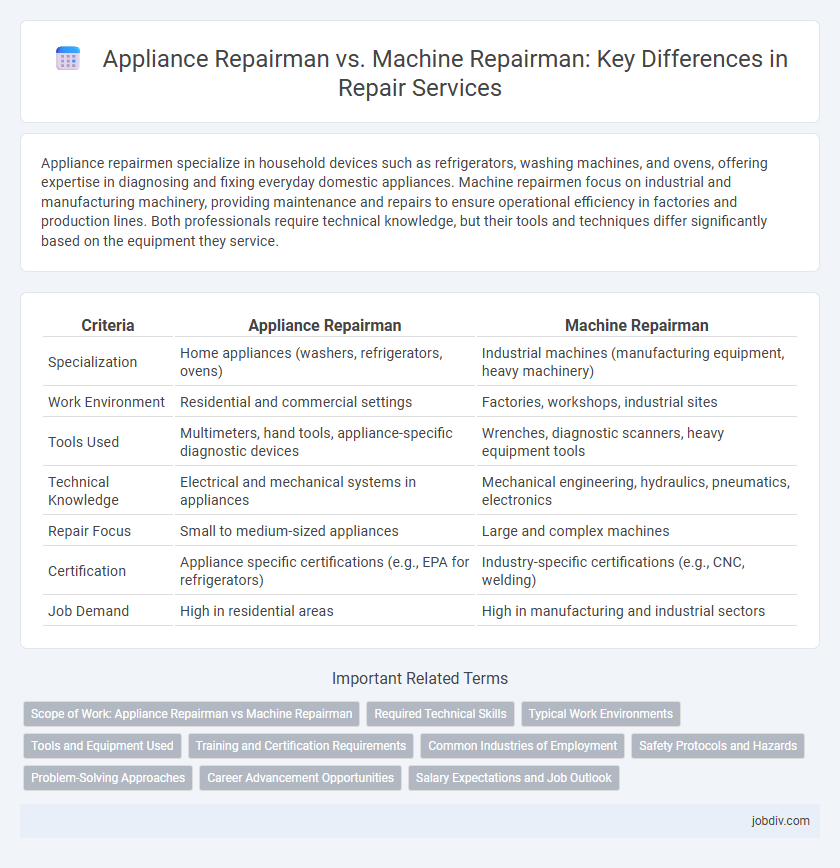
Appliance repairmen specialize in household devices such as refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens, offering expertise in diagnosing and fixing everyday domestic appliances. Machine repairmen focus on industrial and manufacturing machinery, providing maintenance and repairs to ensure operational efficiency in factories and production lines. Both professionals require technical knowledge, but their tools and techniques differ significantly based on the equipment they service.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Appliance Repairman | Machine Repairman |
|---|---|---|
| Specialization | Home appliances (washers, refrigerators, ovens) | Industrial machines (manufacturing equipment, heavy machinery) |
| Work Environment | Residential and commercial settings | Factories, workshops, industrial sites |
| Tools Used | Multimeters, hand tools, appliance-specific diagnostic devices | Wrenches, diagnostic scanners, heavy equipment tools |
| Technical Knowledge | Electrical and mechanical systems in appliances | Mechanical engineering, hydraulics, pneumatics, electronics |
| Repair Focus | Small to medium-sized appliances | Large and complex machines |
| Certification | Appliance specific certifications (e.g., EPA for refrigerators) | Industry-specific certifications (e.g., CNC, welding) |
| Job Demand | High in residential areas | High in manufacturing and industrial sectors |
Scope of Work: Appliance Repairman vs Machine Repairman
An appliance repairman specializes in fixing household devices such as refrigerators, washing machines, ovens, and dishwashers, focusing on residential and consumer appliances. In contrast, a machine repairman handles industrial machinery, including manufacturing equipment, conveyor systems, and heavy-duty mechanical systems used in factories. The scope of work for appliance repairmen is generally limited to consumer appliances, while machine repairmen deal with complex, large-scale machinery requiring specialized mechanical and technical skills.
