Hazmat handlers specialize in managing, storing, and transporting hazardous materials safely, following strict regulations and safety protocols. General warehouse workers perform a broad range of tasks including receiving, storing, and shipping goods, often without the specialized knowledge required for hazardous substances. Understanding these roles ensures compliance with safety standards and efficient warehouse operations.
Table of Comparison
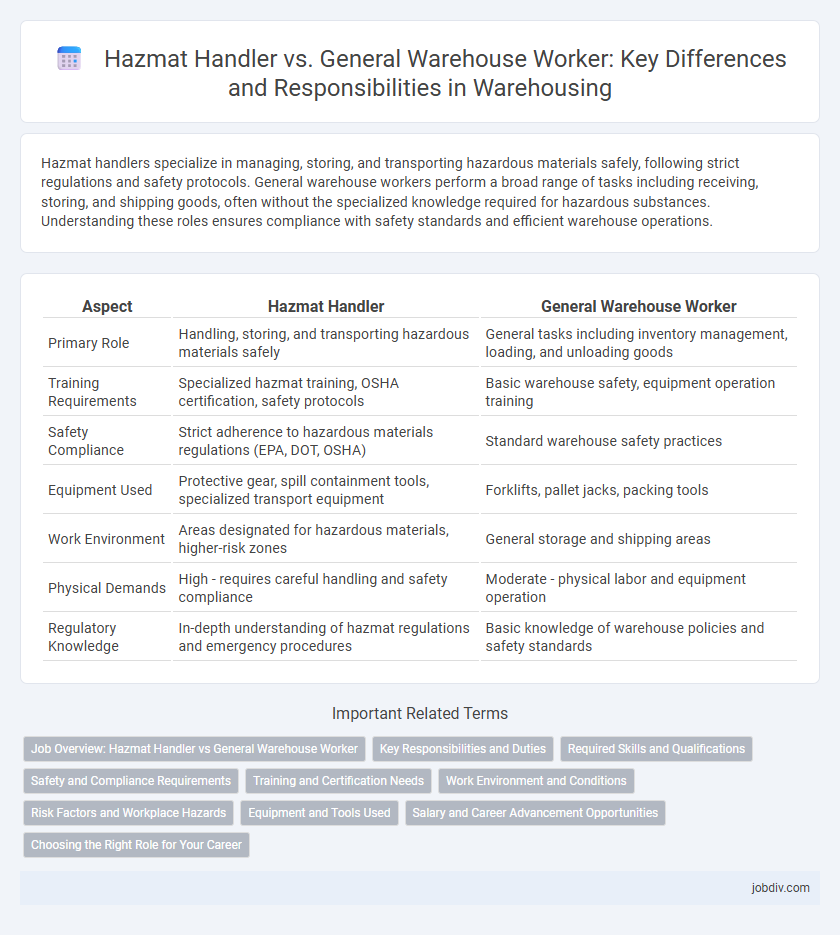
| Aspect | Hazmat Handler | General Warehouse Worker |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Handling, storing, and transporting hazardous materials safely | General tasks including inventory management, loading, and unloading goods |
| Training Requirements | Specialized hazmat training, OSHA certification, safety protocols | Basic warehouse safety, equipment operation training |
| Safety Compliance | Strict adherence to hazardous materials regulations (EPA, DOT, OSHA) | Standard warehouse safety practices |
| Equipment Used | Protective gear, spill containment tools, specialized transport equipment | Forklifts, pallet jacks, packing tools |
| Work Environment | Areas designated for hazardous materials, higher-risk zones | General storage and shipping areas |
| Physical Demands | High - requires careful handling and safety compliance | Moderate - physical labor and equipment operation |
| Regulatory Knowledge | In-depth understanding of hazmat regulations and emergency procedures | Basic knowledge of warehouse policies and safety standards |
Job Overview: Hazmat Handler vs General Warehouse Worker
Hazmat Handlers specialize in the safe storage, transportation, and disposal of hazardous materials, requiring strict adherence to safety regulations and use of protective equipment to prevent contamination or accidents. General Warehouse Workers manage inventory, operate forklifts, and organize shipments, focusing on standard materials handling without the added complexity of hazardous substances. The Hazmat Handler role demands specific certifications and knowledge of chemical hazards, whereas General Warehouse Workers typically require general warehouse skills and operational efficiency.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Hazmat Handlers specialize in the safe storage, transportation, and disposal of hazardous materials, ensuring compliance with OSHA and EPA regulations to prevent accidents and environmental damage. General Warehouse Workers manage inventory control, order fulfillment, and equipment operation, focusing on efficient warehouse organization and logistics support. The primary distinction lies in Hazmat Handlers' expertise in handling dangerous substances versus the broad operational scope of General Warehouse Workers.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Hazmat handlers require specialized training in hazardous materials regulations, chemical safety, and emergency response protocols, often holding certifications such as OSHA HAZWOPER or DOT hazmat endorsements. General warehouse workers need skills in inventory management, forklift operation, and basic safety procedures but usually do not require specialized hazardous materials training. Both roles demand attention to detail and physical stamina, but hazmat handlers must demonstrate rigorous compliance with environmental and safety regulations.
