An IT Support Specialist provides comprehensive technical assistance, addressing complex hardware, software, and network issues across an organization. A Help Desk Technician primarily focuses on troubleshooting common user problems and managing first-level support requests through ticketing systems. Both roles aim to ensure smooth IT operations but differ in scope and technical depth.
Table of Comparison
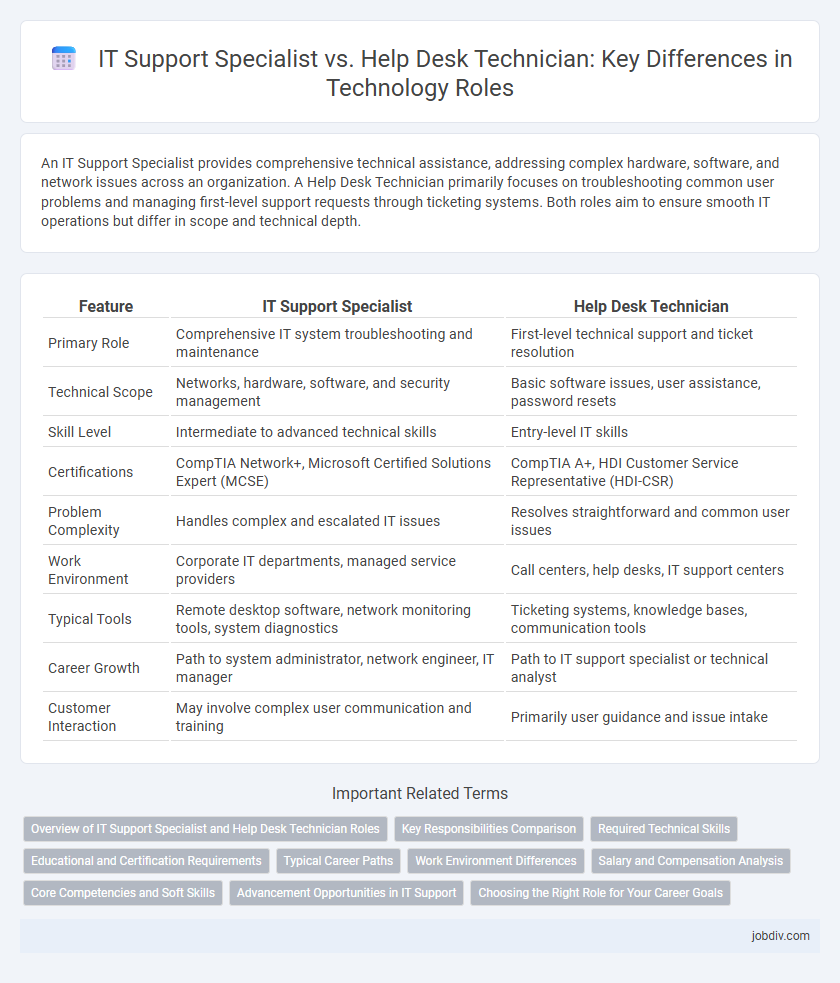
| Feature | IT Support Specialist | Help Desk Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Comprehensive IT system troubleshooting and maintenance | First-level technical support and ticket resolution |
| Technical Scope | Networks, hardware, software, and security management | Basic software issues, user assistance, password resets |
| Skill Level | Intermediate to advanced technical skills | Entry-level IT skills |
| Certifications | CompTIA Network+, Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE) | CompTIA A+, HDI Customer Service Representative (HDI-CSR) |
| Problem Complexity | Handles complex and escalated IT issues | Resolves straightforward and common user issues |
| Work Environment | Corporate IT departments, managed service providers | Call centers, help desks, IT support centers |
| Typical Tools | Remote desktop software, network monitoring tools, system diagnostics | Ticketing systems, knowledge bases, communication tools |
| Career Growth | Path to system administrator, network engineer, IT manager | Path to IT support specialist or technical analyst |
| Customer Interaction | May involve complex user communication and training | Primarily user guidance and issue intake |
Overview of IT Support Specialist and Help Desk Technician Roles
IT Support Specialists manage complex technical issues, providing in-depth troubleshooting, system maintenance, and user training across hardware, software, and network environments. Help Desk Technicians serve as the first point of contact, handling initial support requests by diagnosing problems, resolving basic technical issues, and escalating advanced cases. Both roles are essential in IT service management, with IT Support Specialists focusing on advanced problem-solving and Help Desk Technicians emphasizing prompt user assistance.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
IT Support Specialists manage complex troubleshooting, system maintenance, and network administration to ensure optimal IT infrastructure performance. Help Desk Technicians primarily handle user support, ticket resolution, and basic hardware or software issues, providing frontline assistance. The key distinction lies in the IT Support Specialist's broader scope of technical tasks versus the Help Desk Technician's focus on user-level problem-solving.
