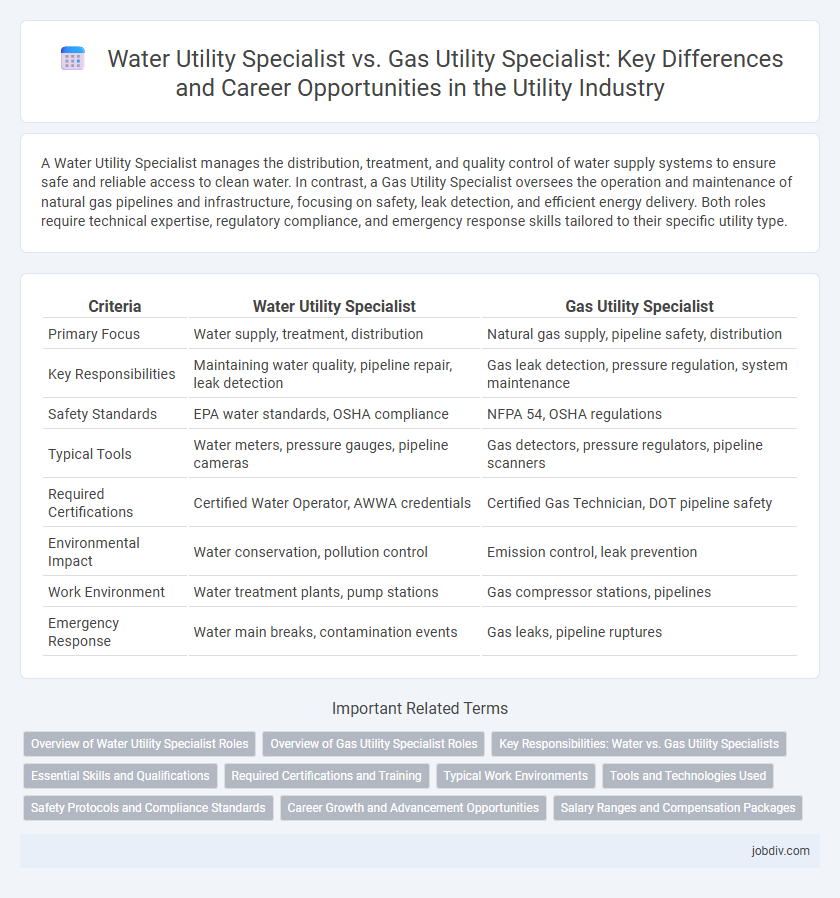
A Water Utility Specialist manages the distribution, treatment, and quality control of water supply systems to ensure safe and reliable access to clean water. In contrast, a Gas Utility Specialist oversees the operation and maintenance of natural gas pipelines and infrastructure, focusing on safety, leak detection, and efficient energy delivery. Both roles require technical expertise, regulatory compliance, and emergency response skills tailored to their specific utility type.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Water Utility Specialist | Gas Utility Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Water supply, treatment, distribution | Natural gas supply, pipeline safety, distribution |
| Key Responsibilities | Maintaining water quality, pipeline repair, leak detection | Gas leak detection, pressure regulation, system maintenance |
| Safety Standards | EPA water standards, OSHA compliance | NFPA 54, OSHA regulations |
| Typical Tools | Water meters, pressure gauges, pipeline cameras | Gas detectors, pressure regulators, pipeline scanners |
| Required Certifications | Certified Water Operator, AWWA credentials | Certified Gas Technician, DOT pipeline safety |
| Environmental Impact | Water conservation, pollution control | Emission control, leak prevention |
| Work Environment | Water treatment plants, pump stations | Gas compressor stations, pipelines |
| Emergency Response | Water main breaks, contamination events | Gas leaks, pipeline ruptures |
Overview of Water Utility Specialist Roles
Water Utility Specialists manage the distribution, maintenance, and quality control of municipal water systems to ensure safe and reliable water supply. Their responsibilities include monitoring water treatment processes, regulating pipeline infrastructure, and addressing contamination issues to comply with health and environmental standards. Unlike Gas Utility Specialists who focus on gas pipeline safety and production, Water Utility Specialists emphasize water resource management and regulatory compliance specific to water utilities.
