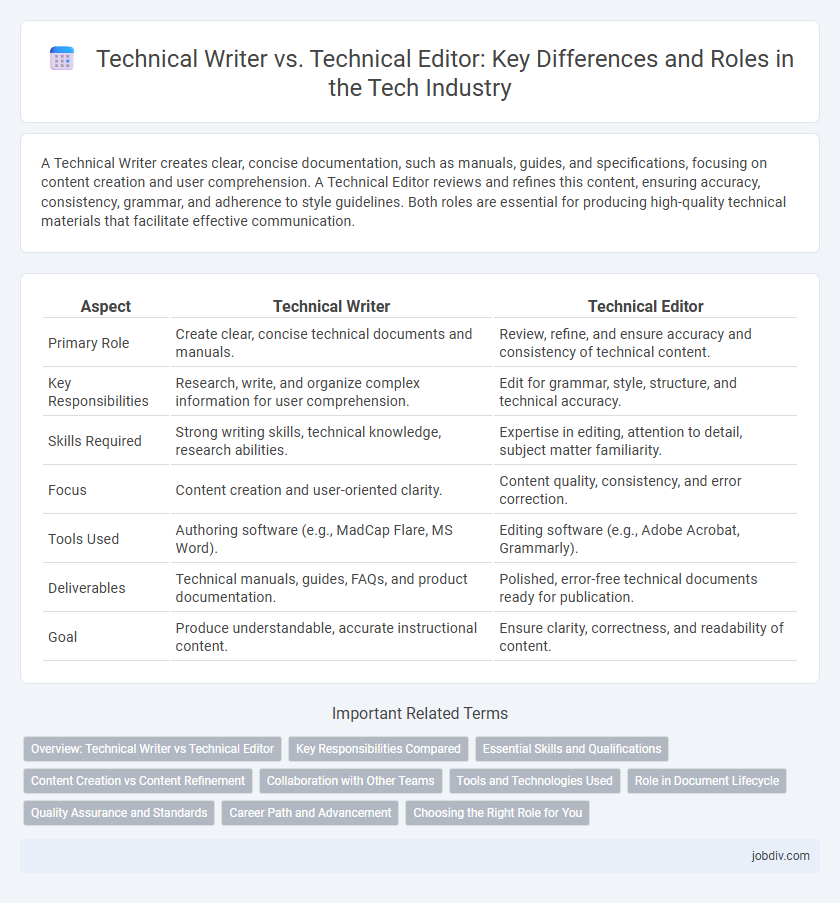
A Technical Writer creates clear, concise documentation, such as manuals, guides, and specifications, focusing on content creation and user comprehension. A Technical Editor reviews and refines this content, ensuring accuracy, consistency, grammar, and adherence to style guidelines. Both roles are essential for producing high-quality technical materials that facilitate effective communication.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Technical Writer | Technical Editor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Create clear, concise technical documents and manuals. | Review, refine, and ensure accuracy and consistency of technical content. |
| Key Responsibilities | Research, write, and organize complex information for user comprehension. | Edit for grammar, style, structure, and technical accuracy. |
| Skills Required | Strong writing skills, technical knowledge, research abilities. | Expertise in editing, attention to detail, subject matter familiarity. |
| Focus | Content creation and user-oriented clarity. | Content quality, consistency, and error correction. |
| Tools Used | Authoring software (e.g., MadCap Flare, MS Word). | Editing software (e.g., Adobe Acrobat, Grammarly). |
| Deliverables | Technical manuals, guides, FAQs, and product documentation. | Polished, error-free technical documents ready for publication. |
| Goal | Produce understandable, accurate instructional content. | Ensure clarity, correctness, and readability of content. |
Overview: Technical Writer vs Technical Editor
Technical writers create clear, concise documentation such as manuals, guides, and FAQs that explain complex technical information to various audiences. Technical editors review and refine this content to ensure accuracy, consistency, grammar, and adherence to style guides, enhancing clarity and overall quality. Both roles collaborate closely to produce precise, user-friendly technical communication that supports product understanding and usage.
Key Responsibilities Compared
Technical Writers develop clear, concise documentation, including user manuals, product guides, and FAQs, ensuring complex information is accessible to target audiences. Technical Editors review and refine these documents for accuracy, consistency, grammar, and style while ensuring compliance with industry standards and company guidelines. Both roles collaborate closely to deliver polished, user-friendly content that effectively communicates technical information.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
Technical writers must excel in clear, concise writing, possess strong research skills, and have proficiency in content management systems and documentation tools like MadCap Flare or Adobe FrameMaker. Technical editors require a keen eye for detail, expertise in grammar and style guides such as Chicago Manual of Style or Microsoft Style Guide, and the ability to ensure consistency and accuracy across complex technical documents. Both roles benefit from knowledge of specific industries, collaboration skills, and familiarity with version control systems like Git.
Content Creation vs Content Refinement
Technical Writers specialize in content creation by developing clear, structured documents such as manuals, guides, and specifications that communicate complex technical information effectively. Technical Editors focus on content refinement, ensuring accuracy, consistency, and clarity by reviewing, revising, and formatting technical documents to meet style guidelines and improve readability. The collaboration between Technical Writers and Editors enhances the overall quality and usability of technical documentation.
Collaboration with Other Teams
Technical Writers collaborate closely with product managers, engineers, and UX designers to gather accurate information and ensure documentation aligns with product functionality. Technical Editors work with content strategists and quality assurance teams to refine language, coherence, and compliance with style guides, enhancing overall document clarity. Both roles require seamless communication across departments to produce comprehensive and user-friendly technical content.
Tools and Technologies Used
Technical writers primarily use content management systems (CMS) like MadCap Flare and document processors such as Microsoft Word or Google Docs to create and organize technical documentation. Technical editors leverage advanced editing software, including Adobe Acrobat for PDF annotations and version control tools like Git to ensure accuracy and consistency across documents. Both roles often collaborate using collaboration platforms such as Confluence and Jira to streamline revisions and track changes efficiently.
Role in Document Lifecycle
Technical writers create and develop content, focusing on clarity, accuracy, and audience comprehension throughout the initial stages of the document lifecycle. Technical editors review, revise, and refine documents to ensure consistency, adherence to style guides, and error-free content during the later stages of the lifecycle. Both roles collaborate to deliver polished and user-friendly technical documentation, with writers driving content creation and editors enhancing quality and coherence.
Quality Assurance and Standards
Technical Writers create clear, precise documentation by adhering to industry standards such as IEEE and ISO, ensuring consistency and accuracy from the initial draft. Technical Editors focus on quality assurance by reviewing content for clarity, grammar, technical accuracy, and conformity to style guides like the Microsoft Manual of Style. Together, they enhance documentation reliability and maintain compliance with organizational and regulatory quality standards.
Career Path and Advancement
Technical writers often begin their careers by mastering content creation and documentation standards, with advancement opportunities leading to senior writer or content strategist roles. Technical editors focus on refining and improving documentation quality, progressing towards senior editor or documentation manager positions. Both career paths offer specialization options in industries like software, engineering, or healthcare, impacting advancement and salary potential.
Choosing the Right Role for You
Technical writers specialize in creating clear, concise documentation such as manuals, user guides, and online help, requiring strong writing skills and subject matter understanding. Technical editors focus on reviewing, revising, and improving existing content for accuracy, consistency, and style, demanding keen attention to detail and expertise in editing tools. Choosing the right role depends on whether you prefer content creation and research or refining and polishing technical materials.
Technical Writer vs Technical Editor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com