Automotive repair primarily involves fixing cars, trucks, and other vehicles, focusing on engine performance, brake systems, and electronic diagnostics. Industrial equipment repair specializes in heavy machinery used in manufacturing, construction, and production, requiring expertise in hydraulics, pneumatics, and specialized mechanical components. Both fields demand technical skills but differ significantly in scale, complexity, and specific tools used.
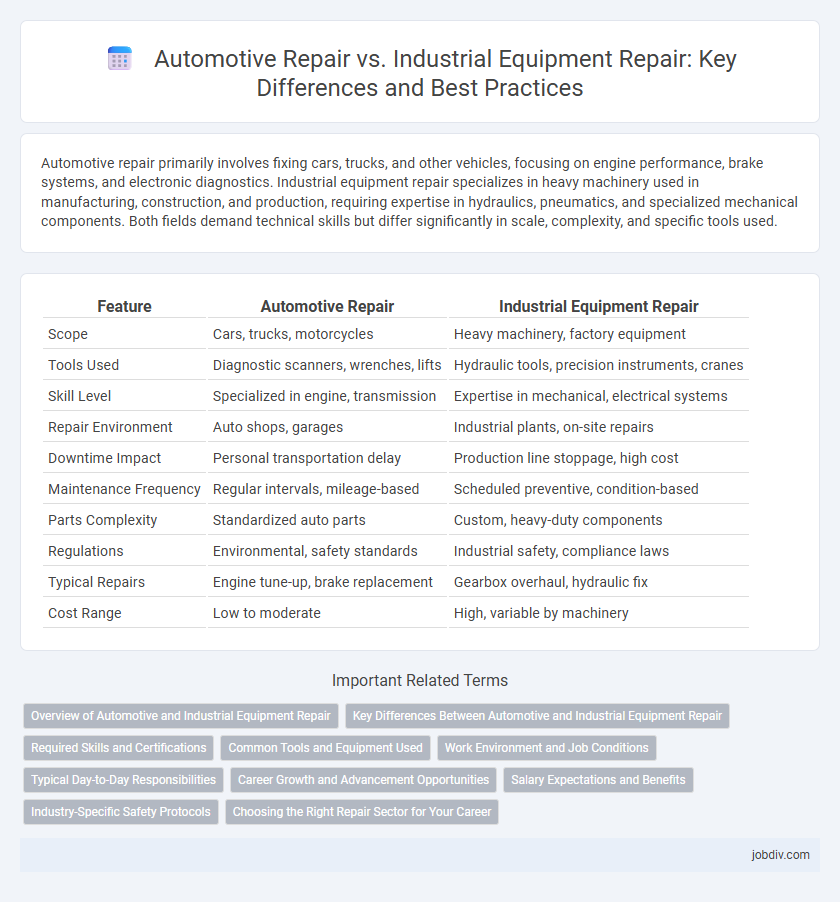
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Automotive Repair | Industrial Equipment Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Cars, trucks, motorcycles | Heavy machinery, factory equipment |
| Tools Used | Diagnostic scanners, wrenches, lifts | Hydraulic tools, precision instruments, cranes |
| Skill Level | Specialized in engine, transmission | Expertise in mechanical, electrical systems |
| Repair Environment | Auto shops, garages | Industrial plants, on-site repairs |
| Downtime Impact | Personal transportation delay | Production line stoppage, high cost |
| Maintenance Frequency | Regular intervals, mileage-based | Scheduled preventive, condition-based |
| Parts Complexity | Standardized auto parts | Custom, heavy-duty components |
| Regulations | Environmental, safety standards | Industrial safety, compliance laws |
| Typical Repairs | Engine tune-up, brake replacement | Gearbox overhaul, hydraulic fix |
| Cost Range | Low to moderate | High, variable by machinery |
Overview of Automotive and Industrial Equipment Repair
Automotive repair involves diagnosing and fixing issues in passenger vehicles, including engines, transmissions, brakes, and electrical systems, using specialized tools and technicians trained in vehicle diagnostics. Industrial equipment repair focuses on maintaining and restoring heavy machinery and manufacturing equipment, emphasizing mechanical components, hydraulics, and electrical controls to ensure operational efficiency and minimize downtime. Both sectors require precision, technical expertise, and adherence to safety standards, but automotive repair typically addresses consumer vehicles while industrial repair caters to large-scale commercial operations.