Overview of Gas Utility Specialist Roles
Gas Utility Specialists manage the installation, maintenance, and repair of gas distribution systems, ensuring safe and efficient delivery to residential and commercial customers. They monitor pipeline integrity, detect leaks, and respond to emergencies to prevent hazardous incidents. Their expertise in regulatory compliance and safety standards is critical for maintaining continuous, reliable gas service.
Key Responsibilities: Water vs. Gas Utility Specialists
Water Utility Specialists manage the distribution, treatment, and quality control of potable water, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and system maintenance for leak detection and pipeline repairs. Gas Utility Specialists focus on the safe transmission and distribution of natural gas, performing pipeline inspections, monitoring pressure levels, and responding to leak emergencies to prevent hazards. Both roles require expertise in regulatory standards, emergency response, and infrastructure integrity but differ in the specific mediums and technologies they handle.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
Water Utility Specialists require expertise in hydraulic systems, water treatment processes, and regulatory compliance related to drinking water standards. Gas Utility Specialists need strong knowledge of pipeline integrity, gas metering technology, and safety protocols specific to combustible gas handling. Both roles demand analytical skills, technical certifications such as EPA Water Distribution or Gas Operator licenses, and proficiency in field equipment operation to ensure reliable utility service.
Required Certifications and Training
Water Utility Specialists typically require certifications such as the Certified Water Operator (CWO) license and training in water quality standards, distribution system maintenance, and regulatory compliance. Gas Utility Specialists need certifications like the Gas Operator Qualification (GOQ) and training in pipeline safety, leak detection, and hazardous materials handling. Both roles demand adherence to OSHA standards and continuous education to stay current with evolving safety protocols and technological advancements.
Typical Work Environments
Water Utility Specialists typically work in environments such as water treatment plants, municipal water supply facilities, and field sites involving pipeline maintenance and repair. Gas Utility Specialists operate in natural gas processing plants, compressor stations, and underground pipeline networks to ensure safe distribution and system integrity. Both roles require adherence to safety standards and may involve outdoor work in variable weather conditions.
Tools and Technologies Used
Water Utility Specialists rely on advanced sensors, smart meters, and GIS mapping tools to monitor water quality, detect leaks, and optimize distribution networks, while Gas Utility Specialists employ infrared cameras, ultrasonic leak detectors, and pipeline inspection robots to ensure gas safety and pipeline integrity. Both specialists utilize SCADA systems for real-time monitoring and control, but their field devices and diagnostic technologies differ according to the unique requirements of water versus gas utilities. Integration of IoT devices and data analytics enhances operational efficiency in both domains, yet sector-specific tools remain crucial for effective utility management.
Safety Protocols and Compliance Standards
Water Utility Specialists implement rigorous safety protocols to prevent contamination, adhering to EPA regulations and OSHA standards to ensure clean, potable water distribution. Gas Utility Specialists focus on leak detection, pipeline integrity, and compliance with PHMSA regulations, enforcing strict monitoring to mitigate explosion and fire hazards. Both roles demand comprehensive training in emergency response and continuous adherence to evolving federal and state safety codes.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Water Utility Specialists typically experience steady career growth due to increasing demand for sustainable water management and infrastructure modernization. Gas Utility Specialists benefit from advancements in renewable natural gas technologies and expanding pipeline networks, offering diverse opportunities for technical specialization and leadership roles. Both fields provide pathways to supervisory positions, with water utilities emphasizing regulatory compliance and gas utilities focusing on safety and innovation.
Salary Ranges and Compensation Packages
Water Utility Specialists typically earn salaries ranging from $50,000 to $80,000 annually, with compensation packages that often include health benefits, retirement plans, and performance bonuses. Gas Utility Specialists generally command higher pay, between $60,000 and $90,000 per year, reflecting the increased risks and technical demands of gas systems, alongside comprehensive benefits such as hazard pay and specialized training reimbursements. Salary variations for both roles depend on location, experience, and company size, with metropolitan areas often offering higher compensation to attract skilled professionals.
Water Utility Specialist vs Gas Utility Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com