A Utility Maintenance Worker performs hands-on tasks such as repairing, inspecting, and maintaining utility systems to ensure operational efficiency and safety. In contrast, a Utility Maintenance Supervisor oversees the maintenance team, manages schedules, coordinates projects, and ensures compliance with safety standards. The supervisor also handles administrative duties, including reporting and resource allocation, to optimize workflow and productivity.
Table of Comparison
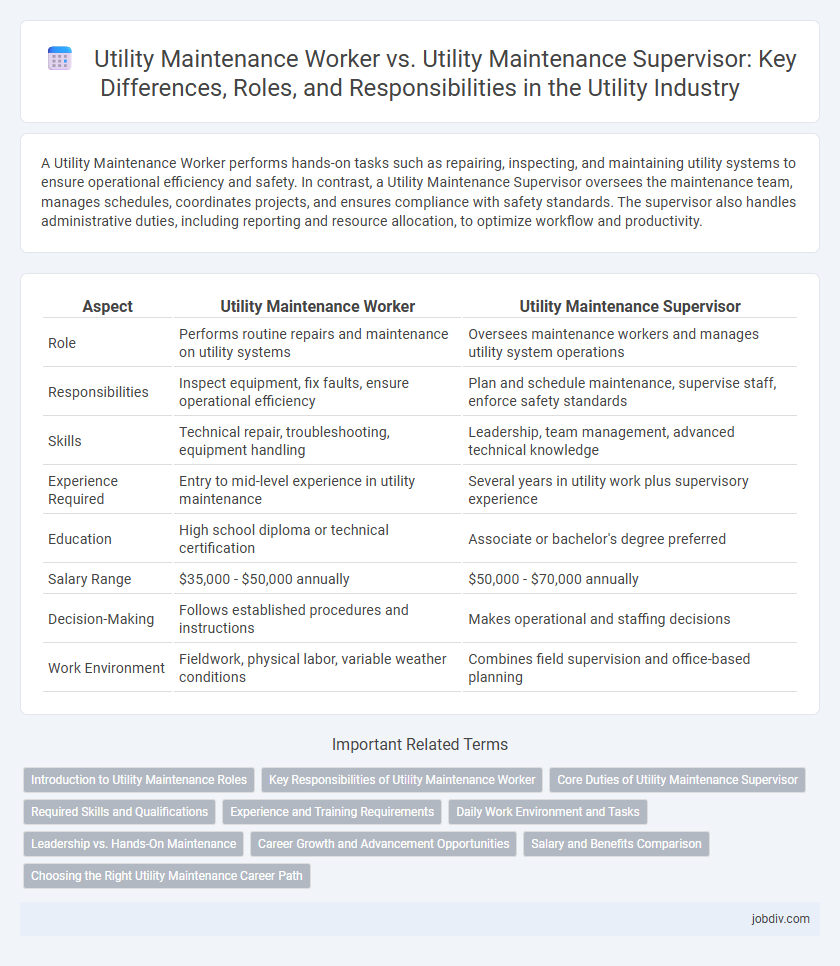
| Aspect | Utility Maintenance Worker | Utility Maintenance Supervisor |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Performs routine repairs and maintenance on utility systems | Oversees maintenance workers and manages utility system operations |
| Responsibilities | Inspect equipment, fix faults, ensure operational efficiency | Plan and schedule maintenance, supervise staff, enforce safety standards |
| Skills | Technical repair, troubleshooting, equipment handling | Leadership, team management, advanced technical knowledge |
| Experience Required | Entry to mid-level experience in utility maintenance | Several years in utility work plus supervisory experience |
| Education | High school diploma or technical certification | Associate or bachelor's degree preferred |
| Salary Range | $35,000 - $50,000 annually | $50,000 - $70,000 annually |
| Decision-Making | Follows established procedures and instructions | Makes operational and staffing decisions |
| Work Environment | Fieldwork, physical labor, variable weather conditions | Combines field supervision and office-based planning |
Introduction to Utility Maintenance Roles
Utility Maintenance Workers perform hands-on tasks such as inspecting, repairing, and maintaining utility systems like water, gas, and electricity to ensure continuous service and safety. Utility Maintenance Supervisors oversee maintenance teams, coordinate work schedules, enforce safety protocols, and manage resources to optimize operational efficiency. Both roles are essential in maintaining infrastructure reliability, with workers handling technical duties and supervisors managing workflow and personnel.