Key Differences Between Automotive and Industrial Equipment Repair
Automotive repair primarily focuses on vehicles such as cars and trucks, emphasizing engine diagnostics, brake systems, and electronic controls, whereas industrial equipment repair involves heavy machinery like conveyors, pumps, and generators with a focus on hydraulics, pneumatics, and large-scale mechanical systems. Automotive technicians commonly use OBD-II scanners for troubleshooting, while industrial equipment repair specialists rely on vibration analysis and thermal imaging to detect faults. The required skill sets differ, with automotive repair demanding knowledge of consumer vehicle systems and industrial repair necessitating expertise in complex mechanical and electrical components found in manufacturing environments.
Required Skills and Certifications
Automotive repair technicians must possess skills in diagnostics, engine repair, and electrical systems, often requiring certifications such as ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) to validate expertise. Industrial equipment repair specialists need advanced skills in hydraulics, pneumatics, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs), commonly holding certifications like ETA (Electronic Technicians Association) or ISA (International Society of Automation). Both fields demand proficiency in troubleshooting and maintenance, but industrial repair emphasizes adherence to safety standards and operational efficiency in complex machinery.
Common Tools and Equipment Used
Automotive repair commonly utilizes tools such as torque wrenches, diagnostic scanners, impact guns, and hydraulic lifts to service cars and light trucks efficiently. In contrast, industrial equipment repair often requires heavy-duty tools like hydraulic jacks, crane hoists, specialized welding machines, and precision alignment instruments to handle large-scale machinery maintenance. Both fields rely on essential diagnostic and mechanical tools, but industrial repair demands more robust and specialized equipment to accommodate higher weight loads and complex machinery systems.
Work Environment and Job Conditions
Automotive repair typically occurs in well-ventilated garages with controlled lighting and requires working closely with smaller, more intricate vehicle systems, often exposing mechanics to chemical fumes and noise. In contrast, industrial equipment repair involves large-scale machinery in diverse settings such as factories or outdoor industrial sites, where technicians face harsher conditions including heavy noise, dust, extreme temperatures, and physical hazards. Both fields demand strong safety protocols, but industrial repair generally requires more protective gear and adherence to stringent industrial safety standards due to the environment's elevated risks.
Typical Day-to-Day Responsibilities
Automotive repair technicians diagnose and fix issues related to passenger vehicles, including engine performance, brake systems, and electrical components, often performing routine maintenance like oil changes and tire rotations. Industrial equipment repair specialists handle heavy machinery, ensuring the functionality of hydraulic systems, conveyor belts, and pneumatic controls, which requires expertise in welding, fabrication, and electrical troubleshooting. Both fields demand precision diagnostics, preventive maintenance, and mechanical skills, but industrial repairs often involve larger-scale, more complex systems compared to automotive repair.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Automotive repair offers numerous entry-level positions with steady career growth through certifications like ASE, leading to specialization in areas such as diagnostics or hybrid systems. Industrial equipment repair demands advanced technical skills in hydraulics, pneumatics, and PLC programming, providing higher salary potential and opportunities to advance into supervisory or engineering roles. Both fields require continuous learning, but industrial repair typically offers broader advancement in complex machinery maintenance and management positions.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Automotive repair technicians typically earn a median annual salary of around $47,000, with benefits often including health insurance, paid time off, and retirement plans, reflecting the industry's competitive wage standards. Industrial equipment repair specialists command higher salaries, averaging $60,000 to $75,000 annually, due to the advanced technical skills required and the critical nature of industrial machinery maintenance. Benefits in industrial repair frequently encompass comprehensive health coverage, performance bonuses, and opportunities for overtime pay, positioning this field as more lucrative compared to automotive repair.
Industry-Specific Safety Protocols
Automotive repair and industrial equipment repair require strict adherence to industry-specific safety protocols due to the distinct hazards involved. Automotive repair focuses on protocols for handling fuel systems, electrical components, and vehicle lifts, while industrial equipment repair emphasizes lockout/tagout procedures, heavy machinery operation, and hazardous material management. Ensuring compliance with these specialized safety standards minimizes workplace accidents and enhances overall repair efficiency.
Choosing the Right Repair Sector for Your Career
Automotive repair offers hands-on experience with a wide range of vehicle systems, making it ideal for those passionate about cars and customer interaction. Industrial equipment repair demands expertise in heavy machinery, electronics, and hydraulics, presenting opportunities in manufacturing and infrastructure sectors. Evaluating your skills, interests, and career goals is essential to select between the dynamic automotive industry and the technically specialized industrial equipment repair field.
Automotive Repair vs Industrial Equipment Repair Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com