Data Engineers design, build, and maintain the infrastructure required for data generation, ensuring data is clean, reliable, and accessible for analysis. Data Scientists leverage this engineered data to develop predictive models, perform statistical analyses, and derive actionable insights. Both roles collaborate closely, but Data Engineers focus on architecture and pipelines, while Data Scientists emphasize data interpretation and decision-making through machine learning.
Table of Comparison
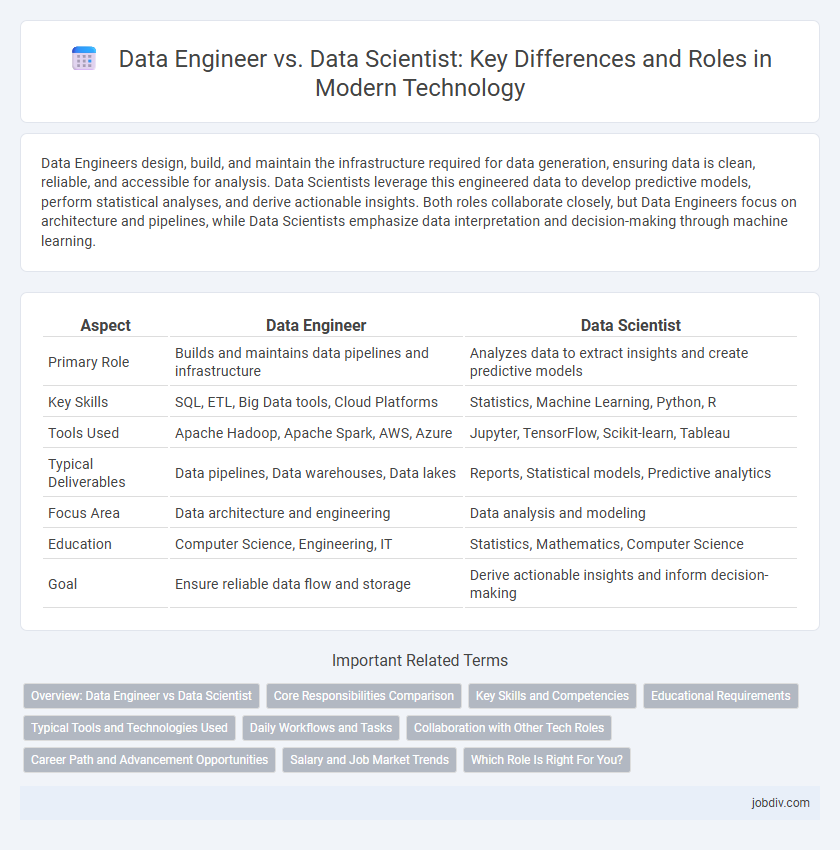
| Aspect | Data Engineer | Data Scientist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Builds and maintains data pipelines and infrastructure | Analyzes data to extract insights and create predictive models |
| Key Skills | SQL, ETL, Big Data tools, Cloud Platforms | Statistics, Machine Learning, Python, R |
| Tools Used | Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, AWS, Azure | Jupyter, TensorFlow, Scikit-learn, Tableau |
| Typical Deliverables | Data pipelines, Data warehouses, Data lakes | Reports, Statistical models, Predictive analytics |
| Focus Area | Data architecture and engineering | Data analysis and modeling |
| Education | Computer Science, Engineering, IT | Statistics, Mathematics, Computer Science |
| Goal | Ensure reliable data flow and storage | Derive actionable insights and inform decision-making |
Overview: Data Engineer vs Data Scientist
Data Engineers design, build, and maintain data pipelines and infrastructure to ensure reliable data flow and storage, enabling scalable analytics. Data Scientists analyze and interpret complex data sets using statistical models, machine learning, and visualization techniques to derive actionable insights and inform decision-making. Both roles are integral to data-driven organizations but differ in focus: engineers optimize data systems, while scientists extract meaning from data.
Core Responsibilities Comparison
Data Engineers specialize in designing, building, and maintaining scalable data pipelines and infrastructure to ensure reliable data flow for analytics. Data Scientists focus on analyzing complex datasets using statistical methods, machine learning, and predictive modeling to extract actionable insights. Both roles collaborate to optimize data quality and usability, but Data Engineers emphasize data architecture while Data Scientists prioritize data interpretation and hypothesis testing.