Key Responsibilities of Utility Maintenance Worker
Utility Maintenance Workers perform routine inspections, repairs, and upkeep of utility systems such as water, gas, and electrical networks to ensure operational efficiency and safety standards. They handle the maintenance of pipelines, valves, pumps, and related infrastructure, addressing issues promptly to minimize service disruptions. These workers also assist with emergency repairs and report system malfunctions to supervisors for further action.
Core Duties of Utility Maintenance Supervisor
Utility Maintenance Supervisors oversee and coordinate the daily operations of utility maintenance teams, ensuring timely repair and upkeep of infrastructure such as water, gas, and electrical systems. They plan work schedules, assign tasks, and enforce safety regulations to maintain compliance with industry standards and minimize service interruptions. Supervisors also manage inventory, monitor equipment performance, and provide training to Maintenance Workers to enhance operational efficiency.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Utility Maintenance Workers need technical skills such as equipment repair, electrical and plumbing knowledge, and the ability to follow safety protocols. Utility Maintenance Supervisors require advanced qualifications including leadership abilities, project management experience, and proficiency in coordinating maintenance teams. Both roles demand problem-solving skills and familiarity with utility systems, but supervisors must also demonstrate strong communication and decision-making expertise.
Experience and Training Requirements
Utility Maintenance Workers typically require a high school diploma or equivalent along with on-the-job training, apprenticeships, or vocational courses to develop essential skills in equipment repair and routine maintenance. Utility Maintenance Supervisors generally need several years of hands-on experience as Utility Maintenance Workers, supplemented by leadership training or certifications in safety and project management to effectively oversee teams and ensure compliance with regulations. The supervisor role demands advanced knowledge in utility systems and proven expertise in coordinating maintenance schedules and emergency responses.
Daily Work Environment and Tasks
Utility Maintenance Workers perform hands-on tasks such as repairing electrical lines, maintaining water systems, and troubleshooting equipment in outdoor and indoor utility environments. Utility Maintenance Supervisors oversee these daily operations, managing workflow, ensuring safety protocols, and coordinating team schedules to maintain system reliability. Both roles demand physical labor, but supervisors focus more on administrative duties and team leadership within utility maintenance settings.
Leadership vs. Hands-On Maintenance
Utility Maintenance Workers perform hands-on maintenance tasks such as equipment repair, routine inspections, and system troubleshooting to ensure operational efficiency and safety. Utility Maintenance Supervisors oversee teams, coordinate maintenance schedules, and enforce compliance with safety protocols while providing leadership and guidance. Supervisors balance administrative responsibilities with a strategic focus, whereas workers concentrate primarily on executing technical maintenance duties.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Utility Maintenance Workers develop hands-on skills in repairing and maintaining utility systems, forming the foundation for career progression within the utility sector. Promotion to Utility Maintenance Supervisor involves managing teams, coordinating schedules, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations, offering a shift from technical tasks to leadership roles. Career growth opportunities expand significantly with supervisory experience, opening pathways to higher management positions and specialized utility operations roles.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
Utility Maintenance Supervisors typically earn higher salaries than Utility Maintenance Workers, with average annual wages ranging from $60,000 to $85,000 compared to $40,000 to $60,000 for workers. Supervisors often receive enhanced benefits packages, including increased paid leave, performance bonuses, and retirement plan contributions, reflecting their managerial responsibilities. Salary growth and career advancement opportunities are more robust for supervisors due to their leadership roles and greater experience requirements.
Choosing the Right Utility Maintenance Career Path
Utility Maintenance Workers perform hands-on tasks such as repairing electrical systems, maintaining water lines, and troubleshooting equipment, requiring technical skills and physical labor. Utility Maintenance Supervisors manage teams, coordinate maintenance schedules, and ensure compliance with safety regulations, emphasizing leadership and project management abilities. Selecting the right career path depends on your preference for direct technical work versus overseeing operations and guiding personnel.
Utility Maintenance Worker vs Utility Maintenance Supervisor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com