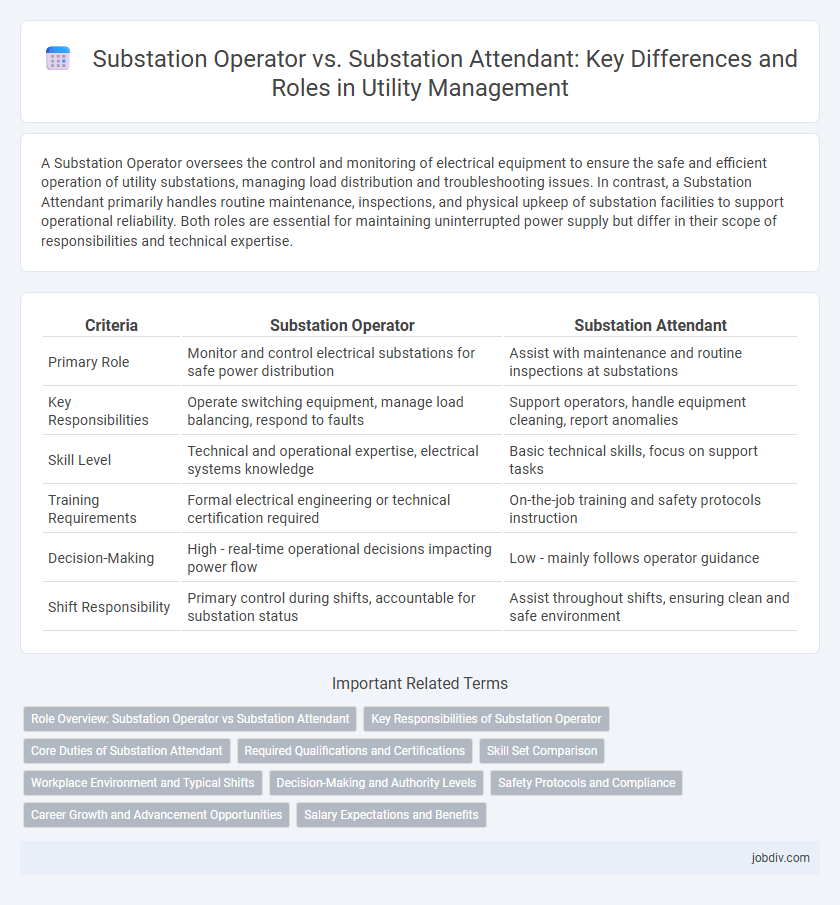
A Substation Operator oversees the control and monitoring of electrical equipment to ensure the safe and efficient operation of utility substations, managing load distribution and troubleshooting issues. In contrast, a Substation Attendant primarily handles routine maintenance, inspections, and physical upkeep of substation facilities to support operational reliability. Both roles are essential for maintaining uninterrupted power supply but differ in their scope of responsibilities and technical expertise.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Substation Operator | Substation Attendant |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Monitor and control electrical substations for safe power distribution | Assist with maintenance and routine inspections at substations |
| Key Responsibilities | Operate switching equipment, manage load balancing, respond to faults | Support operators, handle equipment cleaning, report anomalies |
| Skill Level | Technical and operational expertise, electrical systems knowledge | Basic technical skills, focus on support tasks |
| Training Requirements | Formal electrical engineering or technical certification required | On-the-job training and safety protocols instruction |
| Decision-Making | High - real-time operational decisions impacting power flow | Low - mainly follows operator guidance |
| Shift Responsibility | Primary control during shifts, accountable for substation status | Assist throughout shifts, ensuring clean and safe environment |
Role Overview: Substation Operator vs Substation Attendant
Substation Operators are responsible for controlling and monitoring electrical equipment to ensure the safe and efficient distribution of power within the substation. Substation Attendants primarily support maintenance activities, perform routine inspections, and assist operators by handling minor repairs and equipment cleaning. The operator's role emphasizes real-time operational decisions and system coordination, whereas attendants focus on maintenance support and physical upkeep of the substation environment.
Key Responsibilities of Substation Operator
Substation Operators are responsible for controlling and monitoring electrical substations to ensure safe and efficient power distribution. They manage switchgear, transformers, and circuit breakers, performing real-time system adjustments to maintain grid stability and prevent outages. Unlike Substation Attendants, who primarily handle maintenance and inspections, Operators focus on operational decisions and emergency response coordination.
Core Duties of Substation Attendant
Substation Attendants primarily monitor and maintain electrical equipment within substations, ensuring operational safety and compliance with utility standards. Their core duties include inspecting transformers, circuit breakers, and relays for faults, performing routine maintenance, and assisting with equipment tests. Unlike Substation Operators who control power flow and manage system operations, Attendants focus on hands-on equipment care and supporting system reliability.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Substation Operators typically require advanced technical qualifications such as a diploma or degree in electrical engineering or power systems, along with certifications in high-voltage equipment operation and safety compliance. Substation Attendants generally need basic electrical training, a high school diploma, and certifications in equipment maintenance and emergency response protocols. Both roles demand knowledge of utility regulations, but Operators often require more specialized certifications in control systems and protective relays.
Skill Set Comparison
Substation Operators require advanced technical skills in supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, protective relay settings, and real-time fault analysis, enabling efficient management of electrical equipment and system stability. Substation Attendants typically possess foundational skills in routine maintenance, equipment inspection, and basic operational support, focusing on physical upkeep and adherence to safety protocols. While Operators engage in complex decision-making and system monitoring, Attendants primarily ensure operational readiness and address minor mechanical issues within the substation.
Workplace Environment and Typical Shifts
Substation Operators usually work in controlled indoor environments within electrical substations, managing and monitoring complex high-voltage equipment to ensure reliability and safety. Substation Attendants often perform tasks in broader outdoor settings, requiring mobility to inspect and maintain infrastructure, including transformers and circuit breakers, under varying weather conditions. Operator shifts typically involve 12-hour rotations to maintain continuous system supervision, while Attendants may follow diverse schedules based on maintenance needs and emergency response demands.
Decision-Making and Authority Levels
Substation Operators hold higher authority levels and are responsible for complex decision-making, including managing equipment operations, system controls, and emergency responses to maintain grid stability. Substation Attendants support routine maintenance and inspections but have limited decision-making power and primarily follow established protocols under operator supervision. The distinction ensures operational safety by pairing strategic control with technical support roles in utility substations.
Safety Protocols and Compliance
Substation Operators strictly adhere to safety protocols by monitoring and controlling electrical equipment to prevent hazards and ensure system stability, while Substation Attendants focus on routine inspections and maintenance tasks to detect potential safety risks. Both roles comply with regulatory standards such as OSHA and NERC to maintain a secure operational environment in power substations. Continuous training in emergency response and equipment handling is essential for minimizing accidents and ensuring compliance across utility operations.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Substation Operators typically have greater career growth and advancement opportunities due to their technical expertise in managing complex electrical equipment and ensuring grid stability. In contrast, Substation Attendants often perform routine maintenance and assist Operators, limiting their upward mobility without additional training or certification. Pursuing advanced certifications or specialized training can significantly enhance career progression prospects for both roles within the utility sector.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Substation Operators typically earn higher salaries than Substation Attendants due to advanced technical skills and responsibilities in managing electrical equipment and ensuring grid stability. Benefits for Substation Operators often include comprehensive healthcare, retirement plans, and overtime pay, reflecting their critical role in utility operations. Substation Attendants generally receive base-level benefits with lower salary ranges, focusing on equipment inspection and maintenance support tasks.
Substation Operator vs Substation Attendant Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com