A dispatcher coordinates real-time vehicle movements to ensure timely deliveries and efficient route management, focusing on daily operations and immediate problem-solving. A fleet manager oversees the entire fleet's maintenance, compliance, budgeting, and long-term strategy to optimize performance and reduce costs. Both roles are crucial for smooth transportation operations but differ in scope and responsibility.
Table of Comparison
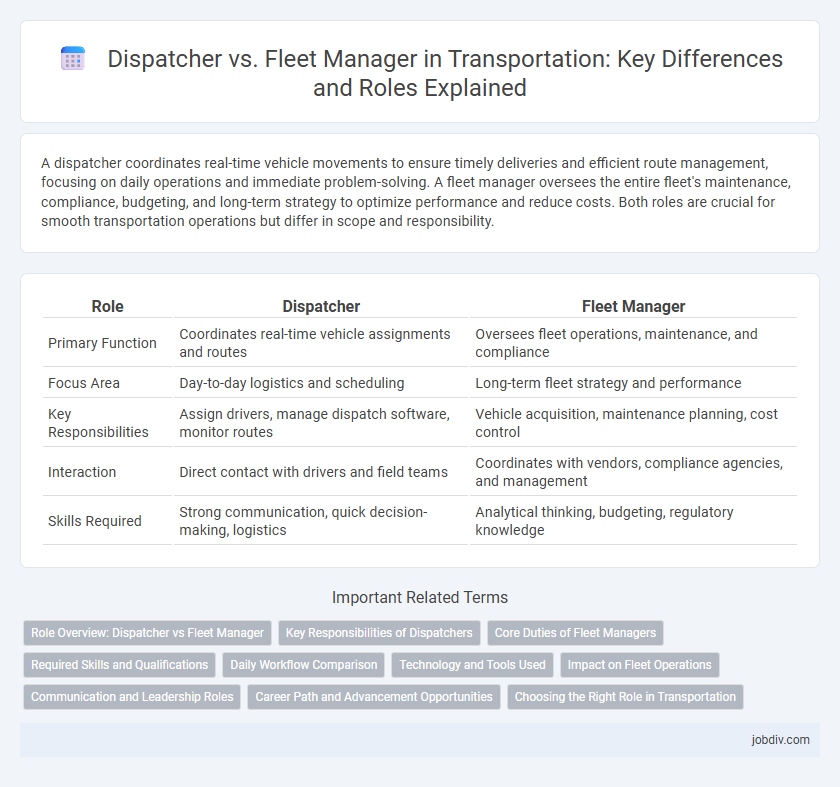
| Role | Dispatcher | Fleet Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Coordinates real-time vehicle assignments and routes | Oversees fleet operations, maintenance, and compliance |
| Focus Area | Day-to-day logistics and scheduling | Long-term fleet strategy and performance |
| Key Responsibilities | Assign drivers, manage dispatch software, monitor routes | Vehicle acquisition, maintenance planning, cost control |
| Interaction | Direct contact with drivers and field teams | Coordinates with vendors, compliance agencies, and management |
| Skills Required | Strong communication, quick decision-making, logistics | Analytical thinking, budgeting, regulatory knowledge |
Role Overview: Dispatcher vs Fleet Manager
A dispatcher coordinates the daily scheduling and routing of vehicles to ensure timely deliveries and efficient communication between drivers and clients. A fleet manager oversees the comprehensive management of vehicle assets, including maintenance, compliance, budgeting, and performance optimization. Both roles are essential for seamless transportation operations, with dispatchers focusing on real-time logistics and fleet managers managing long-term strategic planning.
Key Responsibilities of Dispatchers
Dispatchers coordinate daily vehicle routes and schedules to ensure timely deliveries and pickups while monitoring driver progress using GPS tracking systems. They communicate continuously with drivers, address emergencies or changes in orders, and maintain accurate logs of all dispatch activities. Effective dispatching optimizes fleet efficiency, reduces operational costs, and enhances customer satisfaction by minimizing delays.
Core Duties of Fleet Managers
Fleet Managers oversee vehicle maintenance schedules, driver performance, and compliance with safety regulations to ensure efficient fleet operations. They coordinate route planning, manage budgets, and handle procurement of vehicles and equipment, optimizing cost-effectiveness. Data analysis and reporting on fleet usage and expenses are essential to improve operational efficiency and meet company goals.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Dispatchers require strong communication skills, proficiency in logistics software, and the ability to coordinate real-time vehicle movements efficiently. Fleet Managers must possess advanced knowledge of vehicle maintenance, budget management, regulatory compliance, and leadership capabilities to oversee large transportation operations. Both roles demand problem-solving skills and comprehensive understanding of the transportation industry standards.
Daily Workflow Comparison
Dispatchers coordinate real-time communication between drivers and clients to ensure timely deliveries, managing route adjustments and addressing emergencies throughout the day. Fleet Managers oversee vehicle maintenance schedules, monitor fleet performance metrics, and plan resource allocation to optimize operational efficiency. Both roles require distinct but complementary tasks, with dispatchers focusing on immediate logistics and fleet managers handling long-term asset management.
Technology and Tools Used
Dispatchers rely heavily on real-time GPS tracking systems, communication platforms like two-way radios, and route optimization software to coordinate timely deliveries and driver assignments. Fleet managers use advanced fleet management software integrated with telematics, maintenance scheduling tools, and fuel management systems to oversee vehicle performance, compliance, and cost efficiency. Both roles utilize data analytics and mobile applications to enhance operational visibility and decision-making within transportation networks.
Impact on Fleet Operations
Dispatchers coordinate real-time vehicle scheduling and route adjustments to ensure timely deliveries and minimize delays, directly affecting operational efficiency. Fleet managers oversee overall fleet maintenance, compliance, and long-term asset utilization, driving cost-effectiveness and strategic resource allocation. Together, their roles optimize fleet performance by balancing immediate operational demands with long-term fleet health and productivity.
Communication and Leadership Roles
Dispatchers facilitate real-time communication between drivers and logistics teams, ensuring timely updates and route adjustments, while fleet managers strategize overall operations by leading teams, setting performance goals, and coordinating resources for efficient vehicle utilization. Effective communication from dispatchers involves immediate, clear instructions and problem-solving, whereas fleet managers exercise leadership through decision-making, team motivation, and policy implementation. Both roles require strong interpersonal skills, but fleet managers prioritize long-term planning and leadership, while dispatchers focus on operational execution and direct communication flow.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Dispatchers typically start with entry-level positions coordinating vehicle routes and schedules, gaining experience in logistics and communication. Fleet Managers often advance from dispatcher roles or related logistics positions, taking on broader responsibilities such as vehicle maintenance oversight, regulatory compliance, and budget management. Career progression in transportation favors Fleet Managers due to their strategic role in optimizing fleet operations and leading teams, offering higher earning potential and leadership opportunities.
Choosing the Right Role in Transportation
Choosing between a dispatcher and a fleet manager depends on the scale and complexity of transportation operations. Dispatchers coordinate real-time vehicle assignments and route optimizations to ensure timely deliveries, while fleet managers oversee vehicle maintenance, compliance, and overall fleet performance strategies. Prioritizing operational goals such as efficiency, cost management, and regulatory adherence helps determine the appropriate role for effective transportation management.
Dispatcher vs Fleet Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com