Required Technical Skills
IT Support Specialists require advanced knowledge of network infrastructure, cybersecurity protocols, and system administration, enabling them to manage complex IT environments. Help Desk Technicians typically possess strong troubleshooting abilities, familiarity with operating systems, and customer service skills to resolve common end-user issues efficiently. Both roles demand proficiency in software diagnostics, but IT Support Specialists often need deeper expertise in server management and virtual machine configuration.
Educational and Certification Requirements
IT Support Specialists typically require a bachelor's degree in computer science or information technology, complemented by certifications such as CompTIA A+, Network+, or Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE) to demonstrate advanced technical skills. Help Desk Technicians often enter the field with a high school diploma or associate degree, supplemented by foundational certifications like CompTIA A+ or HDI Support Center Analyst to handle first-level support tasks effectively. Both roles benefit from continuous learning and certifications to keep pace with evolving technologies and industry standards.
Typical Career Paths
IT Support Specialists often advance into roles such as Network Administrator, Systems Analyst, or IT Manager, leveraging their broad technical expertise and problem-solving skills. Help Desk Technicians commonly progress to more specialized positions like Technical Support Engineer or Desktop Support Technician, focusing on resolving end-user issues and hardware/software troubleshooting. Both career paths benefit from certifications like CompTIA A+, Network+, and Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert to enhance job prospects and expertise.
Work Environment Differences
IT Support Specialists typically work in dynamic office settings with direct interaction across multiple departments, managing complex technical issues and implementing system upgrades. Help Desk Technicians often operate in centralized call centers or remote environments, focusing on providing immediate troubleshooting and user assistance for common software and hardware problems. The work environment for IT Support Specialists is generally more collaborative and project-oriented, while Help Desk Technicians handle high-volume, fast-paced ticket resolutions.
Salary and Compensation Analysis
IT Support Specialists generally command higher salaries than Help Desk Technicians due to their advanced technical skills and broader responsibilities, with average annual earnings ranging from $50,000 to $70,000 compared to $35,000 to $50,000 for Help Desk Technicians. Compensation packages for IT Support Specialists often include bonuses, certifications reimbursements, and comprehensive benefits, reflecting their critical role in maintaining and troubleshooting complex IT systems. Industry demand for specialized expertise drives salary growth, making IT Support Specialist roles more lucrative in competitive technology job markets.
Core Competencies and Soft Skills
IT Support Specialists excel in advanced troubleshooting, network management, and system administration, while Help Desk Technicians focus on first-level user support, software installation, and issue documentation. Core competencies for IT Support Specialists include deep technical knowledge, problem-solving, and hardware proficiency, whereas Help Desk Technicians require strong communication, patience, and customer service skills. Soft skills like empathy and adaptability are critical for both roles to effectively resolve technical problems and support end-users.
Advancement Opportunities in IT Support
IT Support Specialists often have greater advancement opportunities compared to Help Desk Technicians due to their broader technical expertise and involvement in complex problem-solving tasks. Specializing in areas such as network administration, cybersecurity, or systems analysis can accelerate career growth for IT Support Specialists. Help Desk Technicians typically start with entry-level roles, gaining foundational experience before progressing to more specialized IT positions.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Career Goals
IT Support Specialists manage complex system troubleshooting and network maintenance, making them ideal for professionals aiming to develop advanced technical skills and pursue higher-level IT certifications. Help Desk Technicians focus on first-level customer support and resolving common software or hardware issues, suitable for those seeking an entry point into the IT industry with opportunities to enhance communication and problem-solving abilities. Choosing between these roles depends on your long-term objectives: prioritize IT Support Specialist for deeper technical expertise or Help Desk Technician for foundational experience and client interaction.
IT Support Specialist vs Help Desk Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com