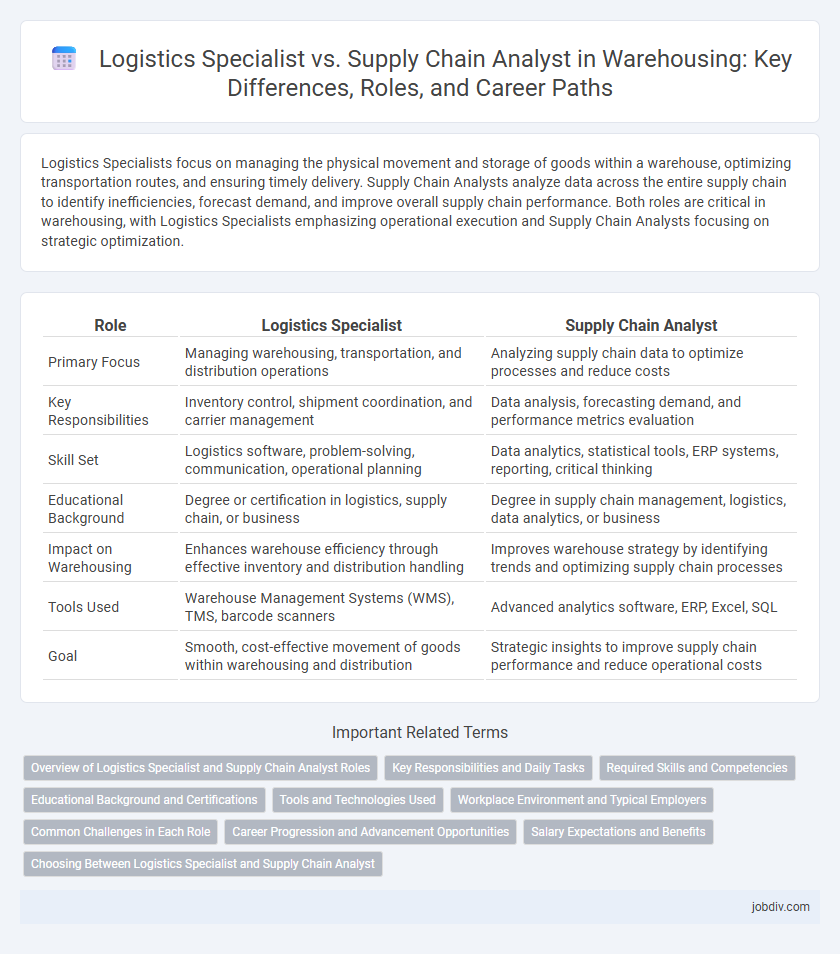
Logistics Specialists focus on managing the physical movement and storage of goods within a warehouse, optimizing transportation routes, and ensuring timely delivery. Supply Chain Analysts analyze data across the entire supply chain to identify inefficiencies, forecast demand, and improve overall supply chain performance. Both roles are critical in warehousing, with Logistics Specialists emphasizing operational execution and Supply Chain Analysts focusing on strategic optimization.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Logistics Specialist | Supply Chain Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Managing warehousing, transportation, and distribution operations | Analyzing supply chain data to optimize processes and reduce costs |
| Key Responsibilities | Inventory control, shipment coordination, and carrier management | Data analysis, forecasting demand, and performance metrics evaluation |
| Skill Set | Logistics software, problem-solving, communication, operational planning | Data analytics, statistical tools, ERP systems, reporting, critical thinking |
| Educational Background | Degree or certification in logistics, supply chain, or business | Degree in supply chain management, logistics, data analytics, or business |
| Impact on Warehousing | Enhances warehouse efficiency through effective inventory and distribution handling | Improves warehouse strategy by identifying trends and optimizing supply chain processes |
| Tools Used | Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), TMS, barcode scanners | Advanced analytics software, ERP, Excel, SQL |
| Goal | Smooth, cost-effective movement of goods within warehousing and distribution | Strategic insights to improve supply chain performance and reduce operational costs |
Overview of Logistics Specialist and Supply Chain Analyst Roles
Logistics Specialists manage the efficient movement, storage, and distribution of goods, coordinating transportation and inventory within warehousing operations. Supply Chain Analysts focus on analyzing data to optimize supply chain performance, identifying bottlenecks, and improving procurement and distribution processes. Both roles are critical for warehousing efficiency, with Logistics Specialists emphasizing operational execution and Supply Chain Analysts driving strategic improvements through data insights.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Logistics Specialists coordinate the movement, storage, and distribution of goods, ensuring on-time deliveries and maintaining inventory accuracy through daily tracking and scheduling. Supply Chain Analysts analyze data to optimize supply chain processes, forecast demand, and identify cost-saving opportunities by monitoring KPIs and supply chain performance metrics. Both roles collaborate to improve warehouse efficiency but focus respectively on operational execution and strategic analysis.