Safety and Compliance Requirements
Hazmat handlers must adhere to stringent safety protocols and regulatory compliance, including OSHA standards and EPA regulations for hazardous materials storage, handling, and transportation, while general warehouse workers primarily follow basic workplace safety guidelines such as OSHA's general industry standards. Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements are more rigorous for hazmat handlers due to exposure risks, and they often require specialized training in hazard communication, spill response, and emergency procedures. Compliance documentation like Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and hazardous waste manifests are critical for hazmat handling but are rarely necessary for general warehouse operations.
Training and Certification Needs
Hazmat Handlers require specialized training and certification in hazardous materials management, including courses on chemical safety, emergency response, and regulatory compliance such as OSHA HAZWOPER standards. General Warehouse Workers typically need basic safety training and forklift operation certifications without the complex regulatory requirements involved in handling hazardous substances. Effective training programs for Hazmat Handlers emphasize risk mitigation and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) to prevent accidents and ensure regulatory adherence.
Work Environment and Conditions
Hazmat handlers operate in highly regulated environments requiring compliance with strict safety protocols to manage hazardous materials, often wearing specialized protective gear and working in designated areas with ventilation and spill control measures. General warehouse workers experience more varied conditions, typically involving physical labor such as lifting and sorting in open spaces with standard safety equipment. Both roles demand attention to safety, but hazmat handlers face greater exposure risk and stringent handling procedures.
Risk Factors and Workplace Hazards
Hazmat handlers face elevated risks involving exposure to toxic chemicals, flammable substances, and corrosive materials, requiring specialized training in handling, storage, and emergency response. General warehouse workers primarily encounter workplace hazards such as heavy lifting, equipment operation, and slips or falls, with fewer risks related to chemical exposure. Proper protective equipment and adherence to safety protocols significantly reduce injury rates across both roles.
Equipment and Tools Used
Hazmat handlers utilize specialized equipment such as spill containment pallets, chemical-resistant gloves, and respirators to safely manage hazardous materials, while general warehouse workers typically rely on standard tools like forklifts, pallet jacks, and hand trucks for routine material handling. Advanced detection devices and decontamination kits are essential for hazmat handlers to prevent contamination and ensure regulatory compliance. In contrast, general warehouse workers prioritize efficiency with conveyor belts, barcode scanners, and inventory management software without the need for hazardous material-specific gear.
Salary and Career Advancement Opportunities
Hazmat Handlers typically earn higher salaries than General Warehouse Workers due to specialized training in handling hazardous materials and compliance with safety regulations. Career advancement for Hazmat Handlers often includes roles such as Safety Supervisor or Compliance Officer, reflecting their expertise in risk management. In contrast, General Warehouse Workers generally advance through operational roles like Inventory Manager or Logistics Coordinator with a broader skill set but lower pay scale.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Career
Hazmat Handlers specialize in managing, storing, and disposing of hazardous materials following strict safety protocols and regulatory guidelines such as OSHA and EPA standards. General Warehouse Workers perform a broad range of tasks including inventory management, order fulfillment, and equipment operation, typically requiring less specialized training and certifications. Choosing the right role depends on your career goals, willingness to undergo specific hazardous materials training, and interest in compliance-heavy environments versus versatile warehousing duties.
Hazmat Handler vs General Warehouse Worker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com