Required Technical Skills
Appliance repairmen require in-depth knowledge of household systems, including refrigeration, heating, and electrical components, to diagnose and fix diverse domestic devices such as refrigerators, washers, and ovens. Machine repairmen focus on industrial machinery, necessitating expertise in mechanical systems, hydraulics, pneumatics, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for maintaining and repairing factory equipment. Both professions demand strong troubleshooting abilities, proficiency in using diagnostic tools, and understanding of safety protocols, but appliance repairmen emphasize consumer electronics while machine repairmen specialize in industrial technology.
Typical Work Environments
Appliance repairmen typically work in residential kitchens, laundry rooms, and commercial settings where household appliances such as refrigerators, washers, and ovens are used. Machine repairmen often operate in industrial environments, including factories, manufacturing plants, and workshops, maintaining and repairing heavy machinery and equipment. Both professionals require specialized tools but differ significantly in workplace safety protocols due to the varying operational hazards specific to their environments.
Tools and Equipment Used
An appliance repairman typically uses specialized tools such as voltage testers, multimeters, and nut drivers tailored for household appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens. Machine repairmen rely more on industrial-grade instruments including torque wrenches, hydraulic jacks, and diagnostic software designed for heavy machinery and manufacturing equipment. Both professions require a strong understanding of mechanical systems, but the specificity of tools emphasizes the difference between domestic appliance repair and industrial machine maintenance.
Training and Certification Requirements
Appliance repairmen typically require certifications such as EPA 608 for handling refrigerants and may complete vocational training focused on household appliances like refrigerators, washers, and ovens. Machine repairmen often need more specialized training in mechanical and electrical systems, with certifications from organizations like the National Institute for Metalworking Skills (NIMS) or specific equipment manufacturers. Both roles demand ongoing education to keep up with evolving technologies and safety regulations.
Common Industries of Employment
Appliance repairmen frequently work in residential services, retail appliance stores, and home warranty companies, specializing in fixing household appliances like refrigerators, ovens, and washing machines. Machine repairmen are commonly employed in manufacturing plants, industrial facilities, and construction sites, focusing on maintaining and repairing heavy machinery and equipment. Both roles are essential in sectors requiring technical expertise to ensure operational efficiency and minimize downtime.
Safety Protocols and Hazards
Appliance repairmen adhere to strict electrical safety protocols to prevent shocks and fires when servicing household devices like refrigerators and ovens. Machine repairmen focus on mechanical hazards, implementing lockout/tagout procedures to avoid accidents with heavy industrial machinery such as conveyor belts and turbines. Both roles require comprehensive training in hazard identification and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) to ensure safe repair environments.
Problem-Solving Approaches
Appliance repairmen specialize in diagnosing and fixing household devices using user manuals, common error codes, and manufacturer guidelines to address typical electrical and mechanical failures. Machine repairmen focus on industrial equipment, employing precision tools, diagnostic software, and root cause analysis to resolve complex mechanical breakdowns and optimize system performance. Both professionals utilize troubleshooting techniques but apply different technical knowledge and problem-solving methodologies tailored to their specific equipment types.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Appliance repairmen often have broader career advancement opportunities due to their ability to service diverse household devices such as refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens, attracting more varied job prospects. Machine repairmen, specializing in industrial equipment and manufacturing machinery, typically advance by gaining expertise in complex mechanical systems and automation technologies, leading to higher positions in industrial maintenance or engineering support. Both career paths benefit from certifications and ongoing training, which enhance skill sets and open doors to supervisory and technical specialist roles.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Appliance repairmen typically earn an average salary of $40,000 to $55,000 annually, with job growth projected at 3% over the next decade according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Machine repairmen, including industrial machinery mechanics, often command higher wages ranging from $50,000 to $70,000 per year, driven by demand in manufacturing and industrial sectors experiencing a 7% job growth rate. Salary expectations for both roles depend on experience, location, and specialization, but machine repairmen generally enjoy better long-term career prospects due to technological advances in automated equipment.
Appliance Repairman vs Machine Repairman Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com