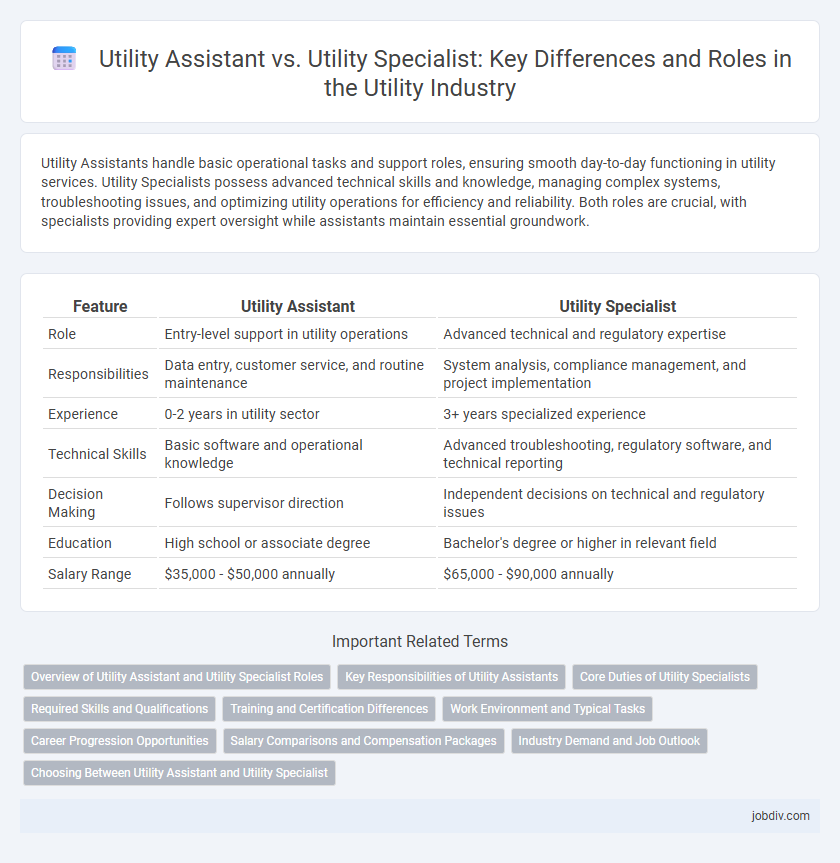
Utility Assistants handle basic operational tasks and support roles, ensuring smooth day-to-day functioning in utility services. Utility Specialists possess advanced technical skills and knowledge, managing complex systems, troubleshooting issues, and optimizing utility operations for efficiency and reliability. Both roles are crucial, with specialists providing expert oversight while assistants maintain essential groundwork.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Utility Assistant | Utility Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Entry-level support in utility operations | Advanced technical and regulatory expertise |
| Responsibilities | Data entry, customer service, and routine maintenance | System analysis, compliance management, and project implementation |
| Experience | 0-2 years in utility sector | 3+ years specialized experience |
| Technical Skills | Basic software and operational knowledge | Advanced troubleshooting, regulatory software, and technical reporting |
| Decision Making | Follows supervisor direction | Independent decisions on technical and regulatory issues |
| Education | High school or associate degree | Bachelor's degree or higher in relevant field |
| Salary Range | $35,000 - $50,000 annually | $65,000 - $90,000 annually |
Overview of Utility Assistant and Utility Specialist Roles
Utility Assistants support daily operations by performing routine maintenance, meter reading, and assisting with customer service tasks to ensure efficient utility service delivery. Utility Specialists possess advanced technical expertise in system analysis, troubleshooting, and project management, leading infrastructure improvements and compliance initiatives. Both roles are essential for maintaining reliable utility services, with Assistants focusing on operational support and Specialists driving technical strategy and problem resolution.
Key Responsibilities of Utility Assistants
Utility Assistants support utility operations by performing basic maintenance tasks, meter reading, and assisting in equipment inspections to ensure smooth service delivery. They handle customer inquiries, process service requests, and maintain accurate records to facilitate efficient utility management. Their role is crucial in supporting Utility Specialists, who focus on advanced technical troubleshooting and system optimization.
Core Duties of Utility Specialists
Utility Specialists primarily manage complex utility systems, ensuring optimal operation, maintenance, and compliance with safety regulations within infrastructure projects. Their core duties include conducting detailed inspections, troubleshooting advanced technical issues, and coordinating with multiple stakeholders to integrate utility services seamlessly. Utility Assistants support these tasks by performing routine maintenance and assisting in data collection, but they typically do not handle the strategic planning or critical decision-making responsibilities central to Utility Specialists.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Utility Assistants typically require foundational skills such as basic equipment operation, data recording, and safety compliance, along with a high school diploma or equivalent. Utility Specialists need advanced technical expertise in utility systems, proficiency in diagnostic tools, and often possess certifications like NACE or OSHA to handle complex troubleshooting and maintenance. Both roles demand strong problem-solving abilities and adherence to regulatory standards, but specialists are expected to have deeper industry knowledge and specialized training.
Training and Certification Differences
Utility Assistants typically require foundational training in utility operations and safety protocols, often completed through on-the-job training or entry-level certification programs. Utility Specialists undergo more advanced training, including specialized certifications such as OSHA safety standards, technical skills in equipment handling, and regulatory compliance courses. The difference in certification emphasizes that Utility Specialists possess deeper expertise in complex utility systems, while Utility Assistants focus on basic operational support.
Work Environment and Typical Tasks
Utility Assistants typically work in field settings or utility offices, supporting day-to-day operations such as meter reading, customer service, and basic maintenance tasks. Utility Specialists operate in more technical environments, handling complex duties like system assessments, infrastructure planning, and regulatory compliance monitoring. Both roles require collaboration with utility teams but differ significantly in skill level and responsibility scope within the utility sector.
Career Progression Opportunities
Utility Assistants typically begin by supporting field operations and administrative tasks, gaining foundational knowledge of utility systems and customer service processes. Utility Specialists advance by acquiring specialized skills in technical operations, regulatory compliance, and project management, enabling them to lead complex utility projects and coordinate cross-functional teams. Career progression from Utility Assistant to Utility Specialist offers increased responsibilities, higher salaries, and opportunities for leadership roles within utility companies.
Salary Comparisons and Compensation Packages
Utility Specialists typically earn a higher salary than Utility Assistants due to their advanced technical skills and greater responsibility in managing utility systems. Compensation packages for Utility Specialists often include performance bonuses, comprehensive health benefits, and retirement plans, reflecting their expertise and critical role. Utility Assistants usually receive a standard wage with limited bonuses, focusing more on entry-level tasks and support functions.
Industry Demand and Job Outlook
Utility Assistants typically handle entry-level tasks such as meter reading and basic maintenance, with steady industry demand driven by infrastructure upgrades and smart grid adoption. Utility Specialists possess advanced skills in utility system management, engineering, and regulatory compliance, experiencing higher job growth due to increasing utility sector complexity and renewable energy integration. The job outlook for Utility Specialists is stronger, supported by evolving technologies and expanding utility services requiring specialized expertise.
Choosing Between Utility Assistant and Utility Specialist
Choosing between a Utility Assistant and a Utility Specialist depends on the level of expertise and responsibility required. Utility Assistants typically handle routine maintenance tasks, equipment inspections, and basic troubleshooting, supporting daily utility operations efficiently. Utility Specialists possess advanced technical knowledge for managing complex utility systems, analyzing data for optimization, and implementing safety protocols to ensure operational integrity.
Utility Assistant vs Utility Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com