Required Skills and Competencies
Logistics Specialists require expertise in inventory management, transportation coordination, and warehouse operations, emphasizing practical skills in route planning and shipment tracking. Supply Chain Analysts focus on data analysis, demand forecasting, and process optimization, leveraging competencies in statistical software, ERP systems, and strategic planning. Both roles demand strong problem-solving abilities and effective communication, but Logistics Specialists prioritize operational execution while Supply Chain Analysts emphasize analytical insight.
Educational Background and Certifications
Logistics Specialists typically hold degrees in logistics, supply chain management, or business administration, with certifications such as Certified Logistics Associate (CLA) or Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP) enhancing their credentials. Supply Chain Analysts often possess educational backgrounds in industrial engineering, data analytics, or business intelligence, complemented by certifications like Six Sigma, Certified Analytics Professional (CAP), or APICS Certified Supply Chain Analyst. Both roles benefit from specialized training in inventory management systems, ERP software, and data-driven decision-making methodologies.
Tools and Technologies Used
Logistics Specialists primarily utilize transportation management systems (TMS), warehouse management software (WMS), and inventory tracking technologies to streamline order fulfillment and distribution processes. Supply Chain Analysts rely heavily on advanced data analytics platforms, ERP systems like SAP and Oracle, and predictive modeling tools to optimize supply chain efficiency and forecast demand. Both roles incorporate barcode scanners, RFID technology, and real-time tracking applications, but Analysts focus more on data visualization software such as Tableau or Power BI for supply chain insights.
Workplace Environment and Typical Employers
Logistics Specialists typically work in fast-paced warehouse settings, distribution centers, or transportation companies, focusing on inventory management and shipment coordination. Supply Chain Analysts are often employed by manufacturing firms, retail corporations, or consulting agencies, analyzing data to optimize supply chain efficiency. Both roles require collaboration with suppliers, vendors, and internal teams but differ in their workplace dynamics, with Logistics Specialists engaging more in operational environments and Supply Chain Analysts operating in office or remote settings.
Common Challenges in Each Role
Logistics Specialists frequently face challenges such as managing inventory accuracy, coordinating transportation schedules, and ensuring timely delivery amidst fluctuating demand. Supply Chain Analysts often struggle with data integration from multiple sources, forecasting supply disruptions, and optimizing supplier performance using advanced analytics. Both roles require adept problem-solving to maintain seamless warehouse operations and minimize delays in the supply chain.
Career Progression and Advancement Opportunities
Logistics Specialists often advance by gaining expertise in inventory management, transportation coordination, and operational efficiency, leading to roles such as Logistics Manager or Distribution Supervisor. Supply Chain Analysts progress through data-driven decision-making, demand forecasting, and performance optimization, opening pathways to senior analyst positions or Supply Chain Manager roles. Both careers benefit from certifications like APICS CPIM or CSCMP SCPro, enhancing opportunities for leadership and strategic supply chain roles.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Logistics Specialists typically earn an average salary ranging from $50,000 to $70,000 annually, with benefits including health insurance, retirement plans, and performance bonuses tailored to operational efficiency. Supply Chain Analysts generally command higher salaries between $65,000 and $85,000 per year, reflecting their analytical role, and often receive comprehensive benefits such as professional development opportunities, stock options, and flexible working arrangements. Salary expectations for both roles vary by industry and location, but Supply Chain Analysts tend to have greater earning potential due to their strategic impact on cost reduction and supply optimization.
Choosing Between Logistics Specialist and Supply Chain Analyst
Choosing between a Logistics Specialist and a Supply Chain Analyst depends on your focus within warehousing; Logistics Specialists concentrate on managing the day-to-day transportation and storage operations, ensuring efficient inventory flow and timely deliveries. Supply Chain Analysts utilize data analytics and forecasting to optimize supply chain strategies, improving overall operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. For hands-on operational roles, Logistics Specialists are ideal, while Supply Chain Analysts are suited for roles emphasizing data-driven decision-making and long-term planning.
Logistics Specialist vs Supply Chain Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com