Utility meter readers are responsible for accurately recording energy or water usage from meters to ensure proper billing, requiring attention to detail and regular route management. Utility meter installers focus on setting up and maintaining meters, ensuring devices function correctly and comply with safety standards, often involving technical skills and physical labor. Both roles are essential for efficient utility management but differ significantly in their daily tasks and required expertise.
Table of Comparison
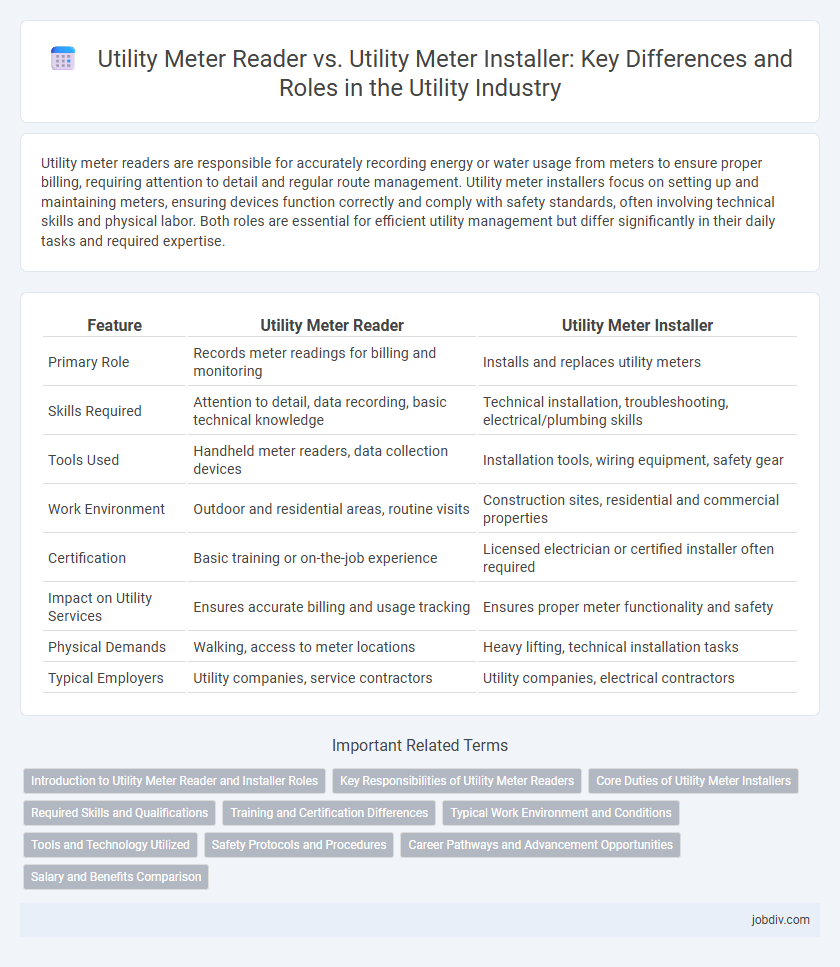
| Feature | Utility Meter Reader | Utility Meter Installer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Records meter readings for billing and monitoring | Installs and replaces utility meters |
| Skills Required | Attention to detail, data recording, basic technical knowledge | Technical installation, troubleshooting, electrical/plumbing skills |
| Tools Used | Handheld meter readers, data collection devices | Installation tools, wiring equipment, safety gear |
| Work Environment | Outdoor and residential areas, routine visits | Construction sites, residential and commercial properties |
| Certification | Basic training or on-the-job experience | Licensed electrician or certified installer often required |
| Impact on Utility Services | Ensures accurate billing and usage tracking | Ensures proper meter functionality and safety |
| Physical Demands | Walking, access to meter locations | Heavy lifting, technical installation tasks |
| Typical Employers | Utility companies, service contractors | Utility companies, electrical contractors |
Introduction to Utility Meter Reader and Installer Roles
Utility meter readers are responsible for accurately recording consumption data from water, gas, or electricity meters to ensure proper billing and resource management. Utility meter installers specialize in fitting, maintaining, and repairing meters, ensuring they comply with safety and regulatory standards. Both roles are crucial in the utility sector for efficient service delivery and customer satisfaction.