Key Skills and Competencies
Data Engineers specialize in building and maintaining scalable data pipelines, requiring proficiency in ETL processes, cloud platforms like AWS or Azure, and programming languages such as Python, Java, or Scala. Data Scientists focus on advanced statistical analysis, machine learning, and data visualization, leveraging tools like R, Python, TensorFlow, and SQL to derive actionable insights from complex datasets. Both roles demand strong data warehousing knowledge, but Data Engineers excel in infrastructure and architecture, while Data Scientists prioritize algorithms and predictive modeling.
Educational Requirements
Data Engineers typically require a strong foundation in computer science, software engineering, and database management, often holding degrees in computer science, information technology, or engineering fields. Data Scientists usually possess advanced degrees, such as master's or PhDs, in statistics, mathematics, computer science, or related disciplines emphasizing data analysis, machine learning, and statistical modeling. Both roles demand continuous learning but differ in educational focus, with Data Engineers prioritizing architecture and systems, while Data Scientists emphasize analytical methodologies and data interpretation.
Typical Tools and Technologies Used
Data Engineers typically use tools such as Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Kafka, and cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud for building and managing data pipelines and storage solutions. Data Scientists frequently rely on Python, R, TensorFlow, Jupyter Notebooks, and data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI for statistical analysis, machine learning, and interpreting complex datasets. Both roles emphasize SQL for database querying and often collaborate on leveraging big data technologies to drive business insights.
Daily Workflows and Tasks
Data Engineers design, construct, and maintain scalable data pipelines, focusing on data ingestion, transformation, and storage to ensure reliable access for analytics. Data Scientists analyze and interpret complex datasets using statistical models and machine learning algorithms to generate actionable insights and predictive models. Daily workflows for Data Engineers emphasize coding in SQL, Python, and ETL tools, while Data Scientists prioritize data exploration, hypothesis testing, and model validation using tools like R, Python, and Jupyter notebooks.
Collaboration with Other Tech Roles
Data Engineers and Data Scientists collaborate closely to optimize data workflows and model deployment; Engineers build and maintain scalable data pipelines, ensuring data quality and accessibility, while Scientists focus on applying statistical models and machine learning algorithms for insights. Effective collaboration requires clear communication standards, shared understanding of data infrastructure, and joint responsibility for performance monitoring. Integrating DevOps practices and utilizing platforms like Apache Airflow or AWS Glue fosters seamless data orchestration and accelerates model lifecycle management.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Data Engineers specialize in building and maintaining the data infrastructure, focusing on pipeline development, database management, and ETL processes, which opens career paths leading to roles like Data Architect or Engineering Manager. Data Scientists concentrate on analyzing and interpreting complex data using statistical methods and machine learning, advancing toward positions such as Lead Data Scientist or Chief Data Officer. Both career paths demand continuous learning of evolving technologies, but Data Engineers often progress through technical architecture roles while Data Scientists move into strategic analytics leadership.
Salary and Job Market Trends
Data Engineers typically command salaries ranging from $90,000 to $140,000 annually, reflecting their expertise in building and maintaining data pipelines, while Data Scientists earn between $95,000 and $150,000, driven by their role in advanced data analysis and machine learning model development. The job market shows a growing demand for Data Engineers as companies prioritize scalable data infrastructure, whereas Data Scientists remain essential for deriving strategic insights, keeping their job outlook robust. Regional variances impact salary scales, with tech hubs like San Francisco and New York offering the highest compensation due to competition and cost of living.
Which Role Is Right For You?
Data Engineers design, build, and maintain the infrastructure for data generation and processing, specializing in ETL pipelines, data warehousing, and database management, making them ideal for those who prefer working with large-scale data architecture and automation. Data Scientists analyze and interpret complex data through statistical modeling, machine learning, and predictive analytics, suited for individuals driven by extracting insights and solving business problems using data. Choosing between these roles depends on whether you enjoy building robust data systems (Data Engineer) or applying analytical techniques to derive actionable intelligence (Data Scientist).
Data Engineer vs Data Scientist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com