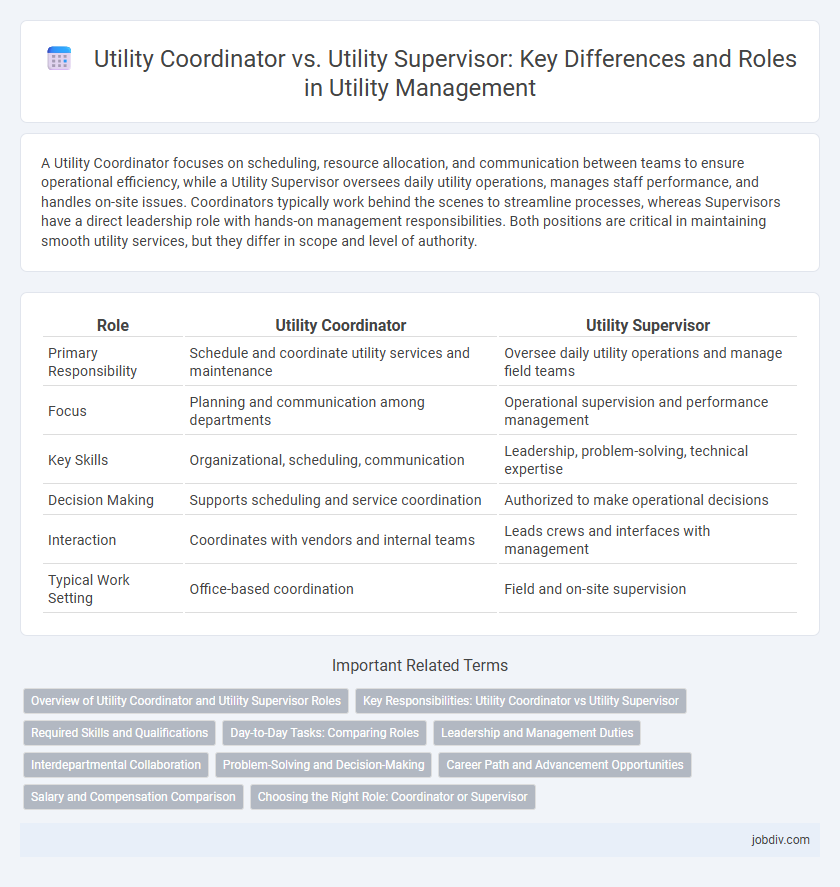
A Utility Coordinator focuses on scheduling, resource allocation, and communication between teams to ensure operational efficiency, while a Utility Supervisor oversees daily utility operations, manages staff performance, and handles on-site issues. Coordinators typically work behind the scenes to streamline processes, whereas Supervisors have a direct leadership role with hands-on management responsibilities. Both positions are critical in maintaining smooth utility services, but they differ in scope and level of authority.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Utility Coordinator | Utility Supervisor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Schedule and coordinate utility services and maintenance | Oversee daily utility operations and manage field teams |
| Focus | Planning and communication among departments | Operational supervision and performance management |
| Key Skills | Organizational, scheduling, communication | Leadership, problem-solving, technical expertise |
| Decision Making | Supports scheduling and service coordination | Authorized to make operational decisions |
| Interaction | Coordinates with vendors and internal teams | Leads crews and interfaces with management |
| Typical Work Setting | Office-based coordination | Field and on-site supervision |
Overview of Utility Coordinator and Utility Supervisor Roles
Utility Coordinators manage the scheduling, communication, and documentation required for utility service installations and maintenance, ensuring seamless coordination between contractors, utility companies, and project stakeholders. Utility Supervisors oversee on-site utility operations, provide leadership to field crews, and ensure compliance with safety standards and regulatory requirements. Both roles play crucial parts in utility project execution, with Coordinators focusing on planning and communication, while Supervisors concentrate on operational supervision and workforce management.
Key Responsibilities: Utility Coordinator vs Utility Supervisor
Utility Coordinators manage the scheduling and communication between field crews and project managers, ensuring efficient utility installations and relocations while maintaining compliance with safety regulations. Utility Supervisors oversee daily operations on-site, directing teams, monitoring workload distribution, and enforcing quality control standards to meet project deadlines. Both roles require strong coordination skills, but Supervisors focus more on leadership and operational management, whereas Coordinators emphasize logistical planning and stakeholder communication.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Utility Coordinators require strong organizational skills, proficiency in project management software, and effective communication abilities to coordinate schedules and resources efficiently. Utility Supervisors need advanced leadership experience, technical knowledge of utility systems, and the ability to manage team performance and compliance with safety regulations. Both roles demand familiarity with industry standards, problem-solving skills, and the capacity to handle emergency situations in utility operations.
Day-to-Day Tasks: Comparing Roles
Utility Coordinators manage daily scheduling, communication with contractors, and coordinate utility installations to ensure project timelines are met. Utility Supervisors oversee work crews, monitor field operations for safety and quality compliance, and resolve technical issues on-site. Both roles require strong organizational skills, but coordinators focus on planning and communication, while supervisors emphasize on-the-ground management and operational oversight.
Leadership and Management Duties
A Utility Coordinator manages daily operations by scheduling tasks, coordinating with field teams, and ensuring compliance with safety standards to maintain efficient utility services. A Utility Supervisor holds a higher leadership role, overseeing multiple teams, implementing strategic plans, and making critical decisions to optimize resource allocation and project execution. Both roles require strong communication skills, but supervisors focus more on leadership, team development, and performance evaluation to drive organizational goals.
Interdepartmental Collaboration
Utility Coordinators facilitate seamless communication between departments, ensuring timely information exchange and efficient project execution. Utility Supervisors oversee teams and manage resource allocation while maintaining coordination with engineering, construction, and safety departments to uphold compliance and project standards. Effective interdepartmental collaboration driven by both roles minimizes delays and enhances overall utility management efficiency.
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
A Utility Coordinator specializes in identifying operational issues and coordinating responses by gathering project data and assigning tasks to field crews, ensuring efficient communication and resource allocation. In contrast, a Utility Supervisor holds greater responsibility in decision-making, overseeing problem resolution strategies, approving corrective actions, and managing team performance to maintain utility service continuity. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but the Utility Supervisor typically exercises higher-level judgment and authority in complex problem-solving scenarios.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Utility Coordinators often begin their careers handling scheduling, documentation, and communication between departments, gaining hands-on experience with utility project logistics. Utility Supervisors typically advance from coordinator roles, taking on leadership responsibilities, managing teams, and overseeing project execution, which positions them for higher management roles in utility operations. Career advancement in utilities generally follows this progression, allowing professionals to develop technical expertise and supervisory skills essential for strategic planning and operational management.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Utility Coordinators typically earn a median salary ranging from $50,000 to $65,000 annually, while Utility Supervisors command higher compensation, with average earnings between $70,000 and $85,000 per year. The salary disparity reflects the increased responsibility, supervisory duties, and project management skills required for the Utility Supervisor role. Benefits and bonuses also tend to be more substantial for supervisors, including performance incentives and additional health or retirement plan contributions.
Choosing the Right Role: Coordinator or Supervisor
Utility Coordinators manage project schedules, coordinate with subcontractors, and ensure compliance with utility regulations to support seamless infrastructure development. Utility Supervisors oversee field crews, enforce safety standards, and resolve on-site utility issues to maintain efficient operations and timely project completion. Choosing between these roles depends on whether one prefers administrative coordination or direct workforce supervision within utility project management.
Utility Coordinator vs Utility Supervisor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com