Key Responsibilities of Utility Meter Readers
Utility Meter Readers are responsible for accurately recording energy, water, or gas consumption data from utility meters to ensure precise billing. They inspect meters for signs of tampering, damage, or malfunction and report discrepancies to utility companies for further action. Their key tasks include entering readings into electronic devices and maintaining detailed logs to support utility billing operations and customer service accuracy.
Core Duties of Utility Meter Installers
Utility meter installers specialize in the precise placement, connection, and activation of utility meters, including water, gas, and electricity meters, ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulatory codes. They conduct site assessments to determine optimal installation locations, perform equipment calibration, and verify system functionality post-installation to guarantee accurate utility consumption tracking. Their role demands technical expertise in electrical and plumbing systems, adherence to manufacturer guidelines, and coordination with utility providers for seamless meter integration.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Utility meter readers require strong attention to detail, basic math skills, and the ability to use handheld data collection devices for accurate readings. Utility meter installers need specialized knowledge of electrical or plumbing systems, technical proficiency with meters, and certification or licensing depending on regional regulations. Both roles demand physical stamina and adherence to safety protocols, but installers typically undergo more rigorous training and qualifications to handle complex installations.
Training and Certification Differences
Utility meter readers typically require on-the-job training and basic certification to accurately record energy consumption data, emphasizing skills in data entry and customer interaction. Utility meter installers undergo more extensive technical training and must obtain certifications related to electrical safety and equipment installation to ensure compliance with regulatory standards. The installer's training focuses on system setup and maintenance, while the reader's certification centers on accuracy and data verification.
Typical Work Environment and Conditions
Utility meter readers typically work outdoors in various weather conditions, walking or driving to multiple locations to record meter readings accurately. Utility meter installers often face physically demanding tasks, including climbing poles or entering confined spaces, and must adhere to safety protocols due to electrical hazards. Both roles require adaptability to changing environments, but installers generally encounter more technical and safety challenges on-site.
Tools and Technology Utilized
Utility meter readers primarily use handheld devices such as mobile data collectors or smartphones equipped with radio frequency identification (RFID) and barcode scanning technology to efficiently capture consumption data. Utility meter installers rely on specialized tools including voltage testers, pipe wrenches, and torque drivers alongside advanced technologies like smart meters and automated meter reading (AMR) systems to ensure accurate installation and integration. The integration of IoT devices enhances both roles by enabling real-time data transmission and remote diagnostics, improving overall utility management.
Safety Protocols and Procedures
Utility meter readers follow strict safety protocols including maintaining safe distances from live wires and using insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks. Utility meter installers implement comprehensive procedures such as proper lockout/tagout practices, wearing protective gear like gloves and helmets, and conducting site hazard assessments to ensure safe meter installation. Both roles require adherence to regulatory standards such as OSHA guidelines to minimize workplace accidents and ensure operational safety.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Utility meter readers primarily focus on collecting accurate consumption data from electric, gas, or water meters, requiring attention to detail and basic technical skills, with career advancement often leading to supervisory or data analysis roles. Utility meter installers engage in the installation, maintenance, and repair of utility meters, demanding more advanced technical knowledge and certifications, opening pathways to technician specialist, project management, or engineering positions. Both career paths offer opportunities for cross-training, skill enhancement, and upward mobility within utility companies or related service providers.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
Utility meter readers typically earn an average salary of $35,000 to $45,000 per year, with benefits including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. In contrast, utility meter installers often command higher salaries ranging from $45,000 to $60,000 annually, reflecting the specialized skills and certifications required, along with superior benefits packages such as hazard pay, overtime opportunities, and enhanced retirement contributions. Salary disparities stem from the technical complexity and safety responsibilities inherent in the installer role compared to the more routine inspection duties of meter readers.
Utility Meter Reader vs Utility Meter Installer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com